International Relations
India's Global Reach Through Its Diaspora
- 11 Jan 2025
- 14 min read
This editorial is based on “How Indian diaspora can contribute to Viksit Bharat” which was published in Hindustan Times on 08/01/2025. The article highlights that Odisha hosts the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas 2025, a key event for the Indian diaspora. The event has grown over the years, fostering a strong sense of community and pride among overseas Indians.
For Prelims: Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), OCI card, India’s GDP, Consumption Expenditure, India-Uk Free Trade Agreement, Gulf Nations, Madad (Help), Emigration Check Required (ECR), Operation Ganga (2022), Operation Kaveri (2023), Operation Rahat (2015), Operation Devi Shakti (2021), Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
For Mains: Significance of Indian Diaspora in Indian Diplomacy, Indian Diaspora, India’s Soft Power.
The Indian diaspora, encompassing over 35 million people globally in 2024, symbolizes India's vast reach and influence. Representing the largest diaspora worldwide, these individuals serve as economic drivers, cultural ambassadors, and strategic allies for India. Their contributions, including $129.1 billion in remittances in 2024, are celebrated during the Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD), held biennially on 9th January to honor their role in shaping India's global identity. With a strong presence in over 200 countries, the diaspora bridges India with the world, fostering innovation, strengthening diplomatic ties, and enhancing India's global stature in the 21st century.
What Defines the Indian Diaspora?
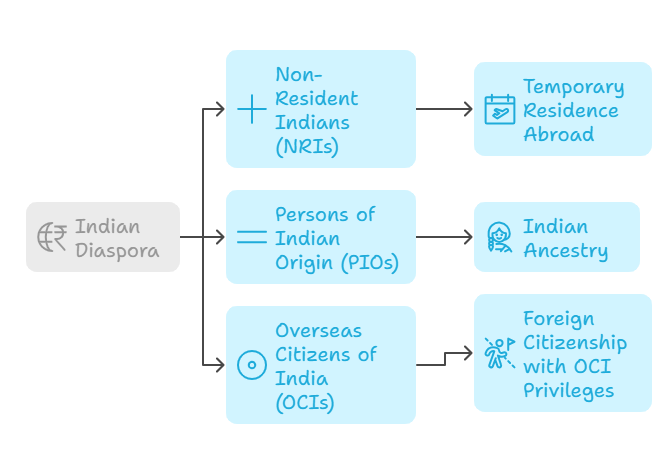
- Indian Diaspora: The Indian diaspora refers to individuals of Indian origin who reside outside India, including both Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs).
- According to the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA), as of November 2024, the total population of Overseas Indians was 35,421,987.
- The top three countries with the largest Indian overseas populations are the United States (5.4 million), the United Arab Emirates (3.6 million), and Malaysia (2.9 million).
- Categories of the Diaspora:
- Non-Resident Indians (NRIs): These are Indian citizens residing abroad temporarily for work, education, or other purposes.
- Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs): These are foreign citizens of Indian ancestry, who may have been born or settled abroad for generations but retain a strong cultural connection to India.
- Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs): This category includes individuals of Indian origin who hold foreign citizenship but are granted specific privileges by the Indian government through the OCI card.
What is the Significance and Contribution of the Indian Diaspora ?
- Economic Significance:In 2024, India received an astounding $129.1 billion in remittances, the highest for any country in a single year.
- This represented 14.3% of global remittances, a remarkable feat that underlines India’s dominance in this sector.
- Remittances accounted for 3.3% of India’s GDP, providing critical support to families and supporting consumption expenditure and investment in local economies.
- By bridging Indian enterprises with global markets and fostering collaborations, the diaspora enriches India's business landscape, supports underserved regions, and propels the country toward its goal of becoming a developed economy.
- Role in Administration and Soft Power:The Indian diaspora plays a crucial role in influencing administrative frameworks and strengthening bilateral relations with key global powers.
- Indian-origin professionals and lawmakers in the US and UK promote India-US collaborations in trade, defense, and technology.
- For example, Indian-origin officials have contributed significantly to the discussions around the India-UK Free Trade Agreement, showcasing their pivotal role in enhancing strategic partnerships.
- Enhancing Cultural Connectivity: Acting as cultural ambassadors, the diaspora strengthens India's soft power by promoting its traditions, art, and heritage in host countries.
- Initiatives like declaring Diwali as a holiday in several US states highlight the successful integration of Indian culture abroad, fostering greater acceptance and appreciation.
- Indian festivals, yoga, Bollywood, and cuisine have gained global popularity, enhancing India’s soft power.
- Knowledge Economy: Indians have a significant presence in global tech hubs, for instance, CEOs of major tech firms like Google, Microsoft, and Adobe are of Indian origin.
- Many diaspora members are returning to India, bringing their expertise and fostering innovation, particularly in sectors like IT and healthcare.
- Philanthropic Contributions: Indian-origin philanthropists contribute generously to causes in India, supporting education, healthcare, and rural development.
- For example, initiatives like the India Development Foundation of Overseas Indians (IDF-OI) facilitate such contributions.
What are Government Initiatives to Engage with the Indian Diaspora?
- Employment and Welfare Support:
- E-Migrate: This online platform regulates recruitment and provides safe avenues for Indian workers seeking overseas employment.
- It ensures transparency, protects workers from exploitation, and simplifies the recruitment process for both employers and employees.
- Madad Portal: The Madad (Help) portal provides a grievance redressal mechanism for Indians abroad.
- It addresses issues ranging from legal assistance to repatriation in emergencies, ensuring timely support to distressed Indians.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Bima Yojana (PBBY): Introduced in 2003, it is a mandatory insurance scheme for Indian emigrant workers in the Emigration Check Required (ECR) category.
- It offers insurance coverage of Rs. 10 lakhs for accidental death or permanent disability, with premiums of Rs. 275 for two years and Rs. 375 for three years.
- E-Migrate: This online platform regulates recruitment and provides safe avenues for Indian workers seeking overseas employment.
- Cultural and Heritage Engagement:
- Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) Scheme: Grants lifelong visa-free travel and other privileges to PIOs, fostering stronger ties with India.
- Benefits include property ownership, financial investments, and access to educational institutions in India.
- Chalo India Programme: Encourages Indian-origin youth worldwide to visit India and reconnect with their heritage.
- This program includes cultural tours, heritage site visits, and interactions with local communities.
- Bharat Ko Jaaniye Quiz (BKJ): An online quiz designed to connect diaspora youth with India’s history, culture, and contemporary developments, fostering a sense of pride and belonging.
- Overseas Citizenship of India (OCI) Scheme: Grants lifelong visa-free travel and other privileges to PIOs, fostering stronger ties with India.
- Research and Academic Initiatives:
- Visiting Advanced Joint Research (VAJRA) Faculty Scheme: Attracts overseas scientists to work in Indian institutions, fostering high-quality collaborative research in cutting-edge areas.
- Ramanujan Fellowship: Provides opportunities for Indian researchers abroad to work in Indian institutions in science, engineering, and medicine.
- Ramalingaswami Re-entry Fellowship: Supports scientists returning to India to pursue research in life sciences and biotechnology.
- Biomedical Research Career Programme (BRCP): Facilitates career development for researchers in biomedical and public health sectors in India.
- For instance, DBT/Wellcome Trust India Alliance is a collaborative partnership between the Department of Biotechnology(DBT), Government of India, and The Wellcome Trust, UK, aimed at supporting the Biomedical Research Career Program (BRCP).
- Scholarship Programmes for Diaspora Children: Offers financial assistance for higher education in India to children of NRIs and PIOs.
- Community Support and Welfare:
- Indian Community Welfare Fund (ICWF): Provides emergency assistance to Indians citizens abroad, including repatriation during crises, legal aid, and financial support in emergencies.
- Pravasi Bharatiya Kendra: A hub for diaspora-related activities and a resource center in New Delhi, offering facilities for conferences and events.
- Senior Research Associateship (SRA) - Scientist's Pool Scheme: Administered by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), the scheme offers temporary placement to highly qualified Indian scientists, engineers, technologists, and medical personnel returning from abroad without employment in India.
- Crisis Management and Evacuations:
- The government has conducted several large-scale evacuation operations to protect its citizens during crises, demonstrating robust crisis management capabilities.
- Operation Ganga (2022), Operation Kaveri (2023), Operation Rahat (2015), and Operation Devi Shakti (2021) were all successful Indian government-led evacuation missions that rescued thousands of nationals and foreign allies from conflict zones.
What are the Challenges Associated with the Indian Diaspora?
- Economic Challenges:
- Indian workers in Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations often face job insecurity due to volatile oil prices and changing labor laws.
- This exposes them to financial instability and uncertain futures.
- Many diaspora members, especially in low-skilled jobs, are unable to fully utilize their potential, leading to underemployment and income disparity.
- Indian workers in Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) nations often face job insecurity due to volatile oil prices and changing labor laws.
- Social and Cultural Challenges:
- Second and third-generation Indians face challenges in maintaining their cultural identity, balancing integration with host cultures while preserving their heritage.
- Instances of racism and xenophobia remain significant concerns in many host countries, affecting the well-being of diaspora members.
- Political and Legal Issues:
- Stricter immigration policies in countries like the US and UK create challenges for NRIs and their families, limiting their opportunities for settlement and growth.
- Marital and property disputes often complicate the lives of overseas Indians, requiring diplomatic and legal interventions.
- Engagement Barriers:
- Many diaspora members are unaware of government schemes aimed at engaging them, resulting in underutilization of these initiatives.
- Complex processes and red tape can deter effective participation in diaspora-focused programs.
What Should be Way Forward to Tap the Potential of Indian Diaspora?
- Economic Strategies: Enhance skill-building initiatives to prepare workers for global markets, focusing on high-demand sectors such as IT, healthcare, and engineering.
- Streamline processes to encourage diaspora investments in India, including simplified taxation and regulatory frameworks.
- Cultural Integration: Develop programs to teach Indian languages to diaspora children, ensuring cultural continuity.
- Organize Indian festivals abroad to strengthen cultural ties and foster community spirit.
- Policy Reforms: Simplify voting mechanisms for NRIs to encourage political participation and representation.
- Offer more privileges to OCIs, such as participation in local governance and access to more public services.
- Strengthening Community Support: Strengthen the ICWF to provide better crisis support, including mental health services and repatriation assistance.
- Develop apps and portals for real-time engagement with the diaspora, ensuring accessibility and ease of use.
- Strategic Partnerships: Leverage the diaspora for stronger bilateral relations and global influence, emphasizing mutual benefits.
- Focus on youth-centric initiatives, such as cultural exchange programs and scholarships, to ensure sustained connections with future generations.
Conclusion
The Indian diaspora stands as a pillar of India’s global identity, significantly contributing to its economy, culture, and soft power. With proactive engagement and robust policies, India can further strengthen these ties, ensuring mutual growth and prosperity.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How does the Indian diaspora act as a bridge for strengthening India's bilateral relations with key global powers? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains:
Q. The Indian Diaspora has an important role to play in South East Asian countries economy and society. Appraise the role of Indian Diaspora in South-East Asia in this context. (2017)
Q. ‘Indian diaspora has a decisive role to play in the politics and economy of America and European Countries’. Comment with examples. (2020)