Agriculture
Surge in Tobacco Prices
- 07 May 2024
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Tobacco, World Health Organization, WHO MPOWER, Indian Tobacco Board, Flue-cured Virginia (FCV), National Tobacco Control Programme
For Mains: Impact of tobacco consumption and measures, Tobacco Consumption in India, Government Policies & Interventions, Global Burden of Cancer
Why in News?
Tobacco farmers in Andhra Pradesh are set to benefit after crop yields in Brazil, Zimbabwe and Indonesia declined due to droughts and untimely rainfall.
- Auction prices in Andhra Pradesh have surged to near-record levels and are expected to rise further.
How are Tobacco Farmers in Andhra Pradesh Benefiting?
- Surge in Auction Prices: Prices have risen to near-record levels, marking a 30% increase from initial expectations.
- Impact of Global Crop Yields: Trade analysts attributed the price increase to crop damage in Brazil and Zimbabwe.
- Drought conditions in Indonesia, another tobacco-producing country, also resulted in crop failures.
- China, another significant producer, has imposed limitations on tobacco exports to protect its domestic cigarette industry in response to reports of global stock shortages, further fueling price increases in tobacco-producing nations.
- Potential Impact on Indian Growers: Tobacco exporters and the Indian Tobacco Board are expecting that the disparity between demand and production is expected to sustain price escalations for another year, which is likely to benefit Indian growers.
Note:
- Indian Tobacco Board: It was constituted as a statutory body on 1st January 1976 under Section (4) of the Tobacco Board Act, 1975.
- The Board is headed by a Chairman with its headquarters at Guntur, Andhra Pradesh. It is responsible for the development of the tobacco industry.
What are the Key Facts About Tobacco Production in India?
- Agro-Climatic Facts:
- Tobacco is of tropical origin but thrives under tropical, subtropical, and temperate climates.
- Ideal conditions include a frost-free period of 100 to 120 days with an average temperature of 80°F and well-distributed rainfall of 88 to 125 mm per month.
- Relative humidity ranges from 70-80% in the morning to 50-60% during midday.
- Various tobacco types have specific soil and climatic preferences for optimal growth.
- FCV thrives on various soils, including sandy loams, red loams, and black cotton soils.
- Tobacco is of tropical origin but thrives under tropical, subtropical, and temperate climates.
- Economic Significance:
- Tobacco ranks among the most economically significant crops globally.
- India's tobacco cultivation covers approximately 0.27% of the net cultivated area, producing around 750 million kg of tobacco leaf annually.
- Annually, tobacco contributes excise revenue of (Rs 14,000 crores), accounting for 4% of the country’s total agri-exports.
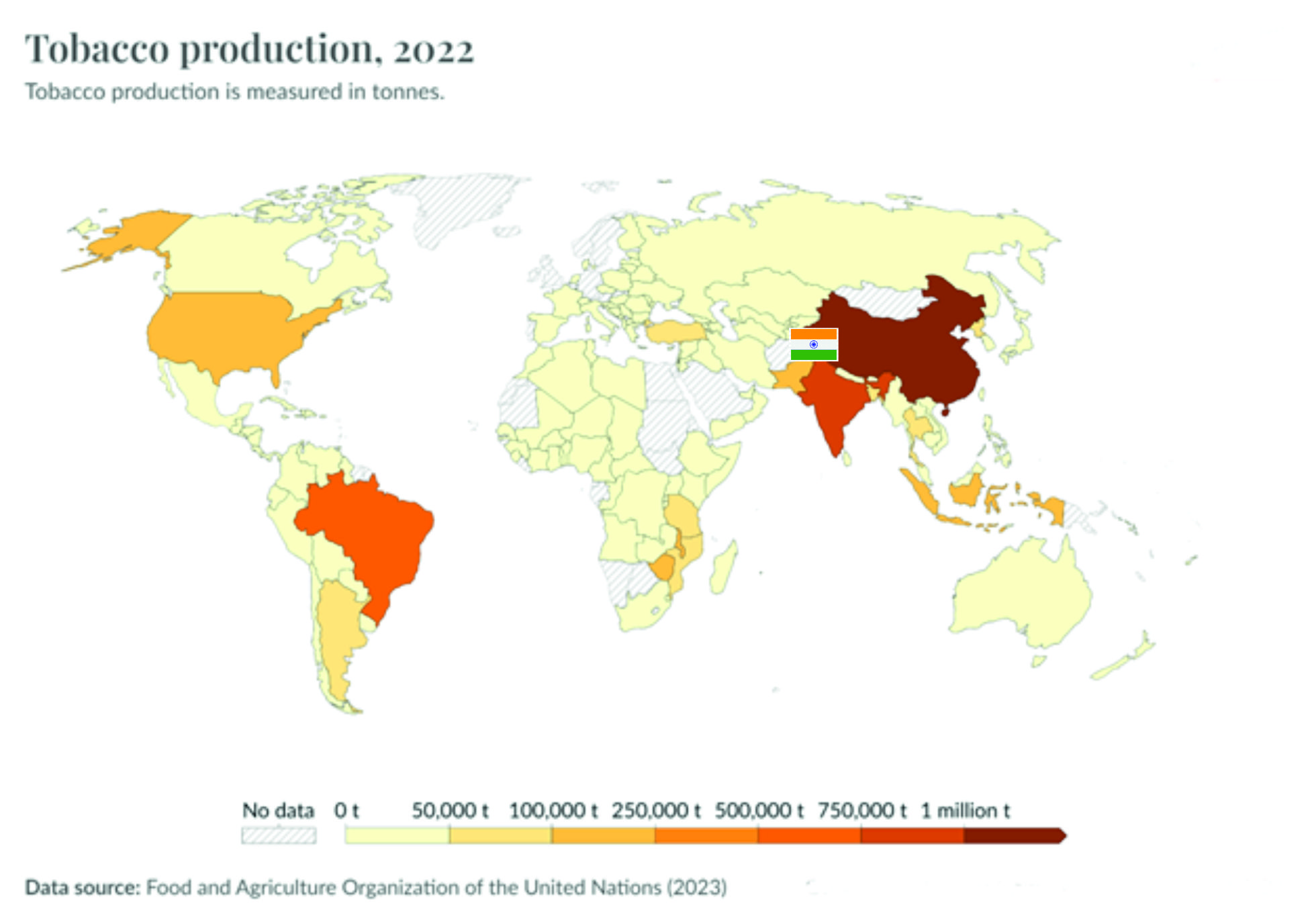
- China, India, and Brazil were rated among the leading producers worldwide.
- As regulations tighten in middle- and high-income countries, tobacco companies are increasingly targeting African countries to scale up tobacco leaf production.
- India is the third largest tobacco-producing nation and second largest consumer of tobacco worldwide.
- Tobacco ranks among the most economically significant crops globally.
- Diversity in Production:
- India produces various types of tobacco, including Flue-cured Virginia (FCV), Bidi, Hookah, Cigar-wrapper, Cheroot, Burley, Oriental, and others.
- Different types of tobacco are cultivated under diverse agro ecological conditions across 15 states in India.
- Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka occupy the top 3 positions in both the area and production of tobacco in the country.
- India produces various types of tobacco, including Flue-cured Virginia (FCV), Bidi, Hookah, Cigar-wrapper, Cheroot, Burley, Oriental, and others.
- Employment and Livelihood:
- Tobacco cultivation provides livelihood security to around 36 million people in India, including farmers, farm labourers, and workers in processing, manufacturing, and exports.
- Bidi rolling alone employs around 4.4 million people, and 2.2 million tribals are engaged in tendu leaf collection.
- Export Market and Competition:
- India exported tobacco and tobacco products worth Rs 9,740 crore during 2022-23 with a major contribution coming from cigarette-type tobacco like FCV and Burley.
- Major importers of Indian FCV tobacco include the UK, Germany, Belgium, South Korea, and South Africa.
- Brazil, Zimbabwe, Turkey, China, and Indonesia are key competitors in the export market.
- Despite a 13% share of the world’s tobacco production, India accounts for only 5% value of global tobacco leaf exports.
- It exports only 30% of the tobacco produced in the country whereas other leading tobacco-growing countries viz. Brazil, USA, and Zimbabwe export between 60-90% of their production.
- India exported tobacco and tobacco products worth Rs 9,740 crore during 2022-23 with a major contribution coming from cigarette-type tobacco like FCV and Burley.
- Competitive Advantage of Indian Tobacco:
- Indian tobacco exhibits lower levels of heavy metals, Tobacco Specific Nitrosamines (TSNAs), and pesticide residues compared to other tobacco-producing countries.
- India's varied agro-climatic conditions allow for the production of different styles of tobacco, meeting diverse customer preferences globally.
- India enjoys a competitive edge in terms of low production costs and export prices, making Indian tobacco considered 'value for money.'
Health Burden of Tobacco
- Global:
- Tobacco kills more than 8 million people each year, including an estimated 1.3 million non-smokers who are exposed to second-hand smoke.
- Around 80% of the world's 1.3 billion tobacco users live in low- and middle-income countries.
- India:
- By 2040, India is projected to witness 2.1 million cancer cases, with oral cavity cancer being the most prevalent form.
- 80-90% of individuals diagnosed with oral cancer are tobacco consumers.
- Both smoking as well as smokeless forms of tobacco have adverse health impacts and contribute to premature deaths.
- Smokeless tobacco products examples include gutkha, khaini, and zarda, which are used as chewing tobacco.
- The risk of diseases attributable to tobacco use in India includes stroke (78%), tuberculosis (65.6%), ischemic heart disease (85.2%), oral cancer (38%), and lung cancer (16%).
- Mortality due to tobacco in India is estimated at upwards of 13.5 lakhs, and it is estimated that by the year 2020, tobacco use will account for 13% of all deaths in India every year if effective steps are not taken to control tobacco consumption.
- Tobacco consumption is deeply ingrained in the lifestyle of certain regions, particularly in northern India.
- By 2040, India is projected to witness 2.1 million cancer cases, with oral cavity cancer being the most prevalent form.
What are the Initiatives Related to Tobacco?
- Global:
- To address the tobacco epidemic, the World Health Organization (WHO) adopted the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) in 2003.
- Currently, 182 countries are parties to this treaty, including India.
- The WHO MPOWER measures are in line with the WHO FCTC and have been shown to save lives and reduce costs from averted healthcare expenditure.
- The Global Tobacco Surveillance System (GTSS) aims to strengthen countries' ability to implement tobacco control measures and monitor WHO's FCTC and MPOWER technical package.
- It involves collecting data through four surveys.
- To address the tobacco epidemic, the World Health Organization (WHO) adopted the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) in 2003.
- India:
- National Tobacco Control Programme (NTCP)
- Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products (Prohibition of Advertisement and Regulation of Trade and Commerce, Production, Supply and Distribution) Act, 2003:
- The law regulates tobacco products by restricting advertisement, promotion, and sponsorship; prohibiting smoking in public places; sale to and by minors; and sale within 100 yards of educational institutions.
- It also requires specified health warnings on all tobacco product packs.
- The production, sale, storage, and distribution of food products containing tobacco or nicotine are prohibited under the Food Safety and Standards Act.
- Promulgation of the Prohibition of Electronic Cigarettes Ordinance, 2019
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the economic significance of tobacco production in India and its role in the livelihood of millions. How does it balance with the health implications? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following: (2012)
- Assessment of land revenue based on nature of the soil and the quality of crops
- Use of mobile cannons in warfare
- Cultivation of tobacco and red chillies
Which of the above was/were introduced into India by the English?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2
(c) 2 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (d)
Q. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists: (2008)
| List-I(Board) | List-II (Headquarters) | ||
| A. | Coffee Board | 1. | Bengaluru |
| B. | Rubber Board | 2. | Guntur |
| C. | Tea Board | 3. | Kottayam |
| D. | Tobacco Board | 4. | Kolkata |
Code: A B C D
(a) 2 4 3 1
(b) 1 3 4 2
(c) 2 3 4 1
(d) 1 4 3 2
Ans: (b)