Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary | 10 Jan 2023
Why in News?
Recently, a Human-Animal Conflict occurred where a local man was attacked by an Elephant and a herd of elephants raided a field of 500 plantains.near Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, Kerala.
- Human-animal conflict has become a serious wildlife management problem in Kerala in the last few years. People living on the fringes of reserve forests and sanctuaries have a heightened sense of insecurity now.
What is Human-Animal Conflict?
- About: It refers to struggles that arise when the presence or behavior of wildlife poses actual or perceived direct, recurring threats to human interests or needs, often leading to disagreements between groups of people and negative impacts on people and/or wildlife.
- Causes: Human population expansion, habitat degradation and fragmentation, land use transformation and rising densities of livestock in protected areas are considered as the major causes of Human-Wildlife conflict.
What are the Key Points of Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary?
- Located in Kerala, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (WWS) is an integral part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve. It was established in 1973.
- Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve was the first from India to be included in the UNESCO designated World Network of Biosphere Reserves (designated in 2012).
- Other wildlife parks within the Reserve are: Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Mukurthi National Park and Silent Valley.
- Spread over 344.44 sq km, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary is contiguous to the tiger reserves of Nagerhole and Bandipur of Karnataka and Mudumalai of Tamil Nadu.
- Kabini river (a tributary of Cauvery river) flows through the sanctuary.
- The forest types include South Indian Moist Deciduous forests, West coast semi-evergreen forests and plantations of teak, eucalyptus and Grewelia.
- Elephant, Gaur, Tiger, Panther,Sambar, Spotted deer, Barking deer, Wild boar, Sloth bear, Nilgiri langur, Bonnet macaque, Common langur, Wild dog, common otter, Malabar giant squirrel etc are the major mammals.
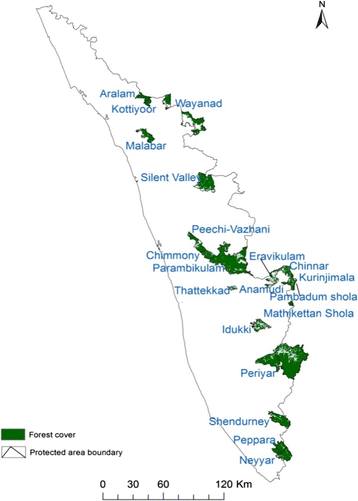
What are the Protected Areas in Kerala?
What is the Conservation Status of Elephants?
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of threatened species:
- African Forest Elephant- Critically Endangered
- African Savanna Elephant- Endangered
- Asian Elephant- Endangered
- Convention of the Migratory species (CMS): Appendix I
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. With reference to Indian elephants, consider the following statements: (2020)
- The leader of an elephant group is a female.
- The maximum gestation period can be 22 months.
- An elephant can normally go on calving till the age of 40 years only.
- Among the States in India, the highest elephant population is in Kerala.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The elephant herd is led by the oldest and largest female member (known as the matriarch). This herd includes the daughters of the matriarch and their offspring. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Elephants have the longest-known gestational (pregnancy) period of all mammals, lasting up to 680 days (22 months). Hence, statement 2 is correct. Females between 14 - 45 years may give birth to calves approximately every four years with the mean interbirth intervals increasing to five years by age 52 and six years by age 60. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- As per Elephant Census (2017), Karnataka has the highest number of elephants (6,049), followed by Assam (5,719) and Kerala (3,054). Hence, statement 4 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q2. Which of the following Protected Areas are located in Cauvery basin? (2020)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)