Sariska Tiger Reserve | 22 May 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court of India clarified that protected areas include not only national parks and wildlife sanctuaries but also critical tiger habitats, i.e., tiger reserves.
- This is in the context of its earlier 2023 order that mining within a national park, wildlife sanctuary, and within an area of 1 km from their boundary shall not be permissible.
- The case in question pertains to the buffer zone created to protect the Sariska Wildlife Sanctuary in Rajasthan.
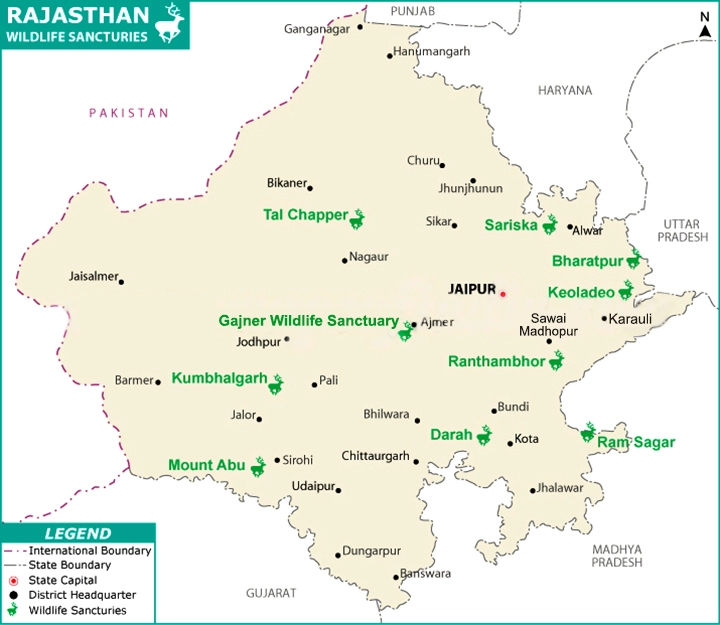
What are the Key Facts About the Sariska Tiger Reserve?
- About:
- Sariska Tiger Reserve is located in Aravali hills and forms a part of the Alwar District of Rajasthan.
- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1955 and was declared a tiger reserve later in 1978, making it a part of India's Project Tiger.
- It encompasses ruined temples, forts, pavilions and a palace.
- Kankarwadi Fort is located in the centre of the reserve. It is said that Mughal emperor Aurangzeb had imprisoned his brother Dara Shikoh at this fort in the struggle for succession to the throne.
- It also houses a famous temple of lord Hanuman at Pandupole related to Pandavas.
- Flora and Fauna:
- It is characterised by rocky landscapes, arid scrub-thorn forests, grasslands, cliffs, and semi-deciduous forests.
- It is dominated by dhok trees, salar, kadaya, gol, ber, banyan, gugal, bamboo, kair, etc.
- It also supports a diverse array of other animals such as Royal Bengal Tiger, leopards, sambhar, chital, nilgai, four-horned antelope, wild boar, hyenas, and jungle cats.
What are the other Protected Areas of Rajasthan?
- Desert National Park, Jaisalmer
- Keoladeo National Park, Bharatpur
- Ranthambore National Park
- Sajjangarh Wildlife Sanctuary, Udaipur
- National Chambal Sanctuary (on the tri-junction of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh).
- Ramgarh Vishdhari Wildlife Sanctuary (4th Tiger reserve of Rajasthan).
What are Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs)?
- About:
- The National Wildlife Action Plan (2002-2016) stipulated that state governments should declare land falling within 10 km of the boundaries of national parks and wildlife sanctuaries as eco-fragile zones or Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs) under the Environmental (Protection) Act, 1986.
- Activities Around ESZs:
- Prohibited Activities: Commercial mining, sawmills, industries causing pollution, major hydroelectric projects (HEP), commercial use of wood.
- Regulated Activities: Cutting of trees, the establishment of resorts, commercial use of natural water, erection of electrical cables, drastic change of agriculture system, widening of roads.
- Permitted Activities: Ongoing agricultural or horticultural practices, rainwater harvesting, organic farming, use of renewable energy sources.
- Significance of ESZs:
- ESZs act as buffer zones around protected areas. They regulate activities around these core areas, minimising the negative impacts of development and human intervention.
- ESZs help in in-situ conservation. Example, the conservation of the One-horned Rhino of Kaziranga National Park, Assam.
- ESZs help to maintain wildlife corridors and reduce instances of man-animal conflict, where wild animals enter human settlements in search of food and water.
- Many ESZs encompass fragile ecosystems like wetlands, mangroves, and reefs which are vital for maintaining biodiversity. By regulating activities around these areas, ESZs help to preserve their health and ecological functions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2014)
- Dampa Tiger Reserve : Mizoram
- Gumti Wildlife Sanctuary: Sikkim
- Saramati Peak : Nagaland
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q. In which one of the following States is Pakhui Wildlife Sanctuary located? (2018)
(a) Arunachal Pradesh
(b) Manipur
(c) Meghalaya
(d) Nagaland
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. “The most significant achievement of modern law in India is the constitutionalization of environmental problems by the Supreme Court.” Discuss this statement with the help of relevant case laws. (2022)