Biodiversity & Environment
Small Modular Reactors for Decarbonization
- 11 Aug 2023
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Low-Carbon Electricity Resources, Decarbonization, International Energy Agency (IEA), Rare Earth Elements, International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), Atomic Energy Act, 1962.
For Mains: Small Modular Reactors for Decarbonization.
Why in News?
The rise in coal consumption despite increased solar and wind power underlines the need for Low-Carbon Electricity Resources such as Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) to ensure Deep Decarbonization.
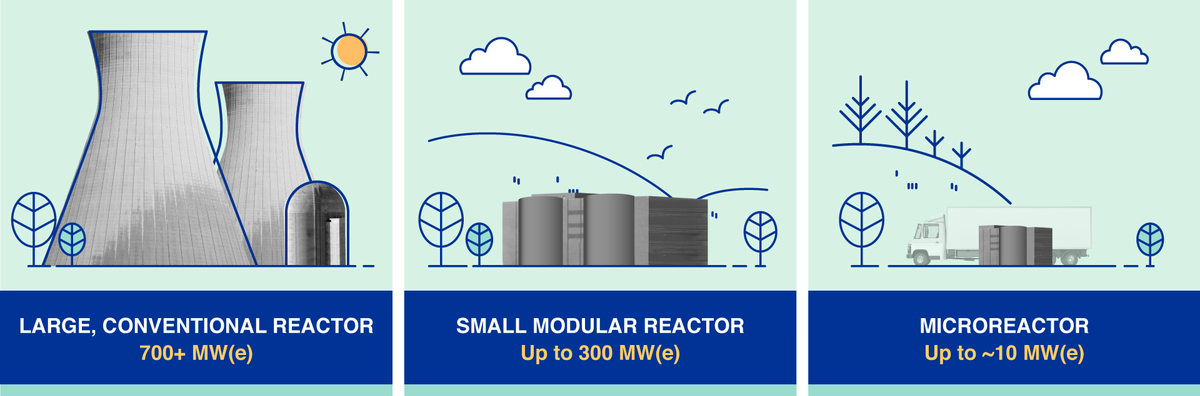
- Conventional NPPs (Nuclear Power Plants) have generally suffered from time and cost overruns. As an alternative, several countries are developing (SMRs) – nuclear reactors with a maximum capacity of 300 MW – to complement conventional NPPs.
What is Decarbonization?
- About:
- Decarbonization refers to the process of reducing the Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Emissions produced by human activities, particularly those related to the burning of fossil fuels such as Coal, Oil, and Natural gas.
- Need:
- The global pursuit of decarbonization aligns with the UN Sustainable Development Goal 7, which emphasizes affordable and sustainable energy access.
- However, the world's heavy reliance on fossil fuels, constituting 82% of energy supply, necessitates the urgent decarbonization of the power sector.
- The rise in coal consumption in Europe despite increased solar and Wind Power underlines the need for reliable low-carbon electricity resources to ensure deep decarbonization, grid stability, and energy security.
- The global pursuit of decarbonization aligns with the UN Sustainable Development Goal 7, which emphasizes affordable and sustainable energy access.
- Challenges of Decarbonization:
- Clean Energy Transition Challenges: The shift from coal to clean energy is a complex challenge globally. Several nations concur that relying solely on solar and wind energy would not suffice reliable and affordable energy access for all.
- In decarbonized power systems dominated by renewables, introducing at least one stable power source enhances grid reliability and reduces expenses, contributing to a balanced energy mix.
- Critical Minerals Demand and Complexities: The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts a potential 3.5x surge in demand for critical minerals like lithium, nickel, cobalt, and Rare Earth Elements by 2030, essential for clean energy technologies.
- However, this demand escalation raises multiple global issues, including the large capital investments to develop new mines and processing facilities.
- Challenges in the Mineral Supply Chain: Rapid development in countries like China, Indonesia, Africa, and South America, coupled with concentration of mineral extraction and processing capacities, presents environmental, social, geopolitical, and supply risks.
- Addressing these challenges becomes critical for sustainable clean energy advancement.
- Clean Energy Transition Challenges: The shift from coal to clean energy is a complex challenge globally. Several nations concur that relying solely on solar and wind energy would not suffice reliable and affordable energy access for all.
What are Small Modular Reactors (SRMs)?
- About:
- SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit, which is about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors.
- SMRs, which can produce a large amount of low-carbon electricity, are,
- Small: Physically a fraction of the size of a conventional nuclear power reactor.
- Modular: Making it possible for systems and components to be factory-assembled and transported as a unit to a location for installation.
- Reactors: Harnessing nuclear fission to generate heat to produce energy.
- Their designs incorporate enhanced safety features, reducing the risk of uncontrolled radioactive material release.
- SMRs are designed to operate for 40-60 years with capacity factors exceeding 90%.
- Advantages:
- Reliable Low-carbon Electricity Source:
- As the demand for electricity is projected to surge by 80-150% by 2050, SMRs could provide a reliable 24/7 low-carbon electricity source that complements intermittent renewables.
- This is crucial for achieving grid reliability and reducing costs in decarbonized electricity systems.
- Minimized Land Acquisition Challenges:
- SMRs generate less spent nuclear fuel and can be safely operated in existing brownfield sites, minimizing land acquisition challenges.
- SMRs are also simpler to design and manufacture, with potential for cost reduction through serial manufacturing.
- Alternatives to Critical Minerals:
- The transition to clean energy requires Critical Minerals for technologies like lithium-ion batteries, leading to concerns about geopolitical risks and environmental impacts.
- SMRs offer an alternative, as they require low-enriched uranium, which is more widely distributed than critical minerals.
- Integration with India's Energy Strategy:
- For India, which aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070, SMRs can play a pivotal role. As coal-based thermal power plants and variable renewable energy sources contribute significantly to the energy mix, SMRs can enhance energy security and grid stability.
- India's Central Electricity Authority envisions SMRs as a crucial element in meeting electricity demands, while private sector investments, including public-private partnerships, are vital for expansion.
- For India, which aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2070, SMRs can play a pivotal role. As coal-based thermal power plants and variable renewable energy sources contribute significantly to the energy mix, SMRs can enhance energy security and grid stability.
- Reliable Low-carbon Electricity Source:
How can Low-Carbon Electricity Resources be Promoted for Decarbonization?
- An efficient regulatory regime comparable to that in the civil aviation sector – which has more stringent safety requirements – is important if SMRs are to play a meaningful role in decarbonising the power sector.
- This can be achieved if all countries that accept nuclear energy direct their respective regulators to cooperate amongst themselves and with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) to harmonize their regulatory requirements and expedite statutory approvals for SMRs based on standard, universal designs.
- To facilitate SMR deployment, India needs to amend the Atomic Energy Act, 1962 to allow private sector involvement.
- While maintaining government control over nuclear fuel and waste, an independent regulatory board should oversee the entire nuclear power cycle.
- The India-US '123 agreement' provides opportunities for India to reprocess spent fuel from SMRs under IAEA safeguards, contributing to resource sustainability.
- It also permits India to set up a facility to reprocess spent fuel from SMRs under safeguards of the IAEA.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The function of heavy water in a nuclear reactor is to (2011)
(a) Slow down the speed of neutrons
(b) Increase the speed of neutrons
(c) Cool down the reactor
(d) Stop the nuclear reaction
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. With growing energy needs should India keep on expanding its nuclear energy programme? Discuss the facts and fears associated with nuclear energy. (2018)