Strengthening India's Spice Industry | 10 Mar 2025
Why in News?
The World Spice Organisation (WSO) highlights that despite being the largest spice producer, India holds just 0.7% of the global seasoning market, and calls for higher production, value addition, to achieve the USD 10 billion export target by 2030.
Note: The WSO, headquartered in Kochi, Kerala, is a not-for-profit organisation focused on food safety, sustainability, and biodiversity in the spice industry.
What is the Status of Spice in India?
- Production: In 2022-23, India produced 11.14 million tonnes of spices, a slight increase from 11.12 million tonnes in 2021-22.
- India produces 75 of 109 International Organization for Standardization (ISO)-listed spice varieties, with chilli, cumin, turmeric, ginger, and coriander accounting for 76% of total production.
- In terms of production, garlic, ginger and chilli were the top three spices produced in FY23.
- Largest Spices-Producing States: Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Assam, etc.
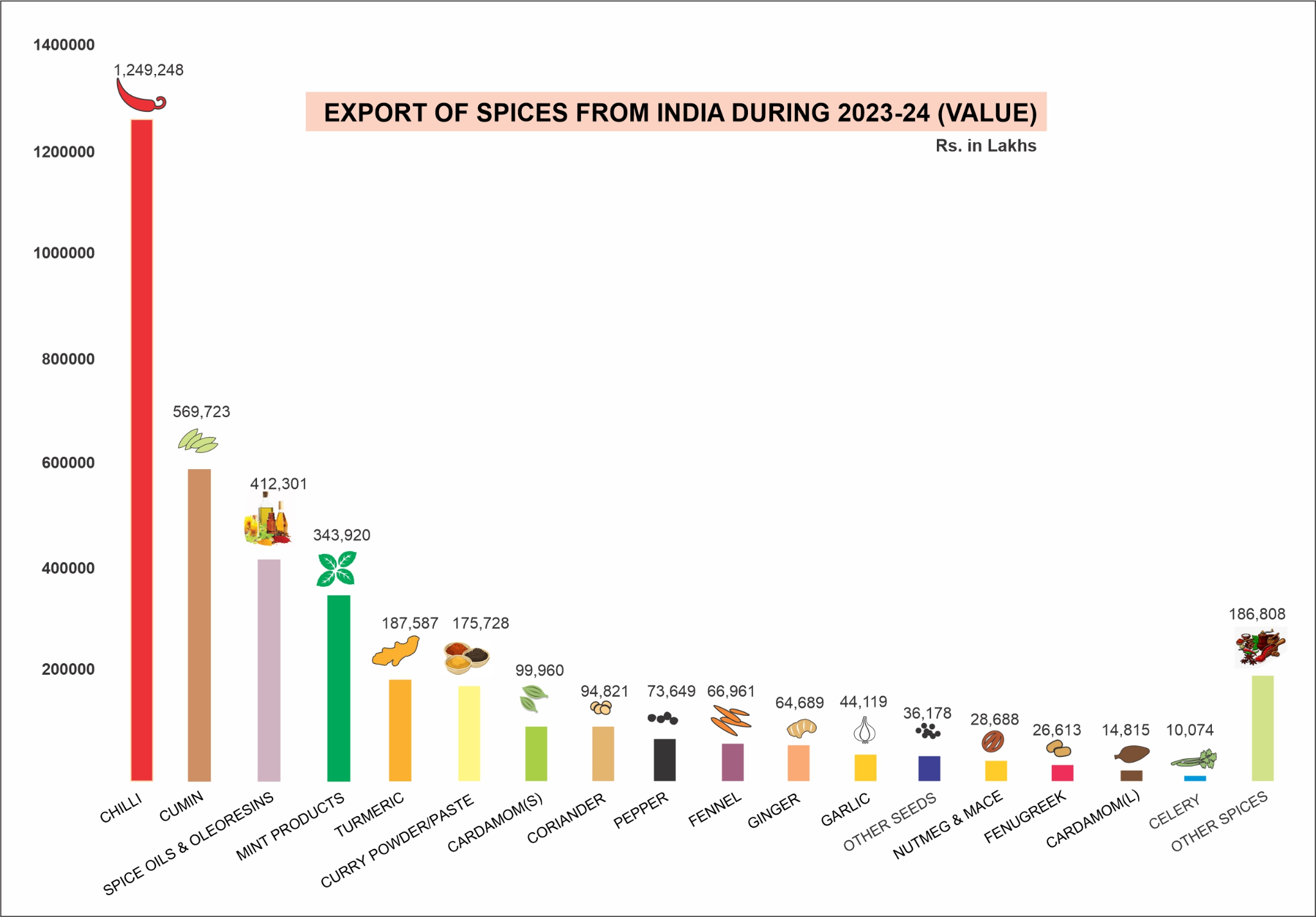
- Exports: Major exports include pepper, cardamom, celery, fennel, fenugreek, garlic, nutmeg, curry powder, and spice oils.
- In 2023-2024, India exported spices worth USD 4.4 billion (nearly 14 lakh tonnes). Chilli is India's top exported spice, accounting for 31% of total spice exports.
- India exports spices to 200 destinations worldwide, with China, Bangladesh, West Asian countries, and the US being key markets.
- Concerns: Despite being a leader in raw spice exports, India holds only 0.7% of the global seasoning market, far behind China (12%) and the US (11%).
- This is due to low value addition, with only 48% of exports being processed products.
- Instances of Adulteration and pesticide residues have led to export rejections, tarnishing India's reputation in international markets.
- Growing competition from Vietnam, Indonesia, Brazil, China, and countries like Thailand, Sri Lanka, and Madagascar further challenges India’s dominance.
- Heavy reliance on traditional crop varieties, poor processing, and inadequate post-harvest handling reduce quality and shelf life. Additionally, limited mechanization increases production costs and lowers efficiency.
- Measures to Expand Market: Country’s share in value-added spices should rise up to 70%.
- India's 15 agro-climatic zones support diverse spice cultivation. Developing high-yielding and climate-resistant varieties can boost production and enhance exports.
Government Initiatives to Boost Spice Production & Exports
- Spices Board of India (SBI): Established under the Spices Board Act 1986, functions under the Ministry of Commerce & Industry.
- SBI, headquartered in Kochi, Kerala, promotes cardamom and 52 spices, regulates quality, supports research, and links Indian exporters to global markets.
- National Sustainable Spice Program (NSSP) under SBI and WSO unites stakeholders to address sustainability in India's spice industry.
- Spices Parks: SBI established eight crop specific Spices Parks across the country, to assist farmers in post-harvest handling, value addition, and better pricing.
- Spice Complex in Sikkim: Aimed at improving spice processing and value addition in the Northeastern region.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the major challenges faced by India’s spice industry in terms of competition, quality control, and processing? Suggest measures to address these issue |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The staple commodities of export by the English East India Company from Bengal in the middle of the 18th century were: (2018)
(a) Raw cotton, oil-seeds and opium
(b) Sugar, salt, zinc and lead
(c) Copper, silver, gold, spices and tea
(d) Cotton, silk, saltpetre and opium
Ans: (d)
Q. In making the saffron spice, which one of the following parts of the plant is used? (2009)
(a) Leaf
(b) Petal
(c) Sepal
(d) Stigma
Ans: (d)
- Safron is one of the most expensive spices in the world. It is made from the stigma of the flower Saffron crocus.
- Female reproductive part of a flower, pistel, consists of ovary, style, and stigma. Stigma is the part that gets pollen from the pollinating agents.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer