Indian Economy
Union Budget 2025-26: India’s Roadmap for Growth & Development
- 07 Feb 2025
- 15 min read
For Prelims: Union Budget 2025-26, Agriculture, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME), Investment, Exports, Taxation, Parliament, Makhana, Exclusive Economic Zone, Made in India, Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), Atomic Energy Act, Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, UDAN scheme, Lithium-ion battery, UPI, e-Shram portal, PM Jan Arogya Yojana, NaBFID, Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana, Kisan Credit Card (KCC), Modified Interest Subvention Scheme, Mission for Cotton Productivity, Atal Tinkering Labs.
For Mains: Significance of the Union Budget in Indian economy for resource allocation, economic planning, fiscal stability, welfare schemes, and national development.
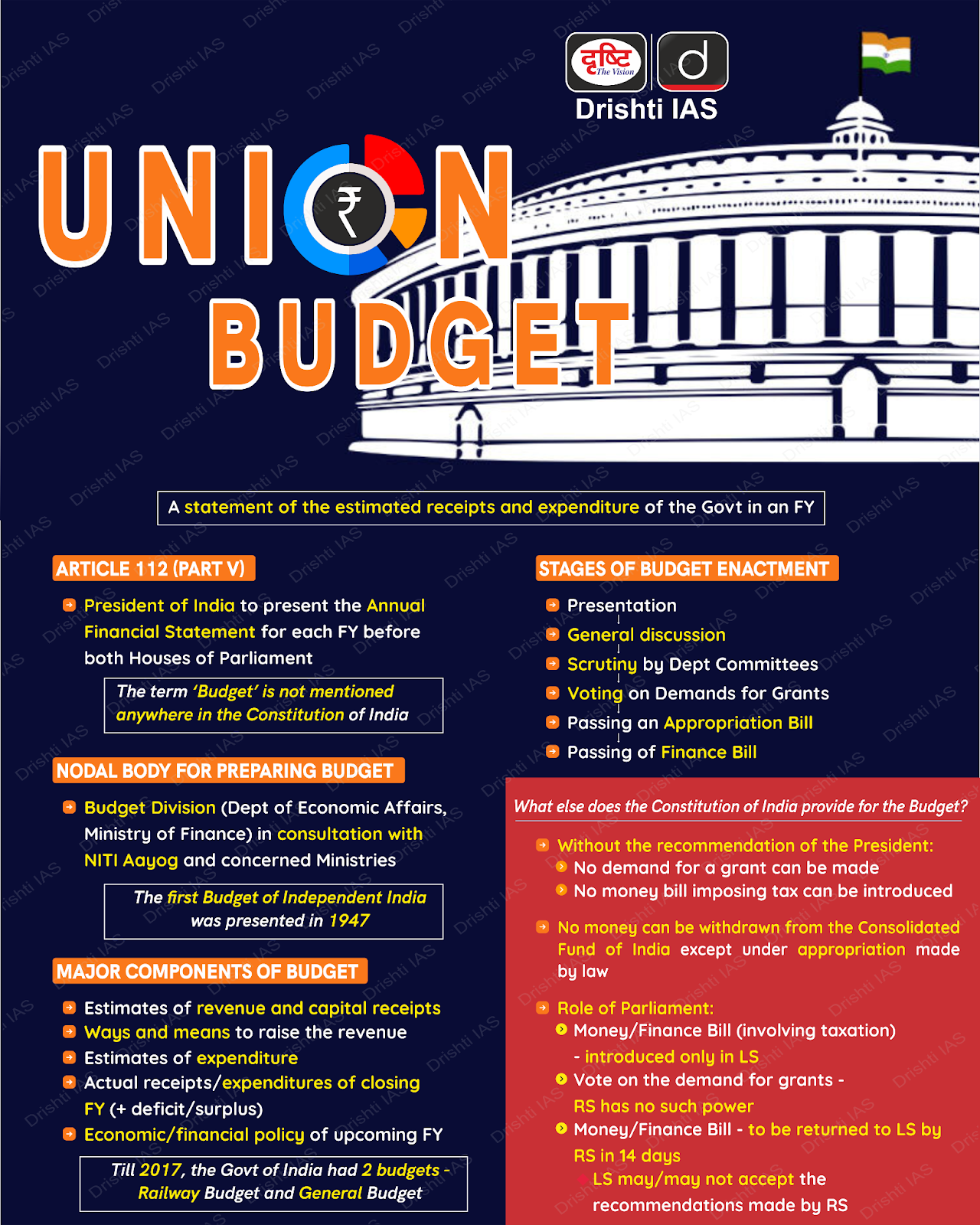
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2025-26, presented by the Finance Minister, outlines a strategic roadmap for economic growth.
- It focuses on agriculture, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME), investment, exports, taxation, and social development to achieve Viksit Bharat.
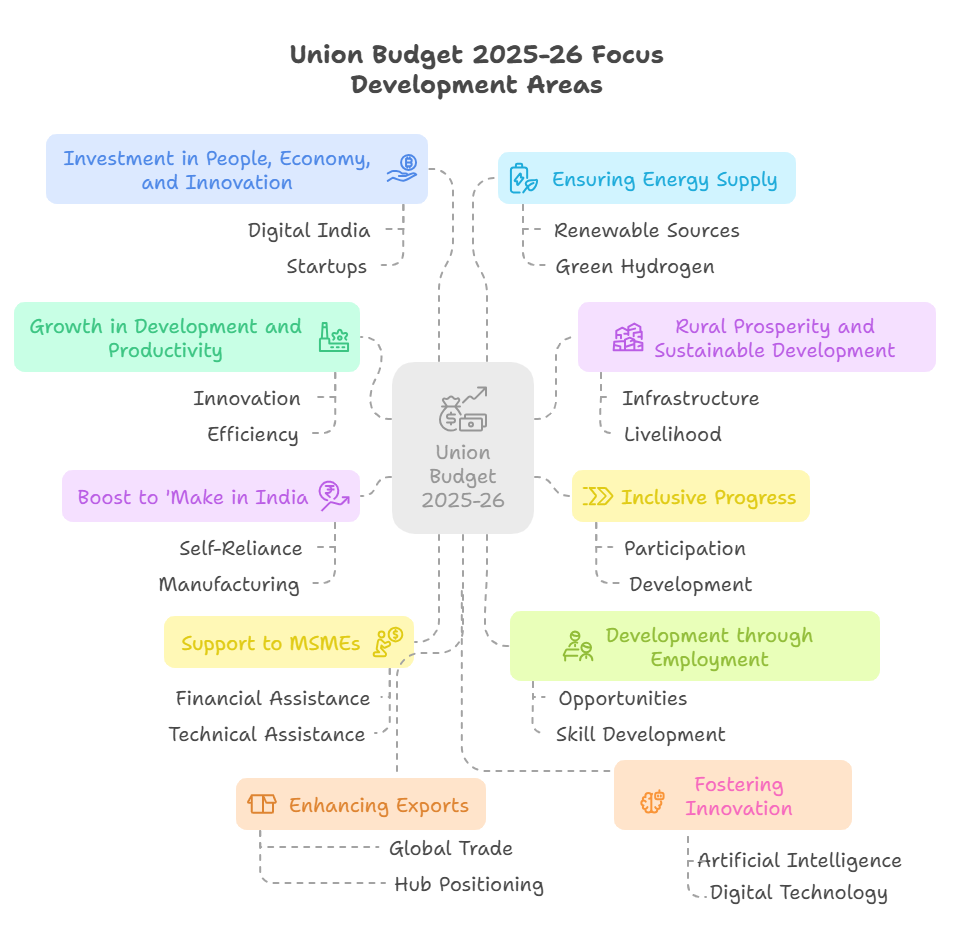
What are the Four Engines for Development of the Budget 2025-26?
- Agriculture: Strengthening Farmers and Rural Economy:
- The Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana aims to cover 100 districts, enhancing crop diversification, irrigation, and post-harvest storage infrastructure.
- This scheme will increase productivity, ensure food security, and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
- A six-year Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses will focus on Tur, Urad, and Masoor dal, ensuring self-sufficiency in domestic production.
- Reduced dependence on imports will stabilize domestic prices and improve farmer incomes.
- The loan limit under the Kisan Credit Card (KCC) has been raised from ₹3 lakh to ₹5 lakh under the Modified Interest Subvention Scheme.
- Analysis: This will increase financial inclusion for farmers, fishermen, and dairy producers, ensuring better investment in agricultural inputs.
- A five-year Mission for Cotton Productivity will enhance scientific farming techniques and technological interventions for improved yields.
- Strengthening cotton farming will boost India’s textile sector and enhance global trade competitiveness.
- India Post will be transformed into a public logistics organization, facilitating rural economic growth and improving agriculture-based trade and supply chains.
- This will connect rural producers with national markets, reducing wastage and increasing farmer profitability.
- The Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana aims to cover 100 districts, enhancing crop diversification, irrigation, and post-harvest storage infrastructure.
- MSMEs: Boosting Manufacturing and Employment:
- The classification limit for MSMEs has been increased to 2.5 times investment and 2 times turnover to help businesses expand and scale operations.
- Enhanced classification criteria will enable more enterprises to avail benefits, fostering growth and job creation.
- The classification limit for MSMEs has been increased to 2.5 times investment and 2 times turnover to help businesses expand and scale operations.
|
₹ in Crore |
Investment |
Turnover |
|
|
Current |
Revised |
|
Micro Enterprises |
1 |
2.5 |
|
Small Enterprises |
10 |
25 |
|
Medium Enterprises |
50 |
125 |
- The MSME Credit Guarantee Scheme has been expanded, offering additional credit support of ₹1.5 lakh crore over five years.
- Increased credit availability will improve liquidity, enabling MSMEs to invest in innovation and infrastructure.
- A new scheme for first-time SC/ST and women entrepreneurs will provide loans up to ₹2 crore for 5 lakh beneficiaries over the next five years.
- This initiative will enhance financial inclusion, empowering marginalized communities and fostering entrepreneurship.
- A National Manufacturing Mission will be launched to support MSMEs, including clusters for toy manufacturing and non-leather footwear production.
- Strengthening manufacturing will increase exports and make India a global production hub.
- The government will support electronic equipment manufacturing, boosting Industry 4.0 capabilities and domestic industrial development.
- This initiative will reduce reliance on imports and position India as a leader in advanced manufacturing.
- Investment: Strengthening Infrastructure and Innovation:
- A 50-year interest-free loan of ₹1.5 lakh crore will be provided to states for capital expenditure and reforms.
- This investment will spur economic growth, creating jobs and improving public infrastructure.
- The second Asset Monetization Plan (2025-30) will raise ₹10 lakh crore, reinvesting in new infrastructure projects.
- Recycling public assets will generate funds for future development, ensuring sustainable economic growth.
- 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs) will be set up in government schools over five years, fostering STEM learning and innovation.
- Investment in education will equip students with future-ready skills, promoting technological advancement.
- A ₹20,000 crore fund for Research, Development, and Innovation will encourage private-sector-driven technological progress.
- This initiative will strengthen India’s global competitiveness in emerging technologies.
- The BharatNet Project will provide broadband connectivity to all government schools and rural healthcare centers.
- Digital expansion will help in bridging the rural-urban digital divide, improving e-governance, education and telemedicine services.
- A 50-year interest-free loan of ₹1.5 lakh crore will be provided to states for capital expenditure and reforms.
- Exports: Expanding Global Trade Prospects:
- The Export Promotion Mission will support MSMEs in accessing global markets, ensuring seamless trade facilitation.
- Strengthening exports will diversify India's trade portfolio and enhance foreign exchange reserves.
- BharatTradeNet (BTN), a digital public infrastructure for international trade, will streamline documentation and financing.
- Digitalizing trade processes will enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and boost investor confidence.
- Infrastructure and warehousing for air cargo, including perishable goods, will be upgraded.
- Strengthening logistics networks will help to improve agricultural and industrial export competitiveness.
- A National Framework for Global Capability Centres (GCCs) will promote Tier-2 cities as global IT and R&D hubs.
- Encouraging technology investment will create high-skilled jobs and boost India's digital economy.
- The government will support domestic electronic equipment manufacturing to integrate with global supply chains.
- Strengthening domestic production will reduce import dependency and increase exports.
- The Export Promotion Mission will support MSMEs in accessing global markets, ensuring seamless trade facilitation.
What are Other Major Highlights of the Budget 2025-26?
- Gender Budget: The gender budget allocation has risen to 8.86% of the total budget, up from 6.8% in 2024-25.
- A total of Rs. 4.49 lakh crore is allocated for the welfare of women and girls, marking a 37.25% increase from the previous year.
- Education: The Ministry of Education has received ₹1,28,650 crore, a 6.22% increase from 2024-25.
- Key initiatives include expanding broadband in rural schools, establishing ATLs in government schools, and enhancing IIT infrastructure.
- Additionally, ₹500 crore is allocated for AI in education and ₹20,000 crore for private sector research and innovation.
- Taxation and Relief for Middle Class:
- No Income Tax for individuals earning up to ₹12 lakh per annum, with ₹12.75 lakh exemption for salaried employees due to standard deductions.
- This puts more money in the hands of taxpayers, boosting consumption, savings, and investments.
- New Tax Slabs introduced, ranging from 5% for incomes between ₹4-8 lakh to 30% for incomes above ₹24 lakh.
- The simplified tax structure will enhance voluntary compliance and reduce litigation.
- TDS exemption limits increased, with interest income exemption for senior citizens raised from ₹50,000 to ₹1 lakh.
- This will benefit retirees by increasing disposable income, supporting financial stability for the elderly.
- Vivad Se Vishwas scheme extended, allowing taxpayers four years (instead of two) to rectify returns.
- Extending the dispute resolution window will reduce litigation and increase tax collection efficiency.
- Presumptive taxation introduced for non-residents providing services to Indian electronics manufacturers.
- This will attract more foreign expertise, fostering domestic industrial growth and innovation.
- No Income Tax for individuals earning up to ₹12 lakh per annum, with ₹12.75 lakh exemption for salaried employees due to standard deductions.
- Financial Sector and Regulatory Reforms:
- FDI limit in insurance sector raised from 74% to 100%, with investments required to remain in India.
- Higher FDI inflows will strengthen the insurance sector, enhancing risk coverage and financial inclusion.
- Regulatory reforms proposed, including a High-Level Committee to review licenses, permits, and compliance rules.
- A business-friendly environment will promote entrepreneurship and ease of doing business.
- Investment Friendliness Index introduced to promote competition among states for attracting investments.
- Competitive federalism will drive states to create better business ecosystems, boosting economic growth.
- Partial Credit Enhancement Facility for corporate bonds to improve infrastructure financing.
- Easier access to corporate debt markets will facilitate large-scale infrastructure projects.
- Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0 to decriminalize over 100 business laws, reducing harassment of entrepreneurs.
- This will encourage risk-taking and investment, fostering a more innovation-driven economy.
- FDI limit in insurance sector raised from 74% to 100%, with investments required to remain in India.
- Energy and Infrastructure Development:
- ₹20,000 crore allocated for Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) as part of the 100 GW nuclear energy goal by 2047.
- This would support clean energy expansion, ensuring sustainable power for industries and households.
- Urban Challenge Fund of ₹1 lakh crore launched to develop cities as economic hubs.
- This fund would enhance urban infrastructure, making cities globally competitive for businesses.
- Jal Jeevan Mission extended until 2028, ensuring 100% rural tap water connectivity.
- Reliable water access will improve public health, reducing waterborne diseases and rural hardships.
- Green manufacturing incentives introduced for solar PV cells, EV batteries, and wind turbines.
- Promoting clean-tech manufacturing will reduce dependence on imports and improve sustainability.
- UDAN Scheme expansion will connect 120 new destinations, targeting 4 crore air passengers in 10 years.
- Improved connectivity will enhance regional tourism, foster trade, and generate employment opportunities.
- ₹20,000 crore allocated for Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) as part of the 100 GW nuclear energy goal by 2047.
- Defence, Cybersecurity, and Space Exploration:
- Increased investments in defence manufacturing, supporting AI-driven security solutions and surveillance systems.
- Enhancing indigenous defence technology will help to reduce reliance on imports and strengthen national security.
- Cybersecurity infrastructure upgraded, with more funds for National Cybersecurity Mission and AI-powered threat detection.
- This will strengthen India’s cyber resilience, protecting critical financial and infrastructure systems.
- ₹25,000 crore Maritime Development Fund launched to upgrade shipbuilding and port modernization.
- Improving maritime infrastructure will boost global trade efficiency and attract foreign investments.
- ISRO funding increased, with a focus on Gaganyaan, SSLV expansion, and private-sector space collaboration.
- Expanding India's space sector is set to position the country as a key player in global satellite markets.
- Public-private partnerships encouraged for nuclear propulsion in space missions, ensuring sustained deep-space exploration.
- Collaboration is set to drive technological advancements and enhance global leadership in space.
- Increased investments in defence manufacturing, supporting AI-driven security solutions and surveillance systems.
- Major Allocations for Bihar: Significant allocations for Bihar include the establishment of a Makhana Board to support farmers with training and government schemes.
- Additionally, a National Institute of Food Technology, Processing, and Innovation will be set up to boost agricultural value and employment.
- The budget also includes greenfield airports, an expanded Patna airport, and financial support for the West Kosi canal project to aid farmers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Along with the Budget, the Finance Minister also places other documents before the Parliament which include ‘The Macro Economic Framework Statement’. The aforesaid document is presented because this is mandated by (2020)
(a) Long standing parliamentary convention
(b) Article 112 and Article 110(1) of the Constitution of India
(c) Article 113 of the Constitution of India
(d) Provisions of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003
Ans: (d)
Q. Which one of the following is responsible for the preparation and presentation of Union Budget to the Parliament? (2010)
(a) Department of Revenue
(b) Department of Economic Affairs
(c) Department of Financial Services
(d) Department of Expenditure
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Distinguish between Capital Budget and Revenue Budget. Explain the components of both these Budgets.(2021)