Sri Lankan President’s India Visit | 25 Dec 2024
For Prelims: India’s Neighbourhood First policy, SAGAR Vision, SAARC, Indian Development and Economic Assistance Scheme (IDEAS), Mitra Shakti, SLINEX, Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre, Illegal Fishing, Indian Ocean, Katchatheevu Island , Afanasy Nikitin Seamount, BIMSTEC.
For Mains: Significance of India-Sri Lanka Relations for India’s Strategic Interests and India’s Neighbourhood First Policy.
Why in News?
Recently, the new Sri Lankan President was on his first visit to India focusing on enhancing trade, energy, and maritime cooperation.
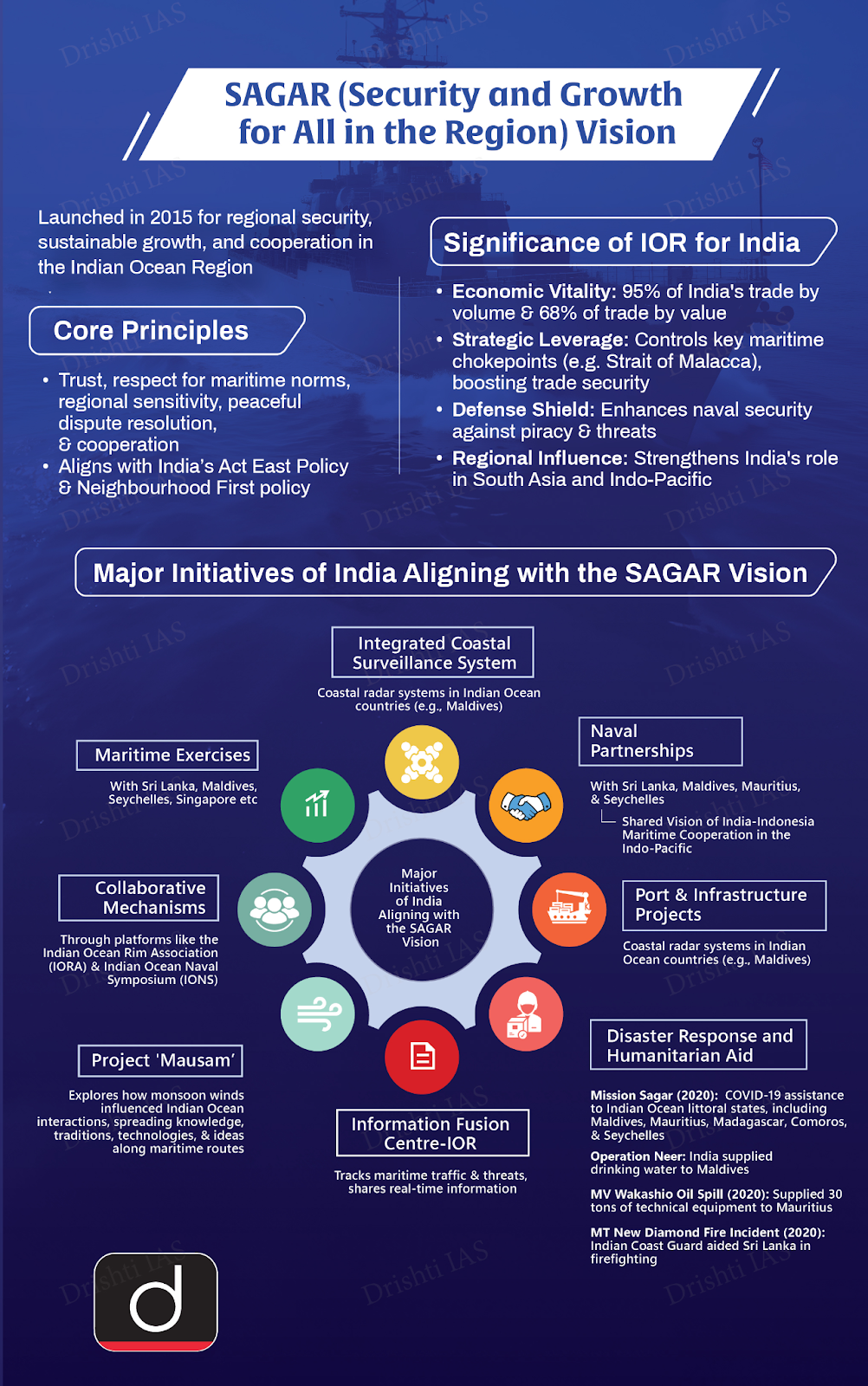
- Discussions with Indian leaders emphasized Tamil aspirations, economic recovery, and countering Chinese influence, reinforcing India’s Neighbourhood First policy and SAGAR Vision.
What are the Outcomes of the Recent Visit?
- Economic and Trade Agreements: Proposed Economic and Technology Cooperation Agreements (ETCAs) aim to integrate services and technology into trade relations was also discussed during the President’s visit to India.
- India has agreed to promote Indian Rupee (INR)-Sri Lankan Rupee (LKR) trade settlements and undertake capacity-building programs, including the training of 1,500 Sri Lankan civil servants.
- Energy Partnership: India agreed to supply LNG to Sri Lanka to address immediate energy needs, while both nations announced an energy pipeline with the UAE to enhance regional energy security.
- Renewable energy projects like offshore wind power and grid interconnection were prioritized, alongside developing Trincomalee as an energy hub.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity: Resumption of ferry services and continued development of Kankesanthurai port, housing, and digital infrastructure under India’s "Neighborhood First" policy.
- Regional Security Cooperation: Both countries committed to deepening security cooperation, particularly in maritime security.
- Financial Support: India’s financial support, including USD 4 billion for food, fuel, and medicines, was crucial in stabilizing Sri Lanka’s economy during its crisis.
- Bilateral Cooperation in Global Forums: Sri Lanka sought India's support in its bid to join the BRICS group and in matters related to the United Nations Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf.
What are Areas of Cooperation Between India and Sri Lanka?
- Economic Cooperation: India is Sri Lanka’s largest trade partner in SAARC, with bilateral trade reaching USD 5.5 billion in FY 2023-24.
- India exports essential goods while Sri Lanka benefits from the India-Sri Lanka Free Trade Agreement.
- Development Assistance: India has extended Development Assistance to Sri Lanka through Lines of Credit (LOCs) under the Indian Development and Economic Assistance Scheme (IDEAS).
- As of 2023, over USD 2 billion in Lines of Credits (LOCs) have been provided to Sri Lanka, supporting key sectors such as railways, hospitals, infrastructure, and power transmission.
- India's LOCs, including projects like the Jaffna Cultural Center and Suwa Seriya ambulance services, strengthen Sri Lanka’s socio-economic framework and improve infrastructure and livelihoods.
- Energy Collaboration: Renewable energy projects, including hybrid systems in Jaffna, reflect India’s push for energy security in the region.
- Defence and Security: Defence ties include joint military exercises (Mitra Shakti) and naval drills (SLINEX).
- The installation of a Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre demonstrates India’s commitment to bolstering Sri Lanka’s maritime capabilities.
- Additionally, India has supported Sri Lanka’s counterterrorism and environmental disaster management efforts .
- Cultural and Educational Exchange: The historical and cultural ties between the nations are reinforced through scholarship programs, restoration of Buddhist temples, and the sharing of Indian technologies in governance and education .
- Maritime Cooperation: Shared concerns over illegal fishing and sustainable resource management in the Indian Ocean have driven collaborations.
- Joint patrols and sustainable fishing initiatives are critical to protecting marine biodiversity and livelihoods .
What are Challenges of Cooperation Between India and Sri Lanka?
- Fishing Disputes: Indian fishermen's use of bottom trawling sometimes in Sri Lankan waters and in surrounding areas has escalated tensions, causing arrests, fines, and friction in both coastal communities and bilateral diplomacy.
- Katchatheevu Island Dispute: The ownership and use of Katchatheevu Island remain contentious, with disputes over enforcement of agreements allowing Indian fishing and pilgrimage rights, straining bilateral relations.
- Ethnic and Political Issues: India’s support for the Tamil population in Sri Lanka has been met with resistance from certain political factions.
- The delay in implementing the 13th Amendment to devolve power to Tamil-majority areas has been a longstanding grievance .
- Geopolitical Rivalries: China’s increasing influence in Sri Lanka, especially in infrastructure projects like the Hambantota Port, challenges India’s strategic interests. India views Chinese-backed projects as threats to its regional security .
- Maritime Boundary Issues:The dispute over the Afanasy Nikitin Seamount highlights overlapping claims in international waters, with both nations using international legal mechanisms, potentially leading to diplomatic friction.
Way Forward
- Enhancing Dialogue: Strengthening diplomatic engagements to address core issues like fishing rights, Tamil reconciliation, and maritime disputes is crucial.
- Regular dialogue through bilateral and regional forums like BIMSTEC can provide a platform for solutions.
- Economic Integration: Expanding trade agreements and infrastructure linkages, such as ferry services and pipeline projects, will boost economic interdependence.
- Collaborative initiatives like the proposed undersea energy cable can enhance shared benefits.
- Fisheries Management: Promoting sustainable fishing practices through joint initiatives, capacity-building programs, and alternative livelihoods for fishermen can resolve conflict and will also protect marine ecosystems.
- Leveraging Development Assistance: India should continue its role as a key development partner, focusing on renewable energy, education, and digital governance.
- Green debt swaps can align economic recovery with sustainability goals.
- Balancing Geopolitics: India must counterbalance Chinese influence through strategic investments and diplomatic outreach.
- This will ensure that its assistance aligns with Sri Lanka’s long-term interests.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- “Textile and textile articles” constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh.
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. In respect of India — Sri Lanka relations, discuss how domestic factors influence foreign policy. (2013)