Social Issues
Rising Drug Abuse Among Youth
- 21 Dec 2024
- 17 min read
For Prelims: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), World Drug Report 2024, Cannabis, NDPS Act, NCB, National Fund for Control of Drug Abuse, National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction
For Mains: Drug: Challenges, Initiatives, Problem of drug abuse and related Initiatives.
Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India has expressed concern over the rising drug abuse among youth, calling it a generational threat.
- This concern emerged during a verdict supporting the National Investigation Agency's (NIA) probe into a heroin smuggling case linked to Pakistan.
- The court emphasized the need for urgent collective action from families, society, and state authorities to address the growing menace of drug abuse.
What is the State of Drug Abuse in the World?
- Global Scenario:
- As per the World Drug Report 2024 released by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), global drug use reached 292 million people, marking a 20% increase over the past decade.
- Drug Preferences: Cannabis remains the most widely used drug (228 million users), followed by opioids (60 million), amphetamines (30 million), cocaine (23 million), and ecstasy (20 million).
- Emerging Threats: The report flags netizens, a new class of synthetic opioids, as a significant threat, more potent than fentanyl, contributing to rising overdose deaths, especially in high-income countries.
- Fentanyl is an opioid drug used as an analgesic (pain relief) and anesthetic
- Treatment Gap: Only 1 in 11 people with 64 million drug use disorders receive treatment.
- Women face greater barriers, with only 1 in 18 women with drug use disorders receiving treatment, compared to 1 in 7 men.
- Drug Prevalence in India:
- Drug Addiction:
- Drug addiction is on the rise, with approximately 100 million people in India affected by various narcotics according to the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB).
- States like Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Punjab recorded the highest number of FIRs under the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS) between 2019 and 2021.
- Drug addiction is on the rise, with approximately 100 million people in India affected by various narcotics according to the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB).
- Alcohol: According to the National Survey on Extent and Pattern of Substance Use in India (2019), conducted by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, 16 crore people (14.6%) between ages 10 and 75 are current alcohol users. Of these, 5.2% are alcohol dependents (alcoholism).
- Alcoholism is a chronic disease that causes people to crave alcohol and be unable to control their drinking.
- Cannabis: 3.1 crore people (2.8%) are cannabis users, with 72 lakh (0.66%) facing cannabis-related issues.
- Opioid Use: 2.06% of the population uses opioids, and nearly 0.55% (60 lakh) require treatment services for opioid dependence.
- Sedative: 1.18 crore (1.08%) individuals use sedatives for non-medical purposes.
- Inhalant: Inhalant abuse affects 1.7% of children and adolescents, significantly higher than the 0.58% prevalence in adults. Approximately 18 lakh children require assistance to address inhalant abuse.
- Injecting Drug Use: Approximately 8.5 lakh people inject drugs, known as People Who Inject Drugs (PWID).
- Drug Addiction:
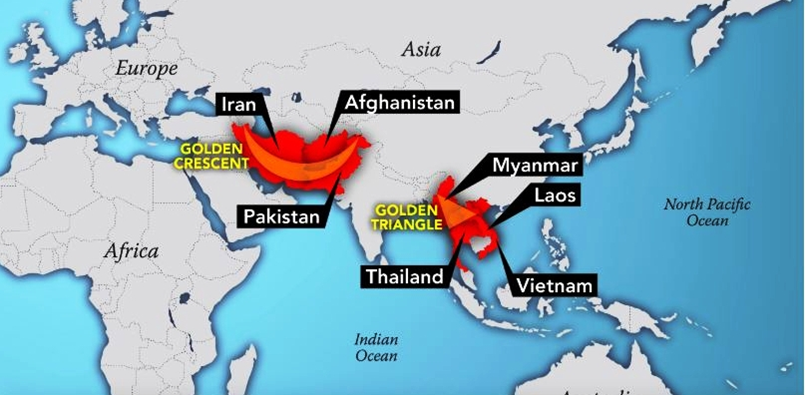
Major Drug-Producing Regions:
- Golden Crescent: Comprising Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan, it remains a primary hub for opium production, impacting Indian states such as Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Gujarat.
- Golden Triangle: Located at the intersection of Laos, Myanmar, and Thailand, this region is notorious for heroin production, with Myanmar producing 80% of the world’s heroin. Trafficking routes pass through Laos, Vietnam, Thailand, and India.
What are Different Drug Types and Substances?
| Drug Type | Characteristics |
| Stimulants |
|
| Depressants |
|
| Hallucinogens |
|
| Dissociative Drugs |
|
| Opioids |
|
| Inhalants |
|
| Cannabis |
|
What are the Factors Contributing to Drug Abuse in India?
- Peer Influence: The desire to fit in with friends and gain social approval often leads to experimentation with drugs, especially in high school and college environments.
- Academic Stress and Mental Health Issues: Pressure to excel academically, coupled with high competition, can cause stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Some youth use drugs as a coping mechanism for managing these pressures.
- Cultural Norms and Media Influence: The glamorisation of drug use in media, movies, and music often normalizes substance abuse among young people, making it appear trendy or acceptable.
- The limited role of state authorities and local governments in addressing drug abuse has contributed to the rise of substance use in India.
- Socio Economic Factors: Poverty, unemployment, and limited access to educational and recreational resources increase the likelihood of substance abuse as young people turn to drugs as a form of escape or coping mechanism.
- Family Environment: Dysfunctional family dynamics, parental substance abuse, and lack of emotional support often correlate with higher rates of youth drug use.
- A supportive family environment can mitigate these risks.
- Legal System Loopholes: Organized crime syndicates exploit legal system loopholes, such as weak border controls, to smuggle drugs. They often misuse trade routes from Africa and South Asia for drug trafficking purposes.
- In 2023, the Border Security Force reported a 35% increase in drug seizures along the India-Pakistan border, highlighting the ongoing challenges in controlling illicit drug flows through these routes.
- Easy Availability: Easy drug availability, particularly due to smuggling in Punjab, has led to widespread abuse.
- Around 15.4% of Punjab’s population uses narcotics, with over 3 million people affected as per a 2022 study by Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER).
- Fear of Strict laws: Strict laws like the NDPS Act can discourage families from disclosing drug abuse due to fear of prosecution, hindering efforts for rehabilitation.
- This not only prevents individuals from seeking help but also allows the illegal drug supply chain to continue, contributing to the rise of drug abuse in India.
What are the Government Measures to Tackle Drug Abuse in India?
- Legislative Measures:
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985: It regulates the production, manufacture, and trafficking of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
- Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Prevention of Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (PITNDPS) Act, 1988 govern the legal framework for controlling and preventing drug trafficking and abuse.
- Institutional Measures:
- National Investigation Agency's (NIA): It is the Central Counter Terrorism Law Enforcement Agency in India.
- It plays a crucial role in tackling drug trafficking, particularly when it involves national security concerns.
- It investigates cases with inter-State and international links, including drug smuggling networks tied to terrorism, arms trafficking, and cross-border infiltration.
- It coordinates with other agencies to disrupt transnational drug trade, seize illicit shipments, and dismantle organized criminal syndicates involved in trafficking.
- National Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB):
- NCB is a nodal drug law enforcement and intelligence agency of India. It coordinates with national and international agencies, and participates in initiatives such as the SAARC Drug Offences Monitoring Desk (SDOMD).
- Other Enforcement Agencies: The Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI), Customs Department, and various law enforcement agencies work together to curb drug trafficking.
- National Investigation Agency's (NIA): It is the Central Counter Terrorism Law Enforcement Agency in India.
- Preventive and Rehabilitation Measures:
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR): The NAPDDR plan focuses on reducing the demand for drugs through awareness campaigns, capacity-building programs, de-addiction, and rehabilitation services.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA): NMBA was launched to raise awareness about the harmful effects of drugs, especially among school children.
- NIDAAN and NCORD Portals: NIDAAN and NCORD Portals are online platforms that maintain detailed databases of drug offenders, supporting law enforcement agencies in tracking drug-related crimes and trends.
- Specific Initiatives:
- Project Sunrise (2016):
- Project Sunrise is addressing the rising HIV prevalence among drugs injecting people in the northeastern states.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat:
- Nasha Mukt Bharat is a nationwide campaign focusing on community outreach to prevent drug use and its social consequences.
- Seizure Information Management System (SIMS):
- SIMS portal was developed by the NCB to track drug offenses and offenders through an online database.
- De-addiction Centers:
- Institutions like the National Drug Dependence Treatment Centre (NDDTC) at AIIMS, and state-run centers offering counseling, medical treatment, and social reintegration for addicts.
- Project Sunrise (2016):
Way Forward
- Strengthening and Reform Existing Laws: Enhance the implementation of the NDPS and PITNDPS Acts through better training, resources, and modern technology.
- The NDPS Act needs to be revisited to integrate rehabilitation alongside punitive measures, strengthening enforcement, and improving coordination between local, state and central authorities.
- Integrated Policy Approach: The government should develop integrated policies that address the root causes of drug abuse, incorporating health, education, and social welfare sectors.
- Continued research is necessary to monitor drug trends and the effectiveness of intervention programs, allowing for data-driven policy adjustments.
- De-addiction Centres and Camps: Establishing district-level de-addiction centers and organizing rehabilitation camps by government agencies can provide crucial support to affected individuals.
- Post-care counseling and rehabilitation efforts are essential for long-term recovery and preventing relapses.
- Education and Awareness: Schools should include drug education in their curricula, teaching students about the risks and consequences of substance abuse from an early age.
- Civil society and religious leaders can significantly contribute to preventing drug abuse through awareness programs in schools and communities, promoting healthy choices and engaging role models like athletes and actors.
- International Cooperation: Strengthen ties with neighboring countries and international organizations such as UNODC and Interpol for effective information sharing and counter-trafficking measures.
- Use of Technology: Utilize AI, Big Data, and drones to track drug trafficking networks and monitor illicit drug cultivation areas. Establish online reporting systems for drug-related activities.
Conclusion
Article 47 of the Constitution calls for the improvement of public health and the prohibition of harmful substances. To effectively address the drug menace, India requires stronger regulations, enhanced laws, and improved coordination among states. Formulating a comprehensive national policy focused on prevention, rehabilitation, and stringent enforcement is essential.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the issue of drug abuse in India. Suggest some measures to tackle the issue of drug abuse. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air’.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its member States to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. India’s proximity to two of the world’s biggest illicit opium-growing states has enhanced her internal security concerns. Explain the linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities such as gunrunning, money laundering and human trafficking. What counter-measures should be taken to prevent the same? (2018)