Economy
IRDAI Vision 2047
- 29 May 2023
- 8 min read
For Prelims: IRDAI, Insurance for all’ by 2047, Economic Survey 2022-23, GDP, Digitization, Bima Trinity.
For Mains: IRDAI Vision 2047.
Why in News?
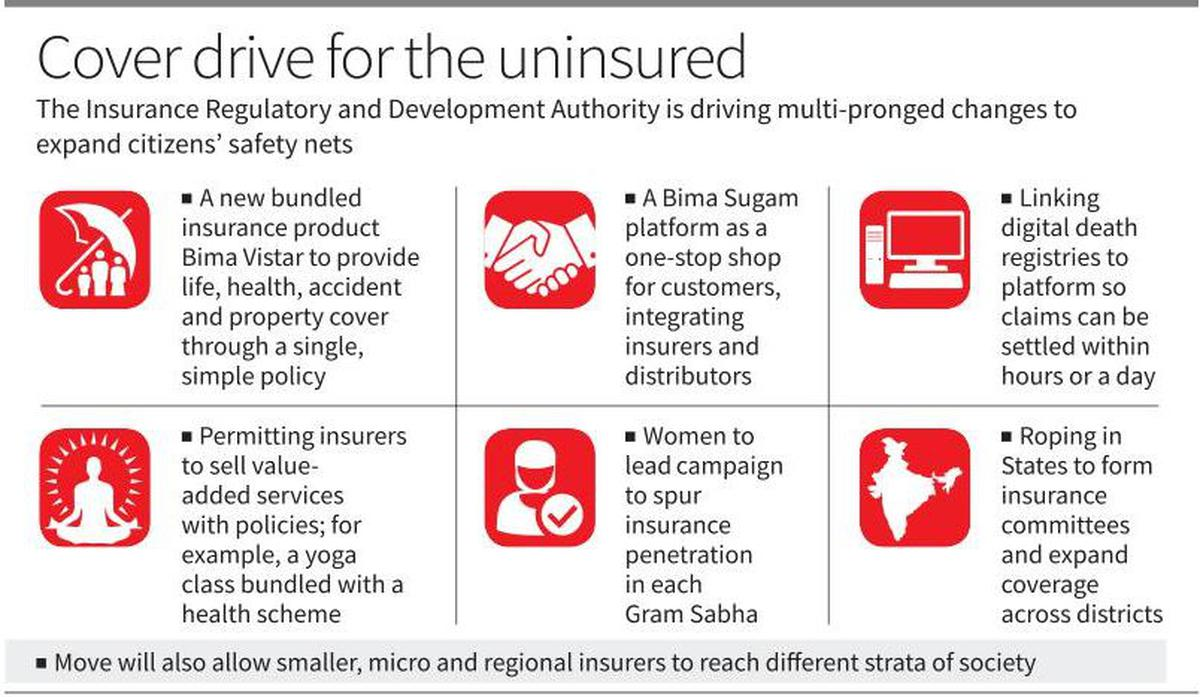
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI), as part of its Vision Insurance for all’ by 2047, has allotted states and union territories to every insurer to increase insurance penetration in India.
- IRDAI is also planning to launch Bima Trinity - Bima Sugam, Bima Vistar, Bima Vaahaks – in collaboration with general and life insurance firms to make insurance activities hassle free.
What is IRDAI Vision 2047?
- Objective:
- Insurance for All by 2047 aims that every citizen has an appropriate life, health and property insurance cover and every enterprise is supported by appropriate insurance solutions.
- It also aims to make the Indian insurance sector globally attractive
- Pillars:
- Insurance customers (Policyholders)
- Insurance providers (insurers)
- Insurance distributors (intermediaries)
- Focus Areas:
- Making available right products to right customers
- Creating robust grievance redressal mechanism
- Facilitating ease of doing business in the insurance sector
- Ensuring the regulatory architecture is aligned with the market dynamics
- Boosting innovation
- Competition and distribution efficiencies while mainstreaming technology and moving towards principle based regulatory regime.
- Significance:
- It can help people in households all over the country to have access to an affordable insurance policy that covers health, life, property, and accidents.
- These policies would offer faster claim settlements, sometimes within hours, and additional benefits like gym or yoga memberships.
What is Bima Trinity?
- Bima Sugam:
- It is a unified platform that combines insurers and distributors. It simplifies policy purchases, service requests, and claims settlement for customers in one convenient portal.
- Bima Vistar:
- It is a comprehensive bundled policy that covers life, health, property, and accidents. It provides defined benefits for each risk category, ensuring quick claim payouts without surveyors.
- Bima Vaahaks:
- It is a women-centric workforce operating at the Gram Sabha level. They will educate and convince women about the benefits of comprehensive insurance, particularly Bima Vistar. By addressing concerns and emphasizing advantages, Bima Vaahaks empower women and enhance their financial security.
What is the State of Insurance Sector in India?
- According to the Economic Survey 2022-23, life insurance density in the country increased from USD 11.1 in 2001 to USD 91 in 2021. Total global insurance premiums in 2021 increased 3.4% in real terms, with the non-life insurance sector registering 2.6% growth, driven by rate hardening in commercial lines in developed markets.
- According to the Economic Survey 2022-23, India's insurance market is poised to emerge as one of the fastest-growing markets globally in the coming decade.
- As per the IRDAI, insurance penetration in India increased from 3.76% in 2019-20 to 4.20%in 2020-21, registering a growth of 11.70%.
- Also, the insurance density increased from USD 78 in 2020-21 to USD 91 in 2021-22.
- Life insurance penetration in 2021 was 3.2%, almost twice as high as the emerging markets and slightly above the global average.
- India is at present the 10th biggest market in the world it is projected to be 6th biggest by 2032.
What are the Challenges Related to Insurance Sector
- Lower Adoption Rate:
- Insurance is not widely adopted in India compared to other countries. This is because many people are not aware of insurance or don't trust it.
- In rural areas, where a large portion of the population lives, only a small percentage have life insurance coverage.
- The insurance industry's contribution to India's GDP (Gross Domestic Product) is less than 5%, which is lower than the global average. In simple terms, insurance is not widely used in India, and efforts are needed to increase awareness and trust in insurance products.
- Lack of Product Innovation:
- The insurance sector in India has been slow in product innovation. Many insurance companies offer similar products, which leads to a lack of differentiation in the market.
- Fraudulence:
- Fraud includes things like making false claims and lying about information.
- The use of digital technology and customer-focused policies may have unintentionally given fraudsters more chances to steal identities and make fake claims.
- Over 70% of Indian insurers have seen an increase in fraud cases in the past two years.
- Talent Management:
- The insurance sector in India faces a talent shortage. The industry needs skilled professionals in areas such as actuarial science, underwriting, claims, and risk management.
- Attracting and retaining talented professionals is a challenge for the industry.
- Slow Rate of Digitalization:
- The insurance sector in India has been slow to adopt digitalization compared to other industries, which has resulted in several challenges such as inefficient processes, lack of transparency, and poor customer experience.
- Claims Management:
- The claims process in India is often seen as complicated, slow, and opaque, which can lead to customer dissatisfaction and loss of trust in the insurance industry.
- This can be due to a lack of transparency, inefficient processes, and poor communication with customers.
What is IRDAI?
- IRDAI, founded in 1999, is a regulatory body created with the aim of protecting the interests of insurance customers.
- It is a statutory body under the IRDA Act 1999 and is under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Finance.
- It regulates and sees to the development of the insurance industry while monitoring insurance-related activities.
- The powers and functions of the Authority are laid down in the IRDAI Act, 1999 and Insurance Act, 1938.
Way Forward
- To improve the insurance sector in India, several steps can be taken to leverage technology, align with customer behavior, optimize data usage, simplify claims management, adopt hybrid distribution models, and tackle fraud.
- Digitalization should be a priority across the value chain to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and support ecosystem development. This involves using technology to enhance employee skills and productivity through upskilling programs.
- Insurers need to align with dynamic changes in customer behavior and preferences. By offering quick personalized products and prioritizing flexibility over mass offerings, insurers can better meet customer needs and manage perceptions.