Indian Economy
Abhinav Pahal | ONDC | Gateway to Progress
- 10 Jan 2025
- 10 min read
For Prelims: Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), Small Businesses, E-Commerce, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), SC/ST entrepreneurs , Digital Marketplace, Financial Services, 14th India Digital Awards, Micro, Small And Medium Enterprises (MSME), Formalization of Small Businesses, Logistics, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Grievance Redressal System.
For Mains: Significance of Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) in Empowering Small Businesses and Promoting Inclusive E-Commerce.
Why in News?
- The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) surpassed 15 million monthly transactions, empowering small businesses and promoting inclusive e-commerce.
- The initiative recorded an all-time high of 8.9 million transactions in May 2024, a remarkable 23% month-on-month growth.
What is Open Network for Digital Commerce?
- About ONDC: The ONDC launched in April 2022 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) under the Ministry of Commerce, aims to democratize e-commerce.
- This open-source platform allows seamless transactions between buyers and sellers, transitioning from a platform-centric to an open-network model.
- ONDC was incorporated as a non-profit Section-8 company with contributions from public and private banks, and authorized capital of ₹500 crore.
- Objectives: The initiative aims to reduce dominance of major e-commerce platforms through interoperability and inclusivity.
- ONDC empowers small businesses, women-led enterprises, and SC/ST entrepreneurs with tools to access the digital marketplace.
- The focus is on lowering customer acquisition costs and transaction processing expenses for businesses on the network.
- ONDC bridges regional and linguistic divides, promoting participation from underserved markets.
- The network ensures consumers have access to diverse sellers, competitive prices, and better-quality services.
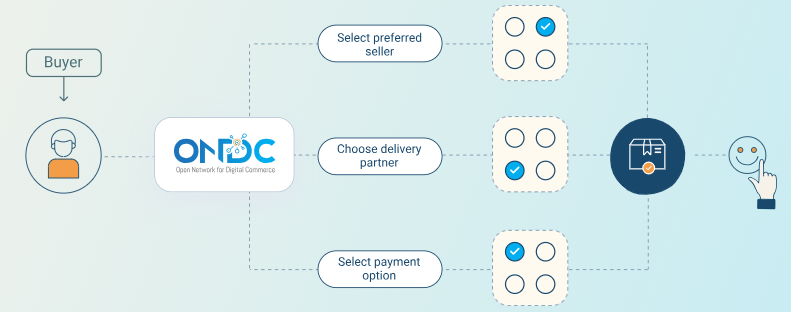
- Working Mechanism: ONDC’s decentralized architecture uses open protocols, enabling buyers and sellers across platforms to transact via standardized APIs.
- Roles are clearly segregated into Buyer Apps, Seller Apps, Logistics Providers, and Technology Enablers, ensuring efficiency and responsibility.
- ONDC facilitates operations across 13 domains, including food, groceries, mobility, fashion, agriculture, and financial services.
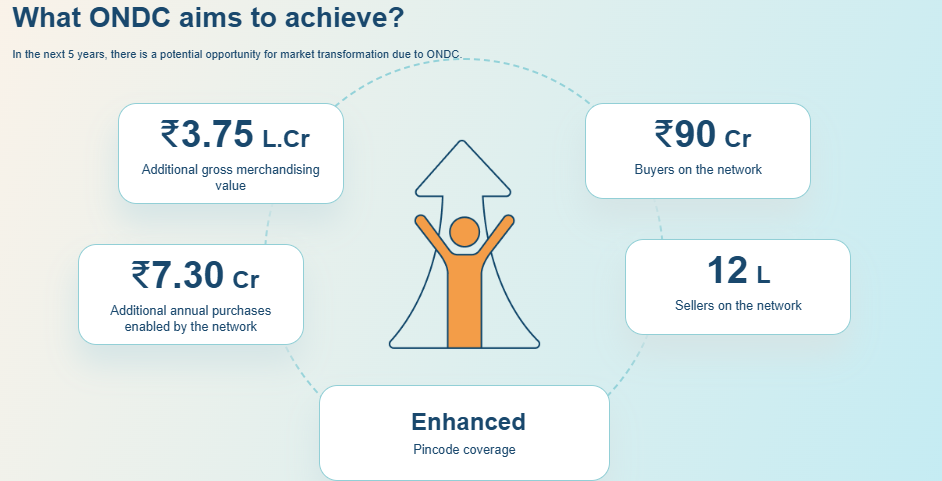
- Achievements So Far: ONDC now spans 616+ cities, significantly expanding its geographical coverage and participation by sellers and buyers alike.
- Initially piloted in Bengaluru and Delhi, ONDC expanded to categories such as mobility, health, beauty, and agriculture.
- The MSME-TEAM scheme, active from 2024 to 2027, targets onboarding 5 lakh MSMEs, including 2.5 lakh women-owned enterprises.
- ONDC won multiple awards, including the "Start-up of the Year" at the 14th India Digital Awards and "Tech Disruptor" in 2024.
What are the Benefits of ONDC?
- Empowering Small Businesses and MSMEs: ONDC empowers Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) by reducing dependency on expensive platform-specific policies, enhancing their reach to a nationwide audience.
- MSMEs benefit from training programs for digital skill development and ONDC's interoperable protocols for cataloging and order fulfillment.
- The MSME-TEAM initiative assists businesses with onboarding, catalog preparation, account management, and logistics, especially for women-led enterprises.
- Expanding Digital Commerce Inclusivity: ONDC enables participation by local vendors, artisans, and rural entrepreneurs, increasing socio-economic inclusion and market accessibility.
- Initiatives like the ONDC Sahayak WhatsApp Bot, available in five languages, simplify platform onboarding for sellers and buyers.
- Enhancing Consumer Experience and Competition: Buyers enjoy access to a broader array of sellers, diverse product choices, and competitive pricing, fostering greater consumer satisfaction.
- ONDC disrupts monopolistic control by encouraging competition among sellers, which leads to innovations and better quality of services.
- Economic Development and Job Creation: The initiative supports formalization of small businesses, creating digital histories that improve access to credit and financing.
- ONDC drives economic growth by generating jobs in logistics, technology, packaging, and last-mile delivery, especially in smaller cities.
- Pioneering Digital Commerce Innovation: ONDC’s open-source methodology encourages technological advancements, allowing developers to innovate within the e-commerce ecosystem.
- The platform’s expansion into domains like health, mobility, and agriculture demonstrates its versatility in addressing India’s digital commerce needs.
What are the Challenges for ONDC?
- Complexity of Transition and Adoption: Unlike simpler systems like Unified Payments Interface (UPI), ONDC’s decentralized architecture demands substantial technological awareness, posing challenges for small businesses.
- Consumers accustomed to dominant platforms may find transitioning to ONDC’s open network challenging without seamless onboarding mechanisms.
- Dispute Resolution and Accountability Issues: ONDC lacks a centralized grievance redressal system, creating ambiguity over accountability for issues like delayed deliveries or product quality.
- As ONDC operates only as a facilitator, disputes might increase, affecting user trust and overall adoption rates.
- Competition from Established Platforms: Existing e-commerce giants dominate with their extensive consumer base, loyalty programs, and bundled services, challenging ONDC’s appeal.
- Without compelling strategies, ONDC may struggle to attract sellers and buyers already invested in established ecosystems.
- Technological and Logistical Barriers: Integrating diverse participants with varied technological capabilities requires significant resources, posing challenges in ensuring uniform network efficiency.
- Ensuring reliable logistics and timely deliveries across 616+ cities, particularly rural areas, is a daunting task for the network.
- Lack of Direct Price Control: Unlike established platforms, ONDC’s facilitator model limits its ability to offer discounts or influence bulk pricing strategies directly.
- The absence of significant cost advantages might deter price-sensitive consumers from switching to ONDC.
Way Forward
- Investing in Digital Infrastructure: The government must focus on bridging the digital divide, ensuring rural areas have robust broadband and mobile connectivity for seamless operations. Enhancing physical and technological infrastructure will help ONDC achieve nationwide scalability and inclusivity.
- Promoting Digital Literacy and Ease of Use: Comprehensive education programs in regional languages and interactive tools can empower sellers and buyers to navigate ONDC effectively. Simplifying user interfaces and providing step-by-step guidance will improve onboarding and encourage participation from non-tech-savvy users.
- Strengthening Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: ONDC should establish a single-window grievance redressal system to handle buyer-seller disputes and foster trust in the ecosystem. Defining clear accountability for logistics, payments, and after-sales services will ensure smoother operations and better user satisfaction.
- Collaborative Strategies and Incentives: ONDC should collaborate with existing e-commerce players, startups, and industry bodies to accelerate adoption and expand its reach. Providing financial support for onboarding and creating tax incentives for early adopters will encourage participation by MSMEs and small businesses.
- Fostering Innovation through Technology: ONDC should leverage emerging technologies like AI for personalized shopping and blockchain for secure transactions to enhance efficiency. Encouraging private-sector innovations within the ONDC ecosystem will drive competition and improve consumer experiences.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to foreign-owned e-commerce firms operating in India, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2022)
- They can sell their own goods in addition to offering their platforms as market-places.
- The degree to which they can own big sellers on their platforms is limited.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Mains:
What are the impediments in marketing and supply chain management in developing the food processing industry in India? Can e-commerce help in overcoming this bottleneck? (2015)