Indian Economy
Social Security for Gig Workers
- 08 Jul 2024
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Rajasthan, Gig Workers, Social Security Schemes, National Human Rights Commission (NHRC), Code on Wages 2019, Code on Social Security 2020, NITI Aayog,
For Mains: Significance of Social Security, and Welfare Schemes for Inclusive Development.
Why in News?
Recently, Karnataka became the second state after Rajasthan to come up with legislation for Gig Workers.
- Through a draft version of the law (Karnataka Platform-based Gig Workers (Social Security and Welfare) Bill), the Karnataka government aims to regulate the social security and welfare of platform-based gig workers in the state by creating a board, welfare fund, and grievance cell among the mechanisms.
Gig Workers Union Demands National Disaster Status for Heatwave
- The Union of gig workers in Telangana have sought National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) to consider the effect of the heatwave on gig workers.
- The Union is demanding that the heatwave be treated as a national disaster and support systems be created for workers.
- The set of 10 demands including intervention of the State government in terms of providing clean drinking water, oral rehydration, accessible toilets, seating areas with shade, a mandatory break with flexible working hours during extreme heat conditions has been put forward.
What are the Key Highlights of the Karnataka Bill?
- Creation of Welfare Board: Board comprising Karnataka labour minister, two aggregator officials, two gig workers, and one civil society member to be formed.
- A two-level grievance redressal mechanism for workers, and more transparency with regards to the automated monitoring and decision-making systems deployed by platforms has been envisaged by the draft bill.
- Timely Payment: The draft mandates aggregators to make payments at least every week and to inform the worker about the reasons for any payment deductions.
- Unique ID: Gig workers can apply to receive a Unique ID applicable across all platforms upon registration with the board.
- Social Security and Grievance Redressal: Access to general and specific social security schemes based on contributions along with a grievance redressal mechanism for gig workers.
- Autonomy and Contractual Rights: The Bill aims to provide greater autonomy to the gig workers to terminate contracts and resist being over worked by employers.
- The aggregator shall not terminate a worker without giving valid reasons in writing and prior notice of 14 days.
- Work Environment and Safety: There is a mandate for aggregators to maintain a safe working environment for gig workers.
- Welfare Fund: Proposed fund financed by a welfare fee from aggregators along with state and worker contributions.
- Penalties: Basic penalty of Rs 5,000 extendable up to Rs 1 lakh for aggregators violating conditions under the Bill.
Who are Gig Workers?
- Gig Workers: As per the Code on Social Security 2020, a gig worker is a person who performs work or participates in a gig work arrangement and earns from such activities outside of traditional employer-employee relationship.
- Gig Economy: A free market system in which temporary positions are common and organisations contract with independent workers for short-term engagements.
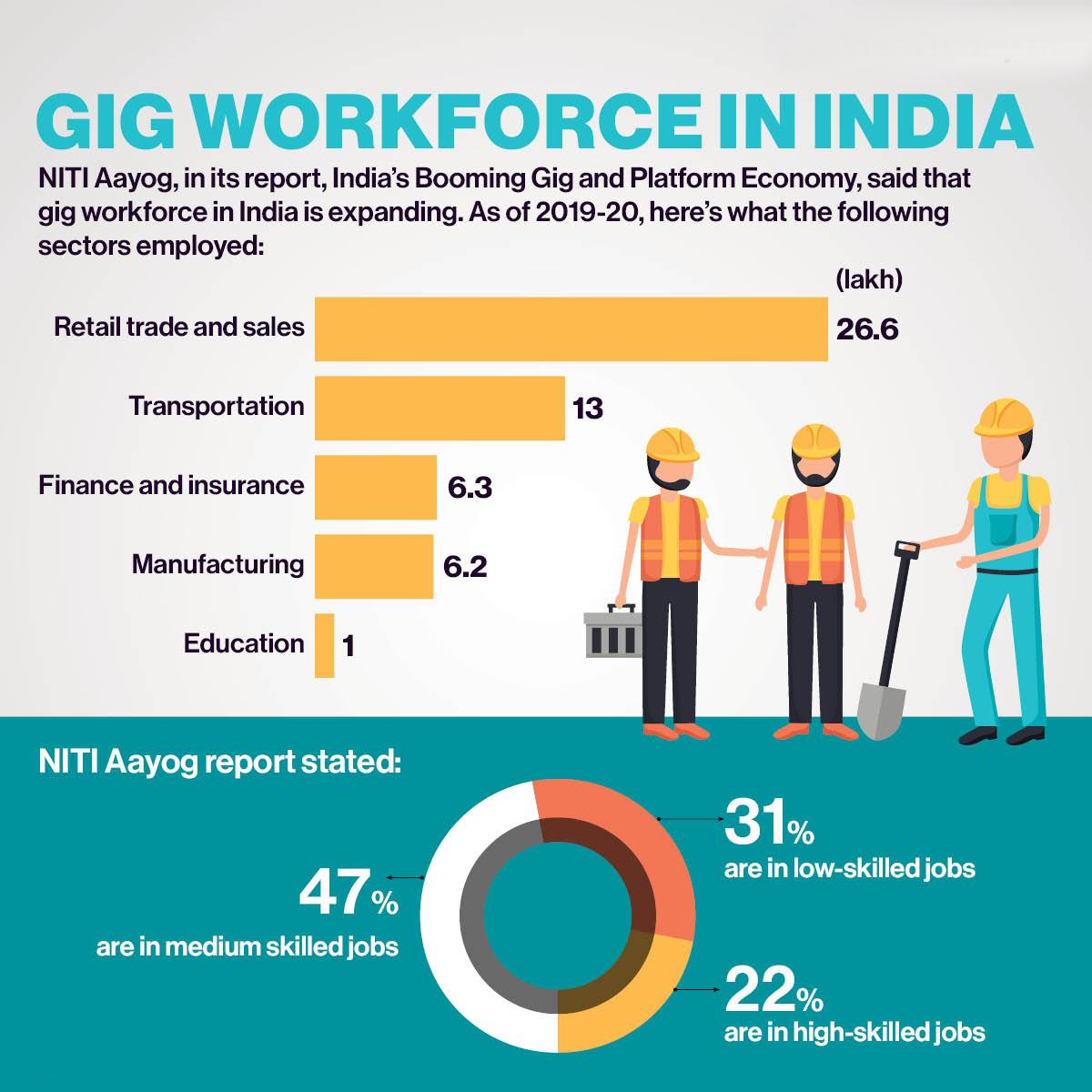
- A 2022 NITI Aayog report estimates that India will have 23.5 million gig workers by 2029-30.
What is the Need to Provide Social Security Benefits to Gig Workers?
- Frequent Termination: The instances of blacklisting workers or terminating them from work without hearing out their side have increased.
-
Economic Security: The sector depends on demand which leads to job insecurity and income uncertainty, highlighting the necessity of providing social security benefits such as unemployment insurance, disability coverage, and retirement savings programs.
-
Health Insurance: Lack of access to employer-sponsored health insurance and other healthcare benefits leaves gig workers vulnerable to unexpected medical expenses. Prioritising their health and well-being will create a healthier and more productive workforce.
-
Level Playing Field: Exemption from traditional employment protections creates disparities where gig workers face exploitative working conditions and inadequate compensation. Providing social security benefits will level the playing field.
-
Long-term Financial Security: Without employer-sponsored retirement plans, gig workers may struggle to save enough for their future like for post retirement needs.
What are the Main Challenges in Providing Social Security Benefits to Gig Workers?
- Classification and Excess Flexibility: The gig economy is characterised by its flexibility, allowing workers to choose when, where, and how much they work.
- Designing social security benefits that accommodate this flexibility and meet the diverse needs of gig workers is a complex task.
- Funding and Cost Distribution: Traditional social security systems depend on employer and employee contributions, with employers typically bearing a significant portion of the costs.
- In the gig economy, where workers are often self-employed, identifying appropriate funding mechanisms becomes complex.
- Coordination and Data Sharing: Efficient data sharing and coordination among gig platforms, government agencies, and financial institutions are necessary to accurately assess gig workers' earnings, contributions, and eligibility for various social security programs.
- However, as gig workers often work for multiple platforms or clients, it becomes challenging to coordinate and ensure proper coverage.
- Education and Awareness: Many gig workers may not fully understand their rights and entitlements regarding social security benefits.
- Raising awareness and providing education about the importance of social security, eligibility criteria, and the application process is a challenging task.
Government’s Initiatives Related to Gig Workers
- The Code on Social Security 2020, contains a separate section on ‘gig economy’ and imposes an obligation on gig employers to contribute to a Social Security Fund to be handled by a government-led board.
- The Code on Wages 2019, provides for universal minimum wage and floor wage across organised and unorganised sectors, including gig workers.
- The Rajasthan Assembly recently passed a bill aimed at extending social security benefits to gig workers.
What can be done to Ensure Social Security of Gig Workers?
- Implementing Code on Social Security, 2020: Although the Code on Social Security, 2020, contains provisions for gig workers, the rules are yet to be framed by the States and not much has moved in terms of instituting the Board. These should thus be taken up expeditiously by the government.
-
Expanding Employer Responsibilities: Strong support for gig workers should come from the gig companies that themselves benefit from this agile and low-cost work arrangement.
- The practice of classifying gig workers as self-employed or independent contractors needs to be eliminated.
- Companies must be provided equal benefits as that of a regular employee.
- Education and Training: The government should invest in education and training programs for gig workers to improve their skills and increase their earning potential.
- Government Support: Collaboration between governments, gig platforms, and labour organisations to establish fair and transparent mechanisms for sharing the responsibility of providing social security benefits.
-
Eg. Schemes similar to Ayushman Bharat should be extended to cover gig workers with cost sharing with the employer.
-
-
Adopting International Examples: The UK has instituted a model by categorising gig workers as “workers,” which is a category between employees and the self-employed.
- This secures them a minimum wage, paid holidays, retirement benefit plans, and health insurance.
- Similarly, in Indonesia, they are entitled to accident, health, and death insurance.
- Linking Women Empowerment with Gig Economy: There is a need to build the right physical and social infrastructure that supports the engagement of women in the gig workforce.
|
Mains Question: Discuss the need and challenges associated with providing social security for gig workers in India. Also, highlight steps taken by centre and state governments in this context. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following: (2012)
- Hotels and restaurants
- Motor transport undertakings
- Newspaper establishments
- Private medical institutions
The employees of which of the above can have the ‘Social Security’ coverage under Employees State Insurance Scheme?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. How globalization has led to the reduction of employment in the formal sector of the Indian economy? Is increased informalization detrimental to the development of the country? (2016)