Virtual Private Network | 29 Apr 2024
Why in News?
Russia's tightening grip on online content in recent years has led to a significant surge in Virtual Private Network (VPN) usage among citizens seeking unrestricted access to information and media platforms.
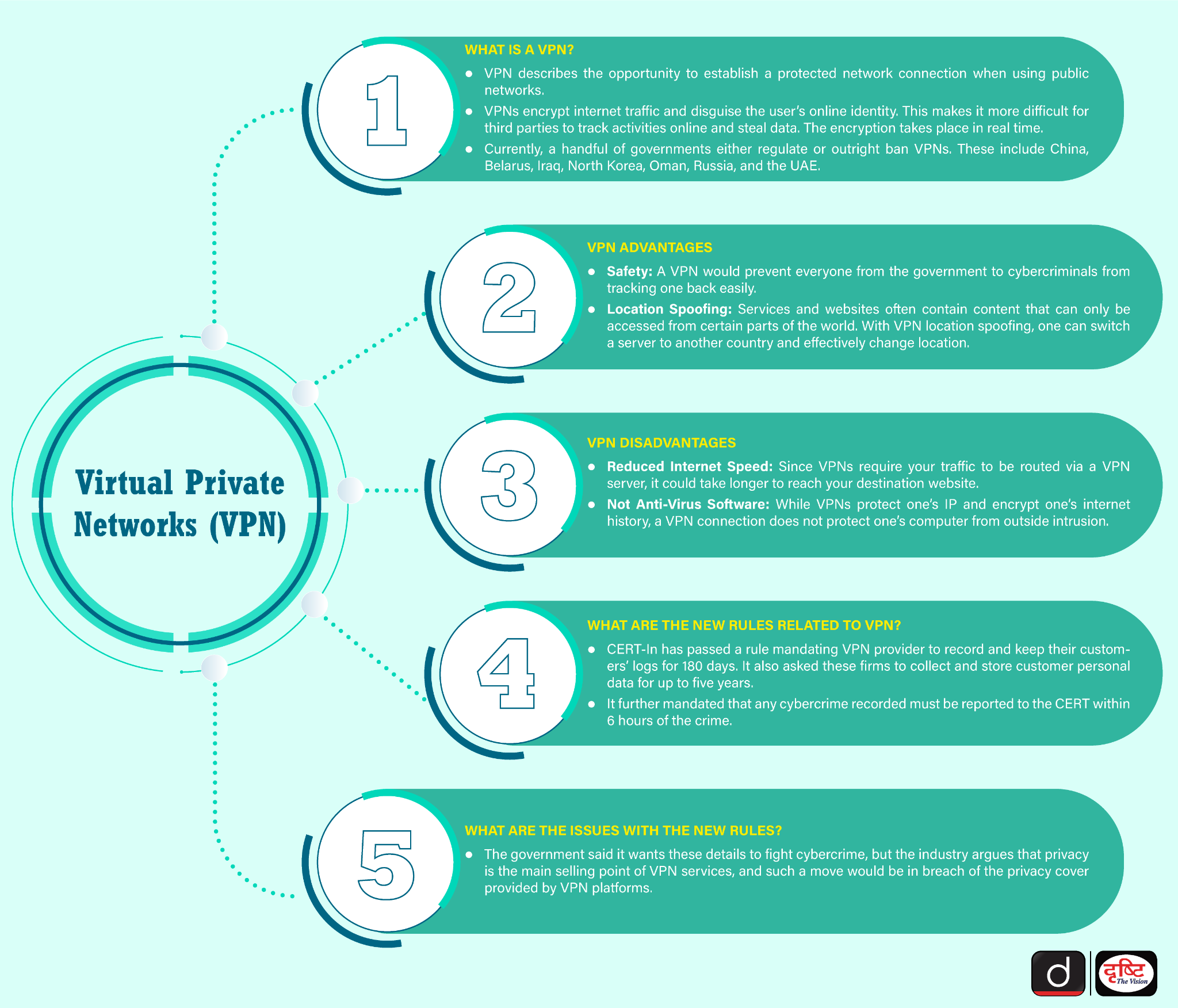
What is a VPN?
- About: A VPN is a technology that establishes a secure and private connection between a user's device and the internet. VPNs encrypt the internet traffic and disguise the user’s online identity.
- VPNs can bypass geo-restrictions and censorship. By connecting to a VPN server in a different location, users can access content and websites that may be restricted or blocked in their region.
- Mechanism:
- Encryption: When a user connects to a VPN, all data transmitted and received is encrypted.
- Encryption converts data into a code that only the user's device and the VPN server can decipher using a decryption key.
- Secure Tunneling: Encrypted data travels through a secure tunnel to the VPN server.
- This tunnel prevents unauthorised parties like Internet Service Providers (ISP), hackers or government agencies from intercepting or monitoring the user's online activities.
- IP Address Masking: The user's real IP address, which can reveal their location and device information, is replaced with the IP address of the VPN server.
- This masking process enhances user privacy and makes it difficult for websites to track the user's actual location.
- Encryption: When a user connects to a VPN, all data transmitted and received is encrypted.
What are Other Key Technologies Similar to VPN?
- Smart Domain Name System (DNS): It provides a proxy server resource for additional protection of a user's identity by masking a user's ISP-generated DNS address with a different address, generated by the Smart DNS device, before sending the user request to the internet.
- The Onion Router: It protects user data by encapsulating the data in multiple layers of secure encryption, using the Onion Protocol, as it routes the data from sender to receiver.
- The process ensures that a user's identity is protected from ISPs and advertisers.
- Proxy Servers: Proxy servers act as intermediaries between a user's device and the internet.
- They can be used to hide the user's IP address, bypass content filters, and improve speed by caching frequently accessed web pages.
Note:
- In 2022, the Indian Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology introduced regulations mandating VPN providers, data centres, virtual service networks, and cloud providers to record users' personal details for five years.
- They must also log usage patterns, and service purposes, and report cybersecurity incidents to CERT-In within six hours.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. What is “Virtual Private Network”? (2011)
(a) It is a private computer network of an organization where the remote users can transmit encrypted information through the server of the organization.
(b) It is a computer network across a public internet that provides users access to their organization’s network while maintaining the security of the information transmitted.
(c) It is a computer network in which users can access a shared pool of computing resources through a service provider.
(d) None of the statements (a), (b) and (c) given above is a correct description of Virtual Private Network.
Ans: (b)