Social Justice
Regulator to Oversee Health Insurance
- 26 Dec 2023
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Regulator to Oversee Health Insurance, IRDAI Vision 2047, Health Insurance, Out of Pocket expenditure (OOPE).
For Mains: Regulator to Oversee Health Insurance.
Why in News?
The government is exploring setting up a health sector regulator that will bring private and government health insurance schemes under its purview to facilitate affordable insurance coverage for all.
What is the Need for Setting up a Health Sector Regulator?
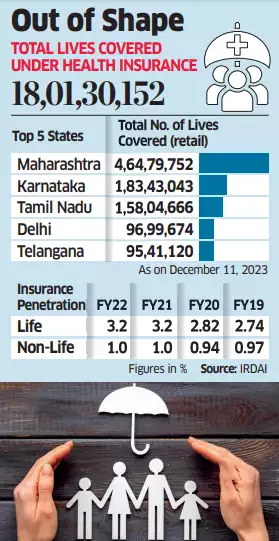
- Lower Penetration:
- Under the IRDAI Vision 2047, the government aims to provide ‘Insurance for All by 2047’, which means that every citizen has appropriate life, health, and property insurance coverage and every enterprise is supported by appropriate insurance solutions.
- According to a report by the National Insurance Agency, over 400 million individuals, or about a third of the population, lack Health Insurance due to lower penetration, coverage inadequacy and rising healthcare costs.
- Unified Oversight:
- Bringing both private and government health insurance schemes under one regulator ensures standardized oversight.
- It streamlines regulations, policies, and procedures, creating a cohesive framework for the entire health insurance sector.
- Ensuring Fair Practices:
- A regulator helps ensure fair practices across the board. It can monitor premiums, claim settlements, and coverage criteria, preventing malpractices and ensuring that both private and government insurers operate transparently.
- Enhanced Accessibility:
- With a regulator in place, there's an opportunity to improve the accessibility of healthcare.
- Penetration of private insurance is increasing at a fast rate and along with government-run insurance, India aims to be covering 70% of the population soon.
- Affordability and Sustainability:
- By overseeing insurance schemes, the regulator can work toward maintaining the affordability of health insurance.
- It can help control costs, establish fair pricing structures, and prevent undue premium hikes, making insurance more sustainable in the long run.
- Quality Control:
- The regulator can set and enforce standards for healthcare services covered by insurance. This includes ensuring that empaneled hospitals meet certain quality benchmarks, fostering a higher quality of care for insured individuals.
What is Health Insurance?
- About Healthcare:
- Health insurance is a type of coverage that pays for medical expenses incurred by the insured individual.
- It works by providing financial protection to cover various healthcare costs, including hospitalization, doctor visits, surgeries, medications, and preventive care.
- Significance of Health Insurance:
- It is a mechanism of pooling the high level of Out of Pocket expenditure (OOPE) in India to provide greater financial protection against health shocks.
- Pre-payment through health insurance emerges as an important tool for risk-pooling and safeguarding against catastrophic (and often impoverishing) expenditure from health shocks.
- Moreover, pre-paid pooled funds can also improve the efficiency of healthcare provision.
- Issues related to Health Insurance:
- Life Status is unevenly Distributed: There has been a significant increase in life expectancy of people from 35 years to 65 years since Independence. But the status of life is unevenly distributed in different parts of the country. The health problems in India are still a cause of great concern.
- Low Government Expenditure: Low Government expenditure on health has constrained the capacity and quality of healthcare services in the public sector.
- It diverts the majority of individuals – about two-thirds – to seek treatment in the costlier private sector.
- Significant Population is missed: At least 30% of the population, or 40 crore individuals are devoid of any financial protection for health.
- Related Government Schemes:
- Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY): It offers a sum insured of Rs. 5 lakh per family for secondary care (which doesn’t involve a super specialist) as well as tertiary care (which involves a super specialist).
- In 2019, the government had reconstituted the National Health Agency (NHA) as the National Health Authority (NHA), responsible for implementing Ayushman Bharat.
- The NHA has developed a national Health Claims Exchange (HCX) to enable the interoperability of health claims.
- Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY): It offers a sum insured of Rs. 5 lakh per family for secondary care (which doesn’t involve a super specialist) as well as tertiary care (which involves a super specialist).
Note
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) regulates insurers that provide health cover among other products.