Internal Security
UNODC Report on Illicit Drugs
- 01 Jul 2024
- 12 min read
For Prelims: United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), World Drug Report 2024, Cannabis, NDPS Act, NCB, Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), Golden Crescent and Golden Triangle, National Fund for Control of Drug Abuse, National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction
For Mains: Drug: Challenges, Initiatives, Problem of drug abuse and related Initiatives.
Why in News?
Recently, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) released its World Drug Report 2024, drawing global attention to escalating concerns in the international drug landscape.
What are the Highlights of the Report?
- Rising Drug Use:
-
In 2022, the number of drug users worldwide reached 292 million, representing a 20% increase over the past decade.
-
- Drug Preference:
-
- Cannabis remains the most popular drug, with 228 million users, followed by Opioids, Amphetamines, Cocaine, and Ecstasy.
- Emerging Threats: The report warns about nitazenes, a new class of synthetic opioids more potent than fentanyl.
- These substances are linked to an increase in overdose deaths, particularly in high-income countries.
- Treatment Gap:
- Out of 64 million people suffering from drug use disorders, only one in 11 receive treatment.
- Gender Disparity in Treatment:
-
The report reveals a significant gender gap in treatment access. Only one in 18 women with drug use disorders receive treatment, compared to one in seven men.
-
- Drug Use In India:
- The number of people becoming addicted to drugs has risen sharply. According to data from the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB), there are currently around 100 million people in the country addicted to various narcotic substances.
- According to the Ministry of Home Affairs, Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Punjab are the top three states with the highest number of FIRs registered under the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS Act) in three years between 2019 and 2021
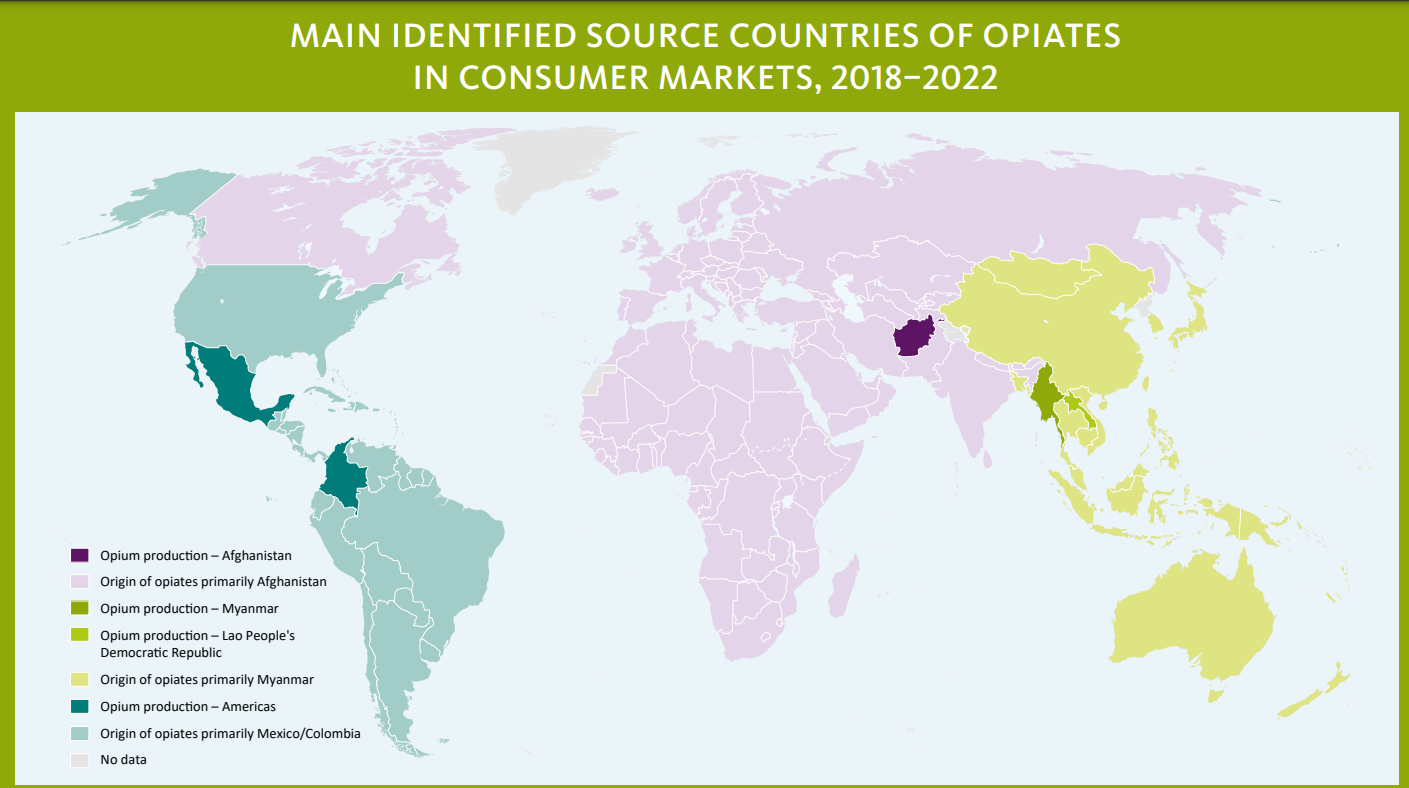
Who are the Major Drug-Producing Regions in the World?
- The Golden Crescent: It comprises Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan, a major global hub for opium production and distribution.
-
It affects Indian states like Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Gujarat.
-
-
The Golden Triangle: It is located at the intersection of Laos, Myanmar, and Thailand notorious for heroin production (Myanmar produces 80% of global heroin).
- Trafficking routes pass through Laos, Vietnam, Thailand, and India.
What are the Factors Contributing to Drug Abuse in India?
- Poverty, Unemployment, and Escapism: Individuals in lower-income groups use cheap, readily available drugs to temporarily escape harsh realities like poverty, unemployment, and poor living conditions.
- A slum rehabilitation program in Chennai reported that 70% of adult drug users cited poverty-related stress as a key factor.
- Peer Pressure and Social Influences: Teenagers experiment with drugs at parties to fit in or appear cool. Youth emulating celebrities or social media influencers who portray drug use as fashionable.
- A 2023 cybercrime unit investigation uncovered a network using Instagram to advertise pharma parties in Goa, reaching over 100,000 potential attendees.
- Legal System Loopholes: Organized crime syndicates exploit legal system loopholes, such as weak border controls, to smuggle drugs. They often misuse trade routes from Africa and South Asia for drug trafficking purposes.
- In 2023, the Border Security Force reported a 35% increase in drug seizures along the India-Pakistan border, highlighting the ongoing challenges in controlling illicit drug flows through these routes.
What are the Various Challenges For India in Drug Trafficking?
- Border Vulnerabilities and Public Health Risks: The India-Myanmar border, characterized by rough terrain and dense forests, presents security challenges.
- Illicit drug flows through India threaten both national security and public health.
- Socio-Economic Factors: Poverty, unemployment, and illiteracy in the North Eastern regions contribute to local involvement in drug-related criminal activities.
- Some local tribes and residents may participate out of economic necessity or misplaced sympathy.
- Global Drug Supply Hub: The Golden Crescent and Golden Triangle regions collectively meet about 90% of the world's drug demand.
- India's proximity to these areas increases its exposure to drug trafficking.
- Evolving Smuggling Techniques: This technological shift presents new challenges for law enforcement. Recent incidents in Punjab have revealed the use of drones for cross-border drug and weapon smuggling.
-
Emerging Cocaine Market: India has unexpectedly become a popular destination for cocaine, controlled by South American cartels. These cartels have established complex networks involving:
- Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) in countries like Canada, Australia, Singapore, Hong Kong, and various European nations.
- Local drug dealers and gangsters in India.
What is the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, of 1985?
- The Act regulates certain operations such as manufacture, transport, and consumption related to narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
- Under the Act, financing certain illicit activities such as cultivating cannabis, manufacturing narcotic drugs, or harbouring persons engaged in them is an offence.
- Persons found guilty of this offence will be punished with rigorous imprisonment of at least 10 years - extendable up to 20 years - and a fine of at least Rs.1 lakh.
- It also provides for forfeiture of property derived from, or used in, illicit traffic in narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances.
- It also provides for the death penalty in some cases where a person is a repeat offender.
- The Narcotics Control Bureau was also constituted in 1986 under the Act.
What are the Initiatives Taken to Tackle Drug Abuse in India?
- Project Sunrise: It was launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in 2016, to tackle the rising HIV prevalence in north-eastern states in India, especially among people injecting drugs.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat: The government has also announced the launch of the ‘Nasha Mukt Bharat’, or Drug-Free India Campaign which focuses on community outreach programs.
- Narco-Coordination Centre: The Narco-Coordination Centre (NCORD) was constituted in 2016 and the “Financial Assistance to States for Narcotics Control” scheme was revived.
- Seizure Information Management System: The Narcotics Control Bureau has been provided funds for developing new software like the Seizure Information Management System (SIMS) which will create a complete online database of drug offenses and offenders.
- National Drug Abuse Survey: The government is also conducting a National Drug Abuse Survey to measure trends of drug abuse in India through the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment with the help of the National Drug Dependence Treatment Centre of AIIMS.
Way Forward
- Comprehensive Strategy: Prevention, treatment, and law enforcement as recommended by UNODC for community-based programs to raise awareness.
- Prevention:
- A national review and consultation organized by the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) and Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) focused on a 'Joint Action Plan to Prevent Drug and Substance Abuse and Combat Illicit Trafficking'.
- Media campaigns targeting vulnerable populations.
- Early intervention strategies in schools and workplaces
- Treatment:
- Equipping people with knowledge and skills to resist drug use. These programs go beyond simple "Just Say No" campaigns and include:
- Accurate information about drug effects and risks.
- Coping strategies for peer pressure and stress.
- Decision-making skills and self-esteem building.
- Providing comprehensive recovery support services.
- Addressing the stigma associated with seeking help for drug abuse
- Equipping people with knowledge and skills to resist drug use. These programs go beyond simple "Just Say No" campaigns and include:
- Law Enforcement:
- Strengthening border security to intercept drug shipments.
- Improving intelligence sharing between agencies (Interpol) and countries (Golden Crescent and the Golden Triangle).
- Targeting high-level drug traffickers and their financial networks.
- Prevention:
- Use of Technology:
- Develop an online reporting system where citizens can report drug abuse and trafficking activities. Big Data and analytics and AI to identify and track drug trafficking networks.
- The new portal 'Prahari' will be launched to conduct quarterly activities for awareness of drugs and substance abuse in schools.
- Develop an online reporting system where citizens can report drug abuse and trafficking activities. Big Data and analytics and AI to identify and track drug trafficking networks.
- Humanitarian Approach:
- In response to the limitations of punitive measures in addressing drug-related cases, there is a need to amend legislation to adopt more reformative approaches.
- Viewing drug use through a lens of public health and human rights promotes understanding and empathy towards individuals affected by addiction.
- Redirecting resources from incarceration towards rehabilitation can lead to better outcomes for individuals and communities.
|
Drishti Mains Questions: How do drug trafficking challenges intersect with border management issues, particularly in regions like India, and what strategies are being employed to address these complexities? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- The United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC) has a ‘Protocol against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air’.
- The UNCAC is the ever-first legally binding global anti-corruption instrument.
- A highlight of the United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC) is the inclusion of a specific chapter aimed at returning assets to their rightful owners from whom they had been taken illicitly.
- The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) is mandated by its member States to assist in the implementation of both UNCAC and UNTOC.
Which of the statements given above is correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. India’s proximity to two of the world’s biggest illicit opium-growing states has enhanced her internal security concerns. Explain the linkages between drug trafficking and other illicit activities such as gunrunning, money laundering and human trafficking. What counter-measures should be taken to prevent the same? (2018)