Rise in Forex Reserves | 09 Dec 2024
For Prelims: Foreign Exchange, Trade Deficit, Current Account Deficit, Foreign Direct Investment, Foreign Portfolio Investors, External Commercial Borrowings, Tapering, Taper Tantrum, Foreign Currency Non-Resident Bank, Secured Overnight Rupee Rate, Treasury Bills Repurchase Agreement, Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of AI, MuleHunter.AI.
For Mains: India’s foreign exchange reserve and RBI’s initiative to strengthen the banking system.
Why in News?
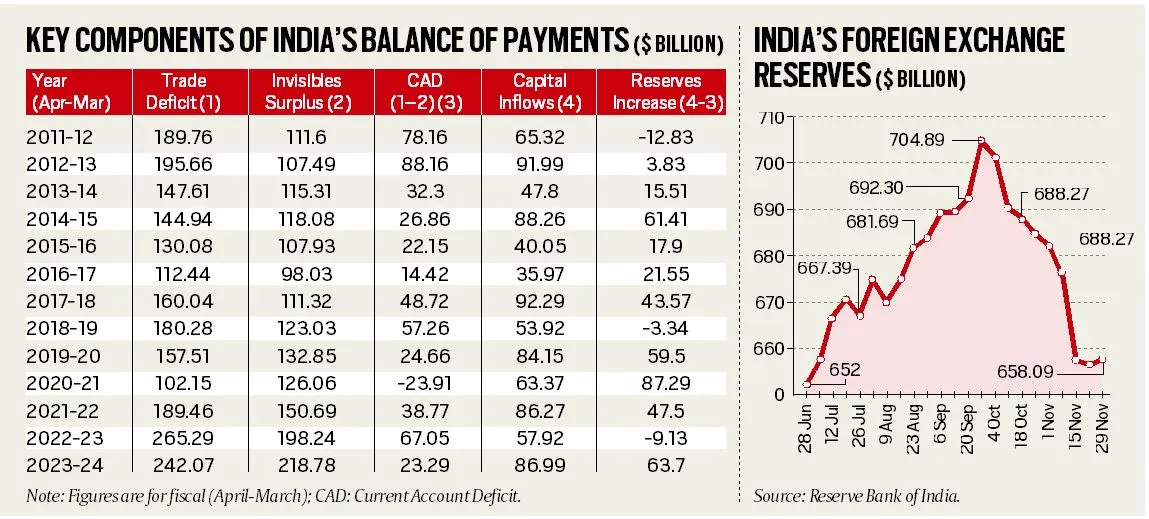
India's foreign exchange rose to USD 658.09 billion in November 2024 after eight weeks of decline, following the peak of USD 704.89 billion in September 2024.
- In another development, RBI has planned several initiatives for a robust banking system.
What are Key Developments in India’s Forex Reserves?
- Forex Reserves Movement: The movement in forex reserves is intrinsically linked to India's merchandise trade deficit and service exports.
- Merchandise Trade Deficit: India has historically run a merchandise trade deficit, with imports (USD 683.55 billion in 2023-24) exceeding exports (USD 441.48 billion), resulting in a trade deficit of USD 242.07 billion in 2023-24.
- Services and Remittances: Software service exports increased from USD 60.96 billion in 2011-12 to USD 142.07 billion in 2023-24, boosted by global digitization post-COVID.
- Private remittances rose from USD 63.47 billion in 2011-12 to USD 106.63 billion in 2023-24.
- Current and Capital Account Position: The Current Account Deficit (CAD) narrowed from USD 78.16 billion in 2011-12 to USD 23.29 billion in 2023-24, despite a consistent merchandise trade deficit.
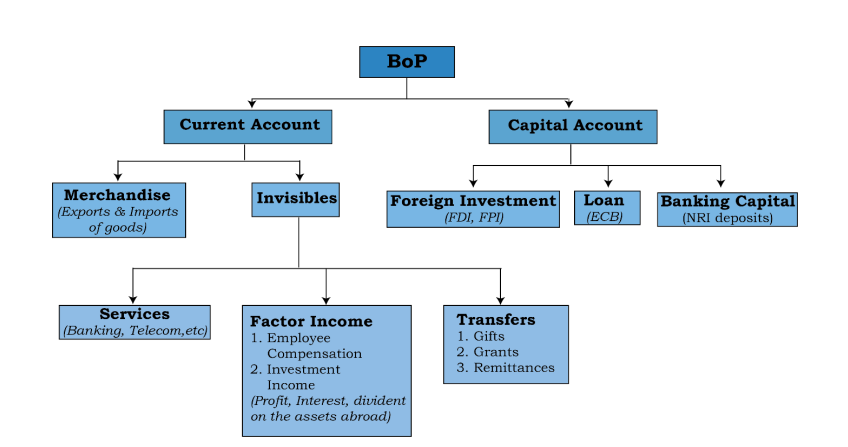
- Capital flows include Foreign Direct Investment (FDIs), Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) , external commercial borrowings (ECBs), and NRI deposits.
- Out of these, FDI flows are considered more stable while the other three sources are either fickle (FPI) or short-term (ECB and NRI deposits) and prone to sudden outflows and withdrawals.
- FDI and FPI Trends: FDI flows into India have dropped from USD 56.01 billion in 2019-20 to USD 26.47 billion in 2023-24.
- Net FPI flows stand at a record USD 44.08 billion in 2023-24.
- Future Outlook: Despite fluctuating FDI and uncertain geopolitical scenario, the situation isn't too bad.
- In 2011-12 and 2012-13, the US Federal Reserve's reduction of bond purchases (tapering) led to reduced capital flows, causing the rupee to drop and forex reserves to shrink.
Note:
The "invisibles" account, including services and remittances, has consistently shown a surplus, helping offset the merchandise trade deficit.
- Tapering is a term used in finance to describe a reduction of monetary stimulus provided by central authorities to the capital markets. It is the reversal of quantitative easing policies, intended to stimulate economic growth.
- Financial markets may experience a downturn in response to tapering, known as a "taper tantrum."
What are Foreign Exchange Reserves?
- About: Foreign exchange reserves are assets held on reserve by a central bank in foreign currencies.
- It can include banknotes, deposits, bonds, treasury bills, and other government securities.
- Following the 1990-91 economic crisis, C. Rangarajan and Y.V. Reddy committee recommended maintaining forex reserves to cover 12 months of imports.
- Components: India’s Forex Reserve include:
- Foreign Currency Assets (FCA): FCA predominantly composed of major global currencies like the US Dollar, Euro, and Japanese Yen.
- Gold Reserves: Gold has long been valued as a key reserve asset offering both stability and universal acceptance.
- Special Drawing Rights (SDRs): SDRs, created by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), are reserve assets that supplement member countries' official reserves.
- Reserve position with IMF: It is a portion of the required quota of currency each member country must provide to the IMF.
What is the Role of Forex Reserves in Economic Stability?
- Economic Buffer: Reserves help countries manage downturns, stabilize currency, and maintain investor trust.
- Trade Equilibrium: Reserves enable countries to address trade imbalances when imports exceed exports.
- Monetary Strategy: Reserves allow central banks to control currency value, manage inflation, and implement monetary policies.
- Fulfilling External Obligations: Sufficient reserves help countries meet external debt, boosting international credibility.
- Exchange Rate Management: Central banks use reserves to intervene in the foreign exchange market, ensuring competitiveness and reducing volatility.
- Liquidity Provision: Reserves ensure a country can meet financial obligations, like debt and imports, during crises.
What are the RBI’s Recent Initiatives to Create a Robust Banking System?
- FCNR(B) Deposits: In order to attract more capital inflows, the RBI has decided to increase the interest rate ceilings on Foreign Currency Non-Resident Bank (FCNR (B)) account deposits.
- FCNR (B) accounts are foreign currency term deposits that non-resident Indians can open with Indian banks.
- SORR Benchmark: RBI is planning to introduce the Secured Overnight Rupee Rate (SORR) as a new benchmark based on all secured money market transactions, including overnight market repos and TREPS (Treasury Bills Repurchase Agreement).
- It will help develop the interest rate derivatives market and enhance the credibility of interest rate benchmarks in India.
- Collateral-Free Agriculture Loans: The RBI has decided to increase the limit for collateral-free agricultural loans from Rs 1.6 lakh to Rs 2 lakh per borrower.
- Panel on AI: The RBI will set up a committee of experts to recommend a Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of AI (FREE-AI) in the financial sector to ensure ethical use and minimize risks.
- The RBI has developed an AI/ML-based model called MuleHunter.AI to help banks manage and combat mule bank accounts.
Conclusion
India's forex reserves are stabilizing after recent declines, bolstered by strong "invisibles" and managed capital inflows. RBI's strategic initiatives, including the introduction of SORR, increased FCNR(B) interest rates, and enhanced AI solutions, aim to fortify the banking system, ensuring stability and fostering sustainable economic growth.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How can the RBI’s management of forex reserves and introduction of new initiatives bolster the resilience of India’s financial sector? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do?(2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)?(2017)
- It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. The product diversification of financial institutions and insurance companies, resulting in overlapping of products and services strengthens the case for the merger of the two regulatory agencies, namely SEBI and IRDA. Justify. (2013)