Ukraine “Path to Peace” Summit | 18 Jun 2024
For Prelims: Russia-Ukraine Conflict, Regions of Donetsk and Luhansk, Black Sea, Cold War, NATO, Minsk Protocols, Warsaw Pact.
For Mains: Ukraine-Russia Conflict and India’s Interests in Ukraine and Russia, Implications of Conflict on India.
Why in News?
- Recently, the two-day Summit on Peace in Ukraine titled “Path To Peace Summit”, held in Switzerland, ended on 16th June 2024.
- Through this summit, participants hoped for an end to the war between Russia and Ukraine.
What were the Key Highlights of the Summit?
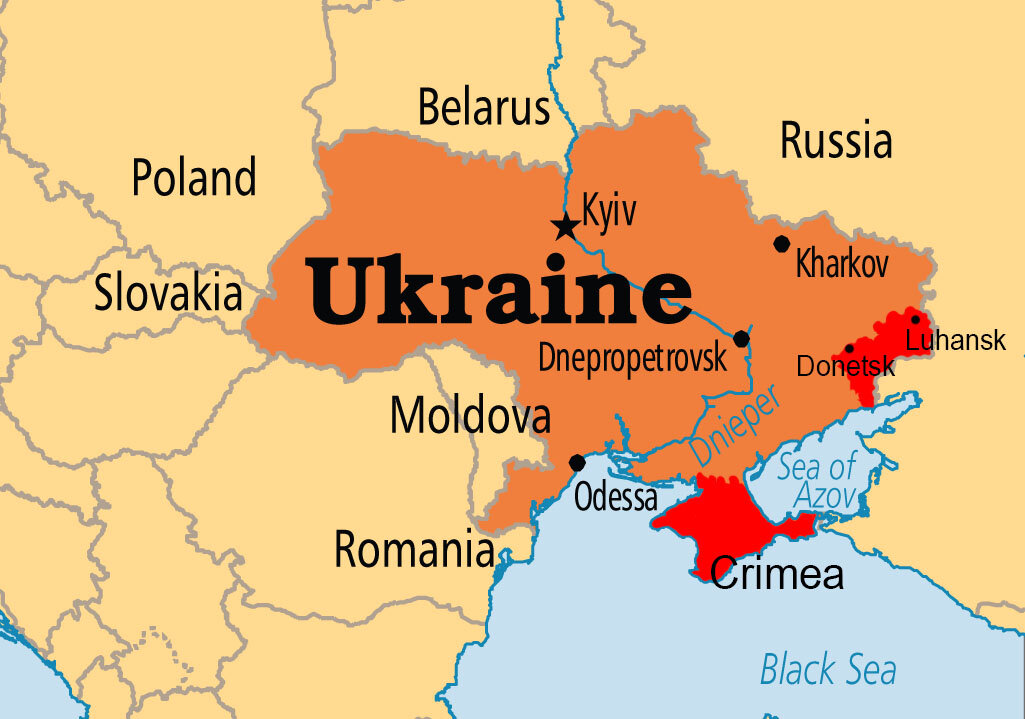
- Call for Territorial Integrity of Ukraine:
- 80 countries have called for the “territorial integrity” of Ukraine to be the basis for any peace agreement to end the Russia-Ukraine war.
- They supported the final joint communiqué that outlined a "Path to Peace" and focused on 3 agendas: nuclear safety, global food security, and humanitarian issues.
- Release of Prisoners of War:
- The declaration emphasised the release of all prisoners of war and the return of all deported and unlawfully displaced Ukrainian children and civilians.
- Absence of Russia from Peace Summit:
- Russia, the primary party to the conflict, was not invited by the host, Switzerland, due to the International Criminal Court's indictment of President Vladimir Putin.
- India’s Refusal to Endorse Ukraine Meet Statement:
- India along with Saudi Arabia, South Africa, and the United Arab Emirates refused to sign onto the final document released at the conclusion of a Peace Summit.
- India emphasised that only proposals acceptable to both Russia and Ukraine can lead to peace.
What is India’s Stand in the Russia-Ukraine Conflict?
- Commitment to Non-Alignment:
- India's non-aligned foreign policy, with its origins in the Bandung Conference of 1955, has been a central tenet of its approach to international conflicts.
- India has opted to abstain on UN Security Council (UNSC) resolutions regarding Russia's actions in Ukraine. This aligns with their established policy of neutrality in major power disputes.
- Preserving Strategic Partnership with Russia:
- India regards Russia as a crucial strategic partner, with Russia being a significant supplier of military hardware and energy resources to India.
- According to data from the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), Russia accounted for approximately 46% of India's total arms imports between 2017-2021.
- India regards Russia as a crucial strategic partner, with Russia being a significant supplier of military hardware and energy resources to India.
- Humanitarian Assistance and Diplomatic Efforts:
- India has taken various steps to address the humanitarian aspects of the conflict by providing humanitarian aid to Ukraine, including medical supplies and relief materials.
- Furthermore, India emphasised the need for a diplomatic solution to the conflict and has urged both Russia and Ukraine to engage in dialogue in various international forums, reflecting India's efforts to promote a peaceful resolution to the crisis.
- Balancing Ties with the West:
- While maintaining its strategic partnership with Russia, India has also tried to balance its ties with the US and the European Union (EU), which are India's largest trading partners.
- This is aimed at protecting India's economic and geopolitical interests in the face of the evolving international landscape.
- While maintaining its strategic partnership with Russia, India has also tried to balance its ties with the US and the European Union (EU), which are India's largest trading partners.
What are the Areas of Cooperation between India and Russia?
- Trade and Economic Cooperation:
- India-Russia relations have been a key pillar of India's foreign policy since the signing of the "Declaration on the India-Russia Strategic Partnership" in 2000, which was further elevated to a "Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership" in 2010.
- In 2021, the two countries held their first 2+2 Dialogue (Foreign and Defence Ministers of both countries), highlighting the deeper collaboration.
- India has announced a USD 1 billion line of credit for the development of Russia's Far East.
- Defence and Security:
- It is guided by the Agreement on the Programme for Military Technical Cooperation signed between the two countries.
- The Agreement on Program of Military-Technical Cooperation from 2021-2031 was signed during the inaugural meeting of the India-Russia 2+2 Dialogue held in Delhi in December 2021.
- India is the top purchaser of Russian military equipment, including the S-400 Triumf Missile system, Kamov 226 helicopters, and T-90S tanks.
- Both countries are also collaborating on developing defence technologies such as the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile and conducting joint military exercises like INDRA & AviaIndra.
- Energy Cooperation:
- Russia has vast natural gas reserves and India is shifting towards using more natural gas, actively importing from the Russian Far East.
- India and Russia signed their first nuclear cooperation agreement in 1963. It led to construction of reactors at Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant commissioned in 2016.
- Both are working on the Rooppur Nuclear Power Project in Bangladesh.
- In 2018, they agreed to jointly develop Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), which are small, efficient nuclear reactors used for electricity generation or industrial heat production.
- International Cooperation:
- India and Russia are members of various multilateral organisations, such as BRICS, Russia-India-China Grouping (RIC), G20, East Asia Summit, and Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), which provide opportunities for cooperation on mutual issues.
- Russia supports India's aspiration for a permanent seat in the UN Security Council (UNSC).
- Russia has endorsed India's membership in the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG) and Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC).
- Russia is considerate of India's stance on the Jammu and Kashmir issue in relation to Pakistan.
- The two countries are involved in connectivity projects like the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC).
- Cyber Security:
- India and Russia have an "Agreement on Cooperation in International Information Security" to work together in cyber security.
- They are also collaborating to combat radicalization and cyberterrorism. Additionally, India plans to work with the Russian Quantum Center to utilise quantum cryptography for enhanced information security in various sectors.
What are the Global Implications of the Russia-Ukraine War?
- Geopolitical Implications: War has led countries to align with Russia, Ukraine, or remain non-aligned. The EU has imposed sanctions on Russia, while the UK supports Ukraine. Many developing countries prioritise pragmatic relationships, staying non-aligned.
- The war has driven increases in European defence budgets, strengthening partnerships like NATO, shifting the global balance of power.
- Turkey doesn't fully align with all NATO proposals, particularly on economic sanctions.
- Strained Global Institutions: The war has exposed limitations of international institutions like the UN to prevent major conflicts. Countries may question the effectiveness of these bodies, potentially leading to a shift in how international disputes are addressed.
- Massive Displacement: The UN estimates over 11 million Ukrainians have fled their homes, creating a significant refugee crisis in Europe and internally displaced populations within Ukraine. This has placed immense strain on neighbouring countries and international aid organisations.
- UNICEF reports that two-thirds of Ukrainian children have been negatively impacted by the war, facing displacement, psychological trauma, and disruptions to education.
- Threatened Food Security: Ukraine is a major agricultural producer, supplying a significant portion of the world's wheat, corn, and sunflower oil. The war has disrupted planting, harvesting, and exports exacerbating existing food insecurity issues and potentially leading to shortages in vulnerable regions.
- Disruption in Global Energy Market: Russia's role as a major energy exporter has caused disruptions in global energy markets. Sanctions and boycotts have led to price hikes for oil and gas, impacting energy security and inflation worldwide.
What are the International Efforts to Establish Peace between Russia and Ukraine?
- Ukrainian 10-Point Peace Plan: It was promoted by the President of Ukraine since the 2023 G-20 Summit and outlined key demands.
- Withdrawal of Russian troops from Ukrainian territory.
- Restoration of Ukraine's territorial integrity as per its internationally recognised borders established in 1991.
- Prosecution of war crimes committed by Russia.
- Minsk Agreements, 2015:
- Minsk Agreements were signed in 2014 and 2015 in the Belarusian capital Minsk.
- The Minsk agreements were discussed and agreed upon with the involvement and support of France, Germany, and the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE). These agreements were signed by Ukraine, Russia, and the representative of the OSCE. It aimed to end the initial phase of the conflict in eastern Ukraine. It included:
- A ceasefire between Ukrainian forces and pro-Russian separatists.
- Withdrawal of heavy weaponry from the conflict zone.
- Full Ukrainian government control over the eastern Donbas region.
- United Nations Efforts: UN experts have consistently called for intensified efforts by the international community to achieve peace in line with the UN Charter. This includes respecting Ukraine's sovereignty, independence, unity, and territorial integrity as outlined by the UN Secretary-General.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the geopolitical and economic implications of the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict. Analyse the appropriate approach need to be adopted in this complex scenario. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Q. Consider the following countries: (2023)
- Bulgaria
- Czech Republic
- Hungary
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Romania
How many of the above-mentioned countries share a land border with Ukraine?
(a) Only two
(b) Only three
(c) Only four
(d) Only five