Important Facts For Prelims
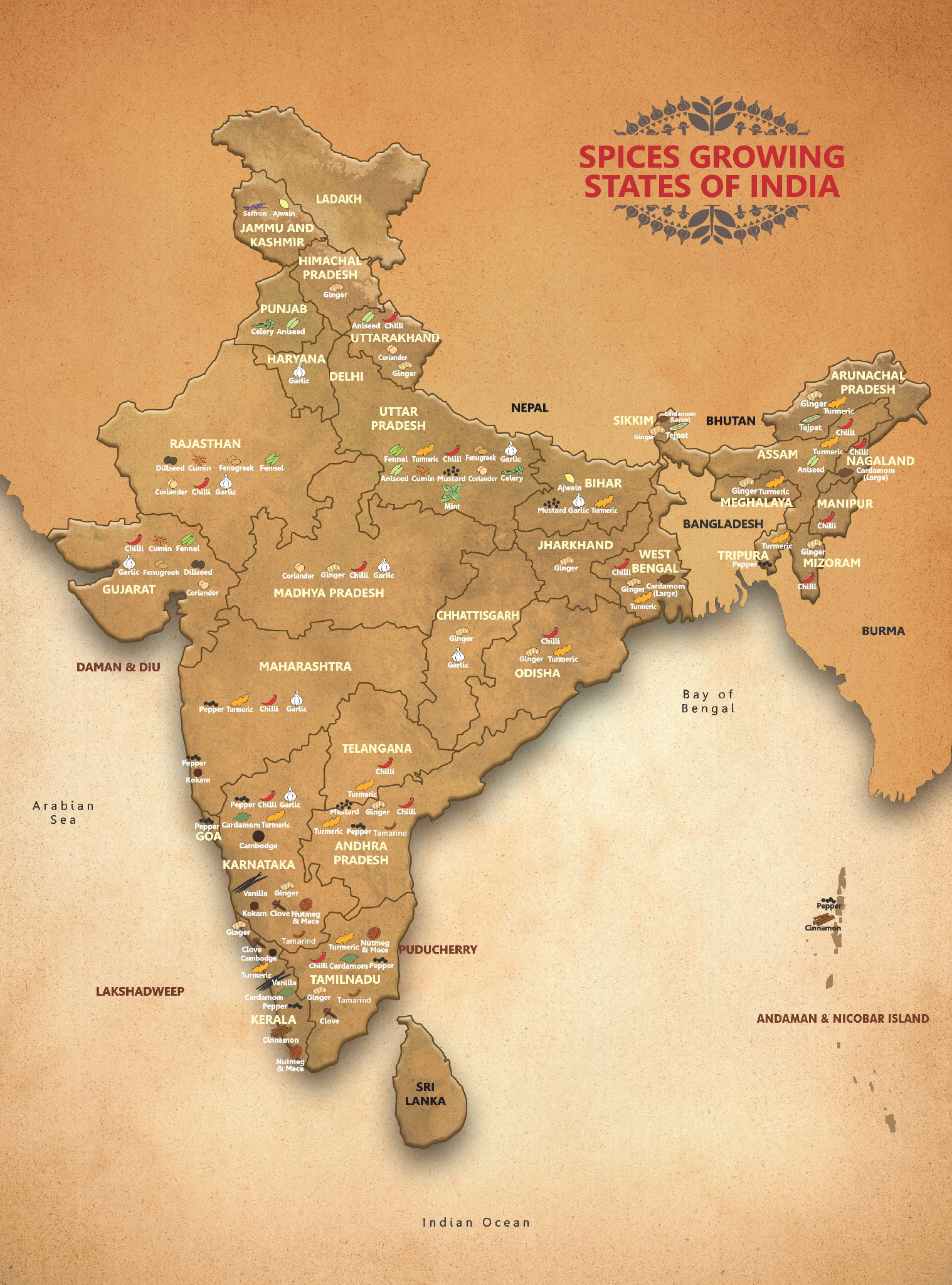
Spices Board of India
- 20 May 2024
- 4 min read
Why in News?
The Spices Board of India has taken up the issue of setting limits for using Ethylene Oxide (ETO) in spices with CODEX, the international food standards body.
- This comes after certain branded spices exported by Indian companies to Hong Kong and Singapore were recalled due to concerns related to ETO contamination, followed by a ban by Nepal on the sale and import of certain spice-mix products due to similar concerns.
What is the Spices Board of India?
- About:
- Spices Board was constituted on 26th February 1987 under the Spices Board Act, 1986 with the merger of the erstwhile Cardamom Board (1968) and Spices Export Promotion Council (1960).
- There are five statutory Commodity Boards under the Department of Commerce.
- These Boards are responsible for production, development and export of tea, coffee, rubber, spices and tobacco.
- It is responsible for the export promotion of the 52 scheduled spices and the development of Cardamom.
- Spices Board is the flagship organisation for the development and worldwide promotion of Indian spices.
- The Board is an international link between the Indian exporters and the importers abroad.
- Issue of Ethylene Oxide (ETO):
- ETO is a chemical used as a sterilizing agent in spices, but it is considered carcinogenic when used beyond certain limits.
- While efforts are being made to prevent ETO contamination, the sample failure rate for Indian spice exports is less than 1% in major markets.
- As of now, CODEX has not established a limit, and there is also no standardized ETO testing protocol available.
- India has taken up with the CODEX committee the need for setting up limits for ETO usage as different countries have different limits.
- The Spices Board released guidelines for exporters to prevent ETO contamination and ensure the safety of all markets.
- It advises against using ETO as a sterilising agent for spices and suggests alternatives like steam sterilisation and irradiation.
- Other countries like the US, New Zealand, and Australia have also raised concerns about the quality of some Indian spices and are determining if further action is needed.
- ETO is a chemical used as a sterilizing agent in spices, but it is considered carcinogenic when used beyond certain limits.
Note:
- India is the world’s largest spice producer. It is also the largest consumer and exporter of spices.
- In 2023-24, India's spice exports reached USD 4.25 billion, capturing a 12% share share of global spice exports.
International Food Standards
- Since 1963, the Codex system has developed openly and inclusively to address new challenges.
- Codex standards are based on sound science provided by independent international risk assessment bodies or ad-hoc consultations organized by the Food and Agriculture Organization’s (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The staple commodities of export by the English East India Company from Bengal in the middle of the 18th century were: (2018)
(a) Raw cotton, oil-seeds and opium
(b) Sugar, salt, zinc and lead
(c) Copper, silver, gold, spices and tea
(d) Cotton, silk, saltpetre and opium
Ans: (d)
Q. In making the saffron spice, which one of the following parts of the plant is used? (2009)
(a) Leaf
(b) Petal
(c) Sepal
(d) Stigma
Ans: (d)