Economy
Threat to Indian Online Gaming Sector
- 29 Oct 2024
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Money laundering, Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR), PMLA 2002, KYC guidelines, Financial Action Task Force (FATF), Information Technology Rules, 2021, Real Money Gaming (RMG) operators, Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, Virtual Private Network (VPNs), geo-blockers.
For Mains: Money laundering through online gaming, Challenges to the gaming sector, Government initiatives to stop Money laundering.
Why in News?
According to a report by the Digital India Foundation (DIF), Money laundering is a major threat to the Indian online gaming sector’s integrity and long-term success.
Note:
Digital India Foundation (DIF) is a not-for-profit think-tank aiming to foster digital inclusion and adoption, and the use of the Internet and related technologies for the developmental process.
What are the Key Points of the Report?
- International Online Betting Threats: The report titled “Combating Money Laundering in Online Gaming Ecosystem” highlights the rising trend of using international online betting sites for money laundering and terror financing in cybercrime.
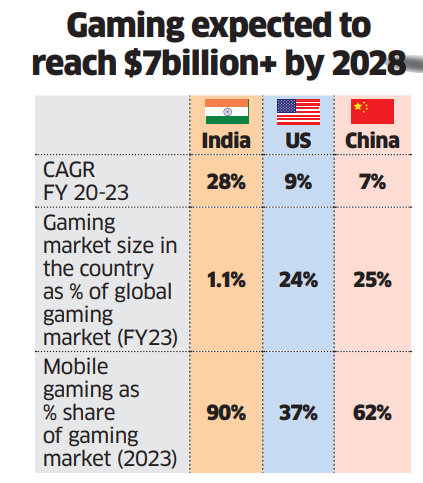
- Sectoral Growth: India's online gaming industry is rapidly growing with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 28% from FY20 to FY23.
- The sector's revenue is expected to reach USD 7.5 billion in five years.
- Employment Generation: India has 568 million gamers, creating significant employment opportunities across various sectors such as fintech, cybersecurity, and cloud services.
- The sector has the potential to create 250,000 jobs by 2025, with over 400 start-ups and 100 million daily online gamers.
- Vulnerabilities and Risks:
- The report identifies various mechanisms used for money laundering within the online gaming sector:
- Illegal operators: Many platforms bypass restrictions through mirror sites and Virtual Private Network (VPNs).
- In-game currencies and assets: Often used for illicit activities.
- Cryptocurrencies: Provide anonymity and facilitate cross-border money laundering.
- Mule accounts: Accounts used to facilitate transactions, obscuring the source of illegal funds.
- Smurfing and money dumping: Techniques where small transactions are used to avoid detection.
- The report identifies various mechanisms used for money laundering within the online gaming sector:
What is Online Gaming?
- About:
- Online gaming involves playing video games with others over the internet. Players can connect via computer, gaming console, or smartphone.
- It enables real-time interaction and competition among players, regardless of location.
- Classification:
- Skill-Based Games: These games are legal in India as long as they emphasize skill rather than chance. E.g Game 24X7, Dream11, Mobile Premier League (MPL).
- Games of Chance: These games are considered illegal if the outcome is primarily determined by chance rather than skill. E.g., Roulette where players are drawn in primarily due to the potential for monetary rewards.
- Current Scenario:
- Youth Demographics: Over 600 million people in India are under 35, comprising 45% of the population, driving the gaming industry's growth.
- Smartphone Penetration: Smartphone usage has reached 75%, enhancing access to gaming and contributing to rising engagement.
- Mobile gaming accounts for 90% of total gaming revenue, primarily through free-to-play games and in-app purchases.
- E-sports Growth: E-sports viewership in India has surged to over 80 million, with government backing and an increasing number of professional gamers.
What is the Legality of Online Gaming and Gambling in India?
- Legal Jurisdiction: The state legislators are, vide Entry No. 34 of List II (State List) of the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India, given exclusive power to make laws relating to Gaming, Betting and Gambling.
- Most Indian states regulate gaming on the basis of a distinction in law between ‘games of skill’ and ‘games of chance’.
- Public Gambling Act, 1867: At present, India has just one central law that governs gambling in all its forms. It's called the Public Gambling Act, 1867, which is an old law, ill-equipped to handle the challenges of digital casinos, online gambling and gaming.
- Recently, the Finance Ministry of India announced a 28% Goods and Services Tax (GST) on online money gaming, casinos, and horse racing.
- The Lotteries Regulation Act, 1998: The lottery is considered legal in India. The lottery should be organised by the state government and the place of Draw should be in that particular state.
Money Laundering
- About:
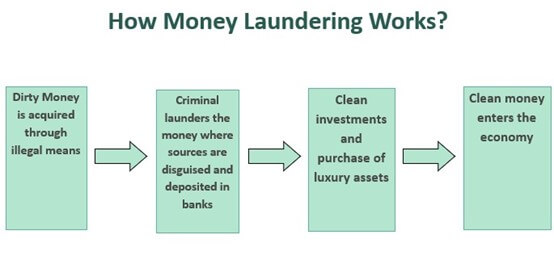
- It is an intricate method employed by individuals and organizations to hide the origins of illegally acquired money, transforming illicit funds into seemingly legitimate ones through multiple transactions.
- Methods of Money Laundering:
- Structuring (Smurfing): Dividing large sums of cash into smaller, less noticeable amounts for bank deposits.
- Trade-Based Laundering: Utilizing trade transactions to transfer value internationally while masking the origins of illegal funds.
- Shell Companies: Establishing businesses with no real activity to route illicit funds through seemingly legitimate transactions.
- Real Estate: Acquiring property with illegal funds and selling it to transform the value into legitimate assets.
- Steps to Prevent Money Laundering in India:
- Enforcement of the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA)
- Formation of the Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU)
- Mandatory Reporting by banks and financial institutions for cash transactions above a certain threshold and suspicious activity
- Strict KYC guidelines to verify customer identities
- Coordination with international organisations like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
- Information Technology Rules, 2021 (oversight in online gaming industry)
What are the Challenges to the Gaming Sector?
- Financial Integrity Issues: India's illegal betting market attracts over USD 100 billion in deposits annually, raising concerns about financial integrity due to easy asset transfers and conversions, which fuel money laundering and fraud.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Cyber Attack risks threaten user safety and data protection in gaming, while users bypass restrictions using VPNs and geo-blockers to access illegal gambling sites.
- Misuse of In-Game Assets: There are risks associated with the potential misuse of in-game assets and cryptocurrencies, which can complicate regulation.
- Operation of Illegal Offshore Platforms: The prevalence of illegal offshore online betting sites poses a challenge to regulatory efforts.
- Circumvention of Regulations: Many platforms circumvent existing regulations using mirror sites, illegal branding, and misleading promises, indicating a need for stronger oversight and enforcement.
What can be the Risk-mitigation steps?
- Establishment of Taskforce: Form a dedicated taskforce of experts to recommend policy measures for better regulation of the gaming sector.
- Mandatory Registration: Require all online and offshore Real Money Gaming (RMG) operators to register under the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017, within 30 days of becoming liable.
- Creation of a Whitelist: Publish and regularly update a whitelist of legal online RMG operators to ensure that payment gateways, hosting providers, and ISPs serve only these operators.
- Advertising Advisory: The Information and Broadcasting Ministry should issue advisories allowing only whitelisted online gaming applications to advertise.
- Collaboration with Financial Institutions: Collaborate with banks and payment service providers to establish protocols for blocking transactions to known illegal gambling operators.
- Cross-Border Cooperation: Lead efforts to develop multilateral agreements with international organizations and other countries to enhance cooperation in combating illegal online gambling.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Critically analyze the vulnerabilities in the Indian online gaming ecosystem that enable money laundering. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Discuss how emerging technologies and globalisation contribute to money laundering. Elaborate measures to tackle the problem of money laundering both at national and international levels. (2021)