Economy
UNCTAD Global Investment Trends Monitor Report
- 29 Jan 2025
- 12 min read
For Prelims: Foreign Direct Investment, United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), Global Investment Trends Monitor for 2024, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
For Mains: Global FDI Trends, India’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), FDI’s role in the development.
Why in News?
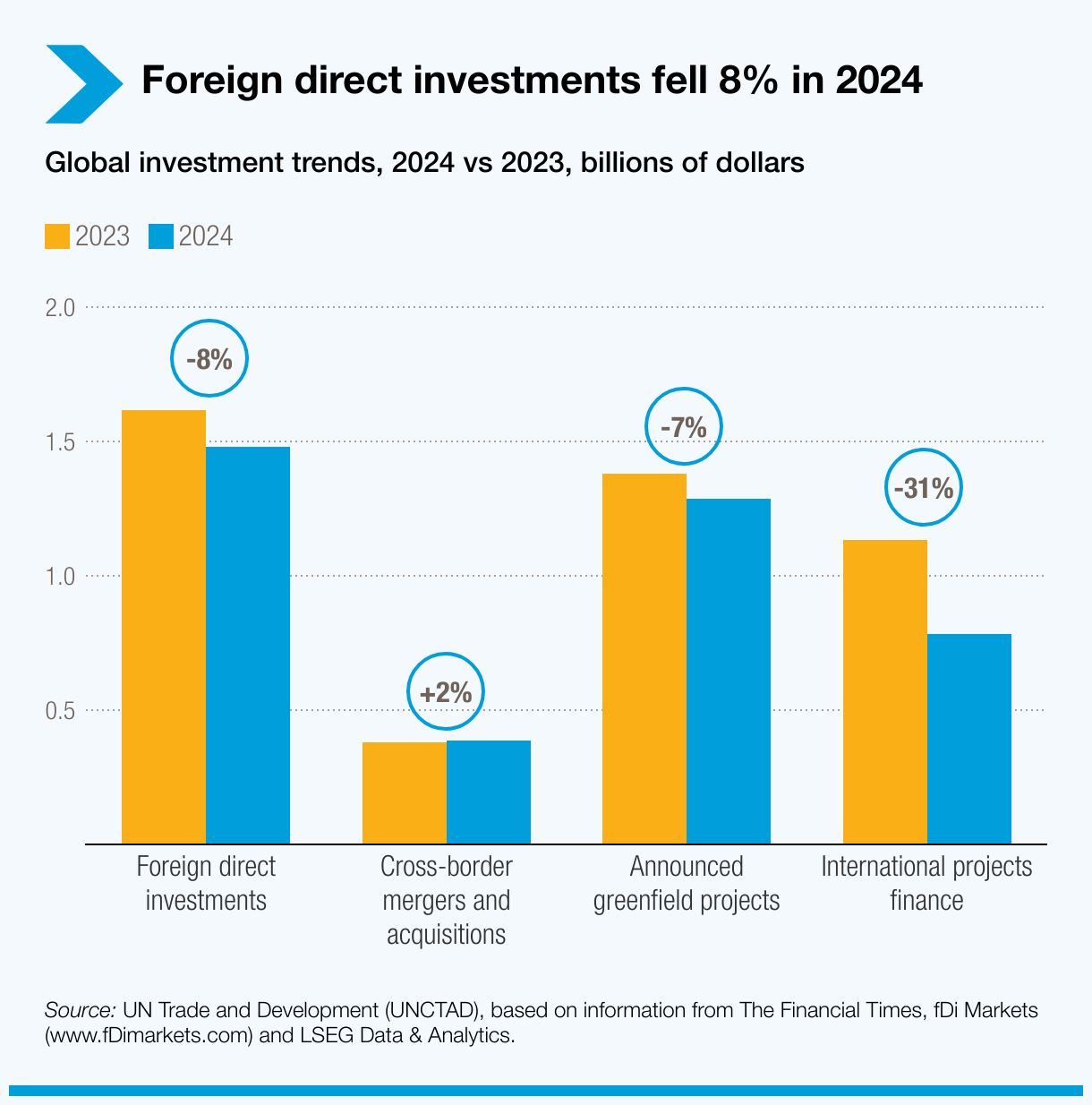
The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) has released its Global Investment Trends Monitor for 2024, reporting an 8% decline in global Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
- This threatens funding for critical sectors like infrastructure and renewable energy which are essential for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- About:
- It is the leading institution of the UN established in 1964, that is focused on trade and development of developing countries.
- It provides expertise and policy advice on issues related to trade, investment, finance, and technology transfer to promote sustainable development.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Structure: It is a part of the UN Secretariat, reports to the General Assembly and Economic and Social Council; has its own membership, leadership, and budget.
- Flagship Reports:
- Trade and Development Report
- World Investment Report
- Digital Economy Report
- Technology and Innovation Report
What are the Key Highlights of the Global Investment Trends Monitor for 2024 Report?
- Global FDI Trends:
- Global FDI: Global Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows increased by 11% reaching about USD 1.4 trillion in 2024. However, when excluding flows through European conduit economies, FDI decreased by around 8%.
- Conduit economies are countries that allow financial flows to be diverted to other countries for tax avoidance. Eg: Ireland, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Switzerland and the UK.
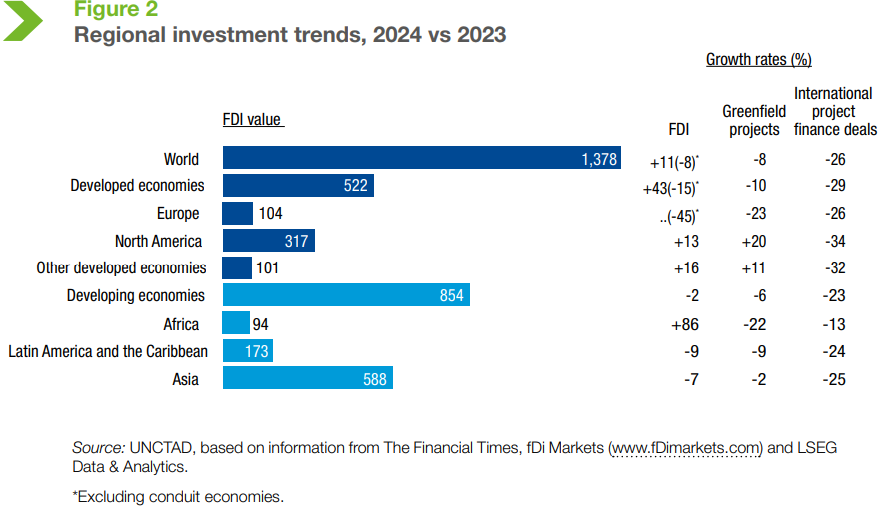
- Developed Economies: FDI into developed economies surged by 43%, driven primarily by multinational transactions passing through conduit economies.
- However, excluding these transactions, FDI into developed economies fell by 15%.
- Developing Economies: FDI flows to developing economies declined by 2% in 2024, following a 6% drop in 2023.
- Global FDI: Global Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) flows increased by 11% reaching about USD 1.4 trillion in 2024. However, when excluding flows through European conduit economies, FDI decreased by around 8%.
- Regional Investment Trends:
- Developed Economies:
- FDI in Europe dropped 45% (excluding conduit economies) but North America saw a 13% rise.
- Greenfield project announcements in developed economies fell by 10%, but the value of greenfield projects rose by 15%, mainly due to semiconductor megaprojects.
- Developing Economies:
- Greenfield investment announcements decreased by 6% in number.
- Africa and Asia saw the largest declines in greenfield project numbers, with nearly 200 fewer projects in Africa and 150 fewer in Asia.
- It also declined in Latin America and the Caribbean.
- FDI in Africa surged by 84% to USD 94 billion, mainly driven by a large project in Egypt.
- FDI in Central America has increased.
- FDI flows to developing Asia decreased by 7%, with China experiencing a 29% decline, while ASEAN saw a 2% increase and India saw a 13% rise.
- India experienced growth in greenfield projects. The international project finance in India dropped by 23% in number and 33% in value.
- Greenfield investment announcements decreased by 6% in number.
- Developed Economies:
- SDG-Related Investments:
- Investments in sectors related to the SDGs, including infrastructure, agrifood systems, and water and sanitation, decreased by 11% in 2024.
- This drop could impact critical sectors such as affordable and clean energy (SDG 7), industry and infrastructure (SDG 9), and water and sanitation (SDG 6).
- Renewable energy project finance slowed, with international deals down 16%, and domestic finance down 60%.
What are the Prospects for Global FDI in 2025 as per UNCTAD Report?
- Global FDI Outlook:
- Global FDI is expected to grow moderately, with the US and EU seeing stronger growth.
- US investment abroad has declined as focus shifts to domestic projects, while Chinese investment abroad has increased.
- ASEAN, Eastern Europe, West Asia, North Africa, and Central America may benefit from global supply chain shifts.
- For India, moderate FDI growth is expected in 2025, driven by improved financing conditions, increased mergers and acquisitions (M&A), and ongoing reforms.
- Global FDI is expected to grow moderately, with the US and EU seeing stronger growth.
- Key Influencing Factors:
- FDI growth will depend on GDP, trade, inflation, market volatility, geopolitical dynamics, technology advancements, and policy changes.
- Private equity and sovereign investors will also play a significant role.
- Economic Growth:
- Stable GDP growth is expected with improved projections for capital formation and trade, benefiting global investments.
- Lower interest rates could reduce borrowing costs, boosting cross-border investments, especially in infrastructure.
- Technology & Sector Trends:
- Investments in sectors like AI, cloud computing, cybersecurity, and renewable energy (green hydrogen, electric vehicles) are expected to rise.
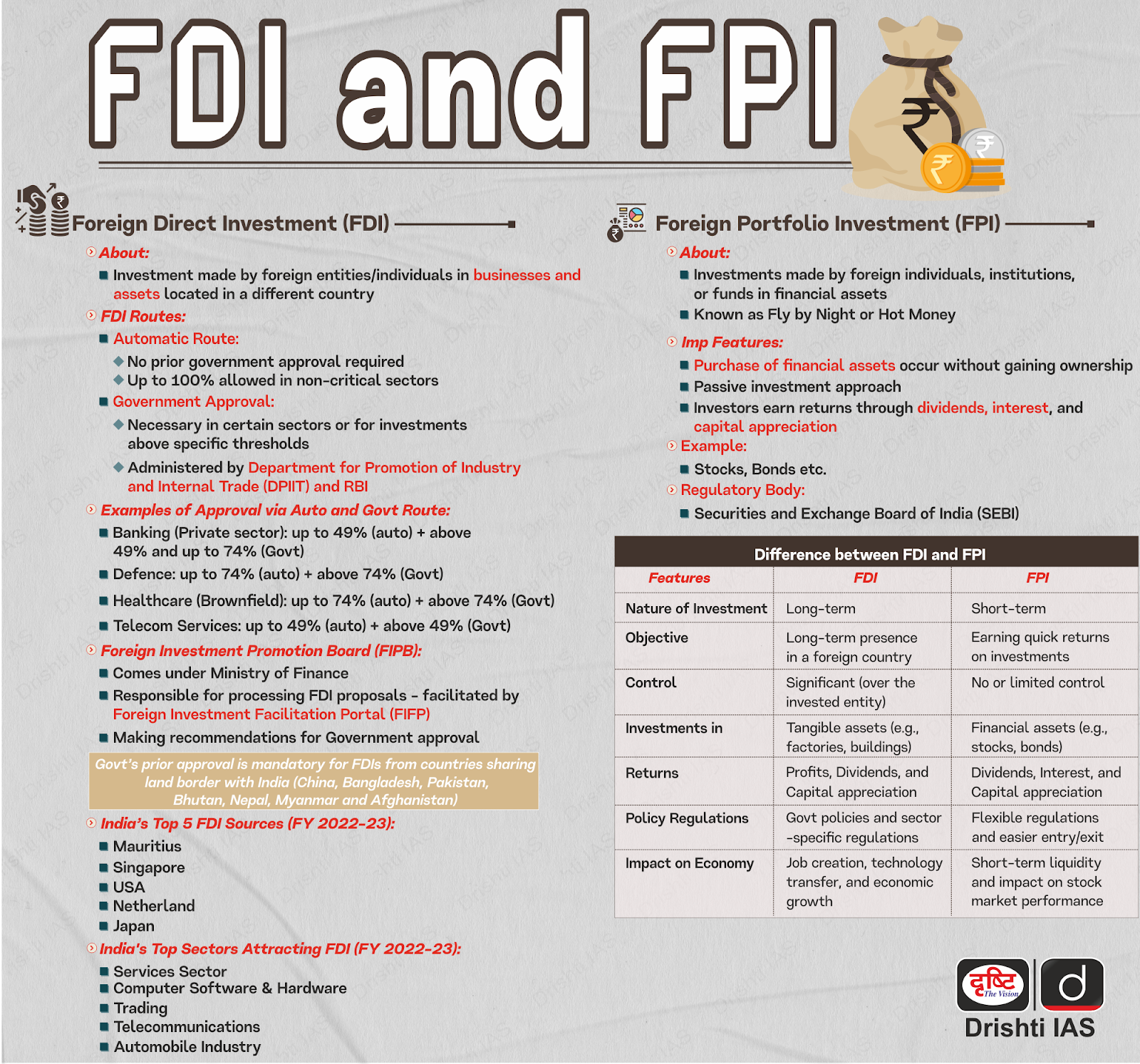
What is Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)?
- About:
- Types of FDI:
- Greenfield Investment: Creating new business operations from the ground up, offering high control and customization.
- Brownfield Investment: Expanding through mergers, acquisitions, or joint ventures by utilizing existing facilities.
- While control may be lower than in Greenfield investments, it still allows significant influence over operations.
- FDI in India:
- Regulation: FDI in India is governed by the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, and is administered by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- FDI Prohibition in India: FDI is strictly prohibited in sectors like atomic energy generation, gambling and betting, lotteries, chit funds, real estate, and the tobacco industry.
- Latest Data Related to FDI: FDI inflows into India crossed USD 1 trillion between April 2000 and September 2024, totaling USD 1,033.40 billion.
- From 2014 to 2024, India attracted USD 667.4 billion in cumulative FDI, a 119% increase from the 2004-2014 period.
What are the Opportunities and Challenges Related to FDI in India?
- Opportunities for FDI in India:
- Large Market Size and Growth: India’s 1.4 billion population drives high demand for both affordable and high value goods.
- India is one of the fastest growing economies and its GDP is projected to grow at 6.5% in 2025 and 2026 as per IMF.
- Favorable Demographics: A young workforce (over 65% below 35 years) provides a relatively skilled and cheap labour pool.
- Government Initiatives: Policies like "Make in India," "Atmanirbhar Bharat," and ease of doing business reforms streamlined requirements and made favourable destinations to attract FDI.
- Strategic Location: India's location acts as a gateway to the emerging markets of South Asia, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia.
- Large Market Size and Growth: India’s 1.4 billion population drives high demand for both affordable and high value goods.
- Challenges in Attracting FDI:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Complex tax systems, inconsistent policies (retrospective taxation), and bureaucratic delays hinder business operations.
- Infrastructure Challenges: Poor infrastructure, particularly in rural and suburban areas, limits ease of doing business.
- Labor Laws: Rigid labor laws and low labor market flexibility create challenges for businesses.
- Expectations from Investors:
- Technology Transfer: India seeks foreign expertise and technology in sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and renewable energy.
- Job Creation: Investors are expected to create employment opportunities for India's growing workforce.
- Sustainable Investments: India encourages green and sustainable investments to meet its climate goals (e.g., National Action Plan on Climate Change).
Conclusion
India’s large market, economic growth, and favorable demographics offer significant opportunities for FDI. While government initiatives like “Make in India” create a favorable environment, challenges such as regulatory hurdles and infrastructure gaps remain. India expects investors to contribute to technology transfer, job creation, and sustainable growth, which will support both economic and social development goals.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the role of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in enhancing India’s competitiveness and innovation ecosystem. How do improvements in global competitiveness influence FDI inflows? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Foreign Direct Investment in India, which one of the following is considered its major characteristic? (2020)
(a) It is the investment through capital instruments essentially in a listed company.
(b) It is a largely non-debt creating capital flow.
(c) It is the investment which involves debt-servicing.
(d) It is the investment made by foreign institutional investors in Government securities.
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following: (2021)
- Foreign currency convertible bonds
- Foreign institutional investment with certain conditions
- Global depository receipts
- Non-resident external deposits
Which of the above can be included in Foreign Direct Investments?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 4
(d) 1 and 4
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Justify the need for FDI for the development of the Indian economy. Why is there a gap between MOUs signed and actual FDIs? Suggest remedial steps to be taken for increasing actual FDIs in India. (2016)