Science & Technology
US to Build Small Modular Reactors in India
- 08 Apr 2025
- 6 min read
For Prelims: Small Modular Reactor (SMR) technology, International Atomic Energy Agency, 2008 India-US Civil Nuclear Deal or 123 Agreement, Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010, Atomic Energy Act, 1962, Union Budget 2025–26.
For Mains: SMR and India, Advancements of Indian in Nuclear Technology
Why in News?
The US has granted approval to Holtec International under its regulation 10CFR810, to transfer unclassified Small Modular Reactor (SMR) technology to 3 Indian private entities.
What are the Key Highlights of India-US SMR Technology Nuclear Deal?
- Validity:
- The authorization, valid for 10 years and subject to review every 5 years, allows Holtec to design and construct nuclear reactors in India.
- Regulatory Safeguards:
- Under the approval, SMR technology can only be used for peaceful civilian purposes, must follow International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) safeguards, and cannot be used for military activities, ensuring compliance with global non-proliferation norms.
- Significance:
- Operationalises the 123 Agreement: Revives the 2008 India-US Civil Nuclear Deal or 123 Agreement by overcoming legal and commercial barriers.
- Encouraging Private Sector: Marks the first direct US tech transfer to Indian private firms, shifting from state-only control to a public-private (PPP) model.
- Boosting Indigenous Capability: Facilitates local manufacturing of SMR and positions India as a future hub for nuclear innovation and exports, especially for the Global South.
- Legal and Policy Challenges:
- Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010: Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010 holds suppliers liable for nuclear accidents, discouraging foreign investment and tech transfer.
- Atomic Energy Act, 1962: Atomic Energy Act, 1962 restricts nuclear power generation to government entities, barring private firms from owning or operating plants.
- The government has formed inter-ministerial committees to amend the Atomic Energy Act, 1962 and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act, 2010, aiming to enable private sector participation in nuclear energy.
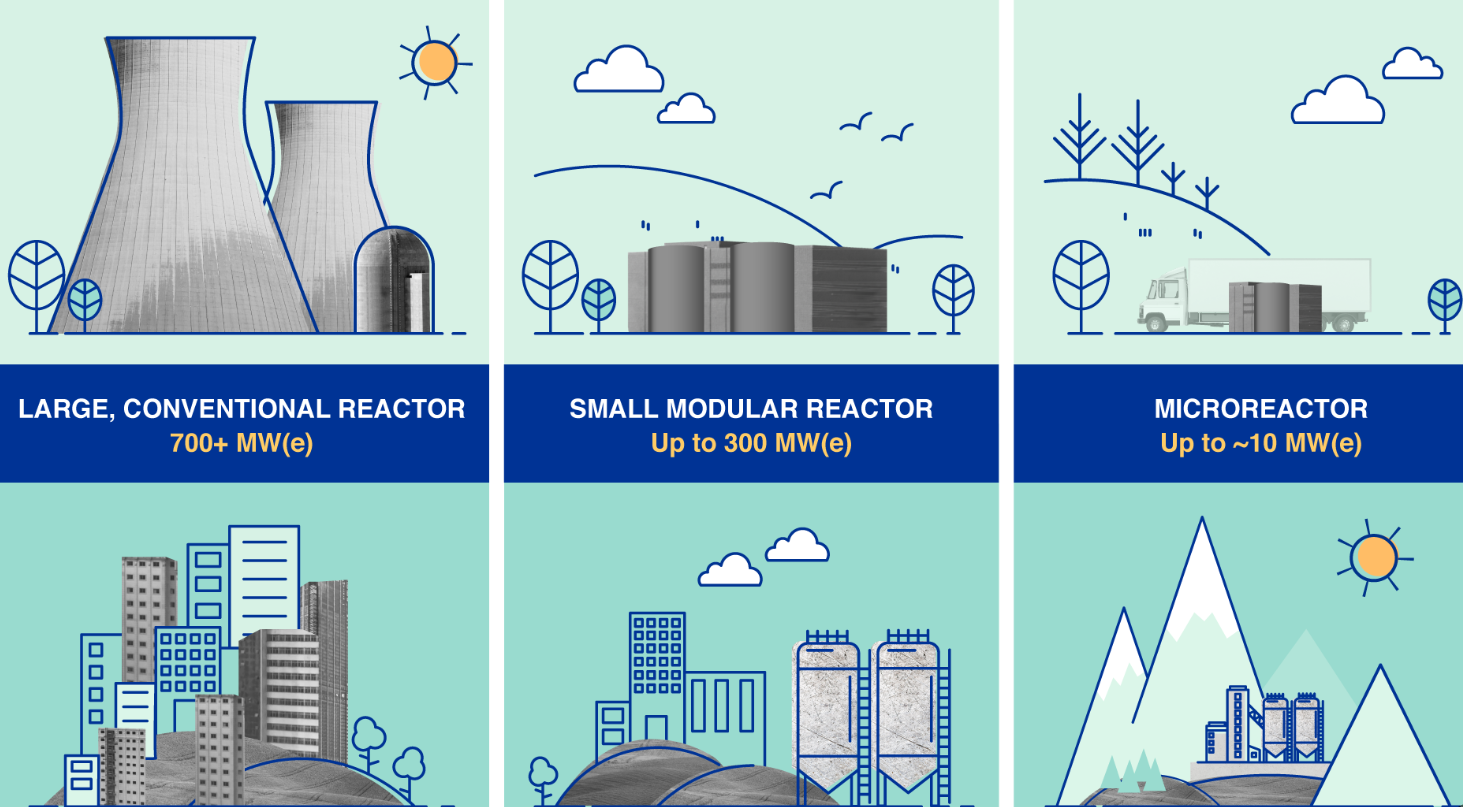
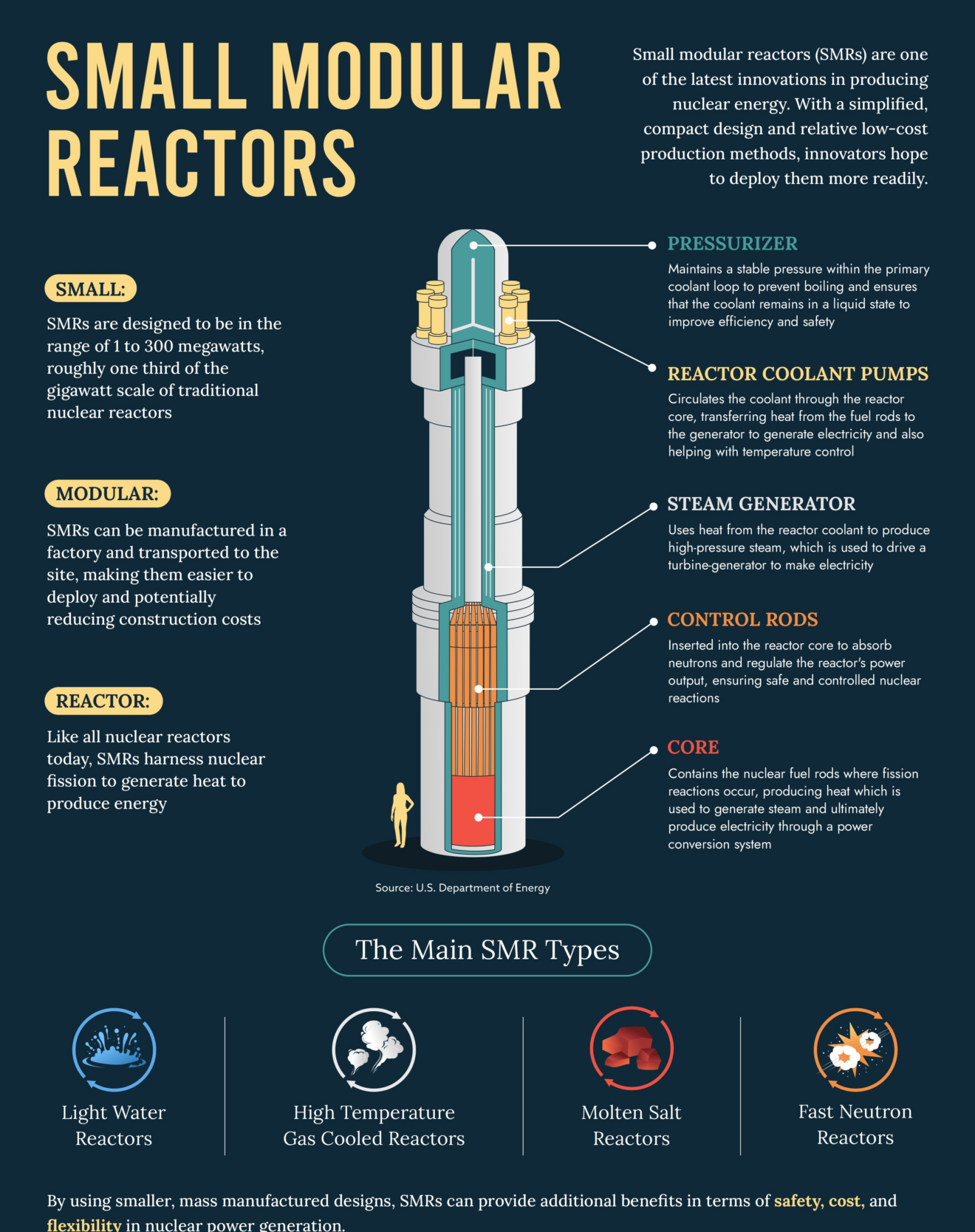
What are Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)?
- About:
- SMRs are advanced nuclear reactors with a capacity of up to 300 MW(e), about one-third of traditional reactors.
- They are compact, factory-assembled, and transported for installation, making them suitable for remote or space-constrained areas.
- Eg: NuScale (USA), CAREM (Argentina)
- Key Features:
- SMRs are compact nuclear reactors that generate low-carbon electricity. They are:
- Small: Much smaller in size compared to conventional nuclear reactors.
- Modular: Factory-built components can be transported and assembled on-site.
- Reactors: Use nuclear fission to produce heat, which is converted into energy.
- SMRs are compact nuclear reactors that generate low-carbon electricity. They are:
- Key Advantages:
- Fuel Efficiency: Require refueling every 3-7 years (as compared to 1–2 years in conventional plants).
- Scalability & Flexibility: Easily integrated into diverse power systems and can be scaled for remote areas or urban grids.
- Reduce reliance on rare reactor-grade fuels or advanced enrichment processes.
- Passive Safety: Incorporate inherent safety systems for enhanced accident resilience.
- Low-Carbon & Reliable: Provide 24/7 clean energy, complementing renewables and aiding grid stability, helping meet rising energy demand and net-zero goals by 2070).
- SMR and India:
- Budgetary Allocation: The Union Budget 2025–26 announces the launch of a Nuclear Energy Mission with focus on research and development of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and develop at least 5 indigenously designed and operational SMRs by 2033.
- Bharat Small Reactors (BSRs): BSR are 220 MW Pressurized Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) with a strong safety record which will be deployed near industries like steel, aluminium, and metals, functioning as captive power plants to aid decarbonization.
- Private entities will provide land, cooling water, and capital, while NPCIL will handle design, quality assurance, and operations.
- This initiative aligns with India's COP26 pledge to achieve 500 GW of non-fossil fuel-based energy and 50% renewable energy by 2030.
- Private entities will provide land, cooling water, and capital, while NPCIL will handle design, quality assurance, and operations.
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) is working on SMRs for repurposing retiring coal-based power plants and meeting the energy needs of remote areas.
- The Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) is also focusing on developing reactors such as high-temperature gas-cooled reactors for hydrogen generation and molten salt reactors to utilize India’s vast thorium resources.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The function of heavy water in a nuclear reactor is to (2011)
(a) Slow down the speed of neutrons
(b) Increase the speed of neutrons
(c) Cool down the reactor
(d) Stop the nuclear reaction
Ans: (a)