Biodiversity & Environment
SDG Progress & Challenges
- 29 Mar 2025
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Index 2024, Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, Addis Ababa Action Agenda, Paris Agreement, ESG Reporting.
For Mains: SDGs, challenges associated with it and way forward.
Why in News?
India has shown significant improvement in its Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) index 2024 ranking which has improved to 109th out of 166 countries.
- States have also demonstrated better performance, with an average increase of five units in the composite index over the past three years.
How Has India Performed on SDGs So Far?
- Overall Progress: India’s SDG index score improved from 57 (2018) to 71 (2023-24).
- States Performance: Kerala & Uttarakhand lead with 8 goals each scoring above 80 (above 80 score is an indicator of achievement).
- However, over 9 states recorded a decline in No Poverty (Goal 1), Gender Equality (Goal 5), Reduced Inequality (Goal 10), and Strong Institutions (Goal 16).
- Target Specific Progress:
- SDG-3: Maternal Mortality Ratio reduced from 130 (2014-16) to 97 (2018-20) per 1,00,000 live births.
- SDG-4: The Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in higher education rose from 23.7% to 28.4% between 2014-15 and 2021-22.
- SDG-6: Over 95% of people in rural areas and 97.2% in cities are having access to improved sources of drinking (potable) water during 2020-2021.
- SDG-7: India’s renewable energy capacity increased from 180.80 GW in December 2023 to 209.44 GW in December 2024.
- Budgetary Allocations: Some states (like Haryana, Odisha, Meghalaya) now publish SDG-specific budgets.
- Developing nations need USD 4 trillion annually to meet SDGs.
What are the Key Highlights of the SDG Report, 2024?Click Here to Read: Key Highlights of the SDG Report, 2024 |
What are Sustainable Development Goals?
- About: SDGs are 17 interconnected goals addressing global challenges like poverty, inequality, climate change, and environmental degradation.
- It was adopted in 2015 by 193 UN Member States as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- Aim: It aims to achieve peace, prosperity, and sustainability by 2030 through global partnership.
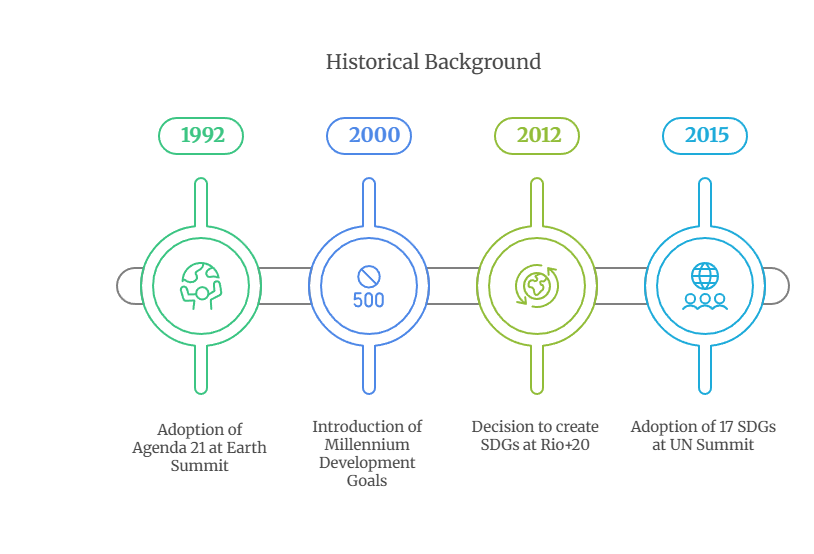
- Historical Background:
- Core Principles of SDGs:
- Universality: Apply to all countries (developed & developing).
- Integration: Progress in one goal affects others (e.g., poverty reduction improves education).
- Leave No One Behind: Focus on marginalized & vulnerable groups.
- Multi-Stakeholder Approach: Requires governments, businesses, civil society, and citizens.
- SDGs List:
- Monitoring: Global Sustainable Development Report (GSDR) assesses progress every 4 years.
- Supporting Agreements:
- Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction to strengthen disaster resilience.
- Addis Ababa Action Agenda for financing sustainable development.
- Paris Agreement on Climate Change for combating climate change.
What are the Challenges in Implementation of SDGs?
- War & Political Instability: Conflicts in key resource-producing nations (e.g., 30% of global wheat exports from Russia & Ukraine) trigger food shortages worldwide.
- In war-torn regions, basic needs like healthcare (SDG 3) and education (SDG 4) become unattainable.
- Economic Disparities: Developing nations rely on forestry, mining, and fossil fuels for economic growth, conflicting with climate goals (SDG 13).
- Wealthier countries push for sustainability, but poorer nations lack funds & technology to transition.
- Governmental Challenges: Some governments prioritize short-term economic gains over sustainability (e.g., fossil fuel lobbying).
- Shutting down polluting industries without alternatives increases unemployment (SDG 8) and poverty (SDG 1).
- Poverty & Inequality: 650 million people still face hunger, while 10% lack electricity—key barriers to SDG 1 (No Poverty) and SDG 7 (Clean Energy).
- Rural areas lag in education, healthcare, and jobs, worsening inequality (SDG 10).
- Global Economic Crises: Covid-19 pushed millions into poverty, reversing years of progress (e.g., 5 million in Southeast Asia alone).
- Economic downturns in one country (e.g., US recession) hurt trade partners (e.g., Mexico), disrupting SDG progress.
Way Forward
- Conflict Resolution: Increase UN-mediated negotiations to resolve ongoing wars (e.g., Ukraine, Sudan).
- Expand initiatives like Finance for Peace to fund post-conflict recovery.
- Finance for SDGs: Developed nations must fulfill their 0.7% GDP aid commitment to unlock USD 4 trillion annually.
- Private sector engagement through impact investing and SDG bonds can support developing nations.
- Country-Specific SDG Strategies: Each nation should focus on most urgent SDGs (e.g., India improving Gender Equality (SDG 5) and Reduced Inequality (SDG 10)).
- Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration: Mandating environmental, social and governance (ESG) reporting for large firms can strengthen corporate SDG commitments, while AI and blockchain can enhance SDG monitoring.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the challenges in achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE), a UN mechanism to assist countries transition towards greener and more inclusive economies, emerged at (2018)
(a) The Earth Summit on Sustainable Development 2002, Johannesburg.
(b) The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development 2012, Rio de Janeiro.
(c) The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change 2015, Paris.
(d) The World Sustainable Development Summit 2016, New Delhi.
Ans: (b)
Q. Sustainable development is described as the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. In this perspective, inherently the concept of sustainable development is intertwined with which of the following concepts? (2010)
(a) Social justice and empowerment
(b) Inclusive Growth
(c) Globalization
(d) Carrying capacity
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).” Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)