Regulating India’s Online Gaming | 18 Mar 2025
For Prelims: Online Gaming, Real Money gaming (RMG) Industry, Digital Payment System, State List, Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA).
For Mains: Factors leading to the rise of the gaming industry in India, Need of code of ethics and deregulating India's online gaming sector.
Why in News?
Many experts have highlighted the challenges of excessive regulation in online gaming, citing heavy taxation and legal uncertainties and urged the government to allow them to operate with greater freedom.
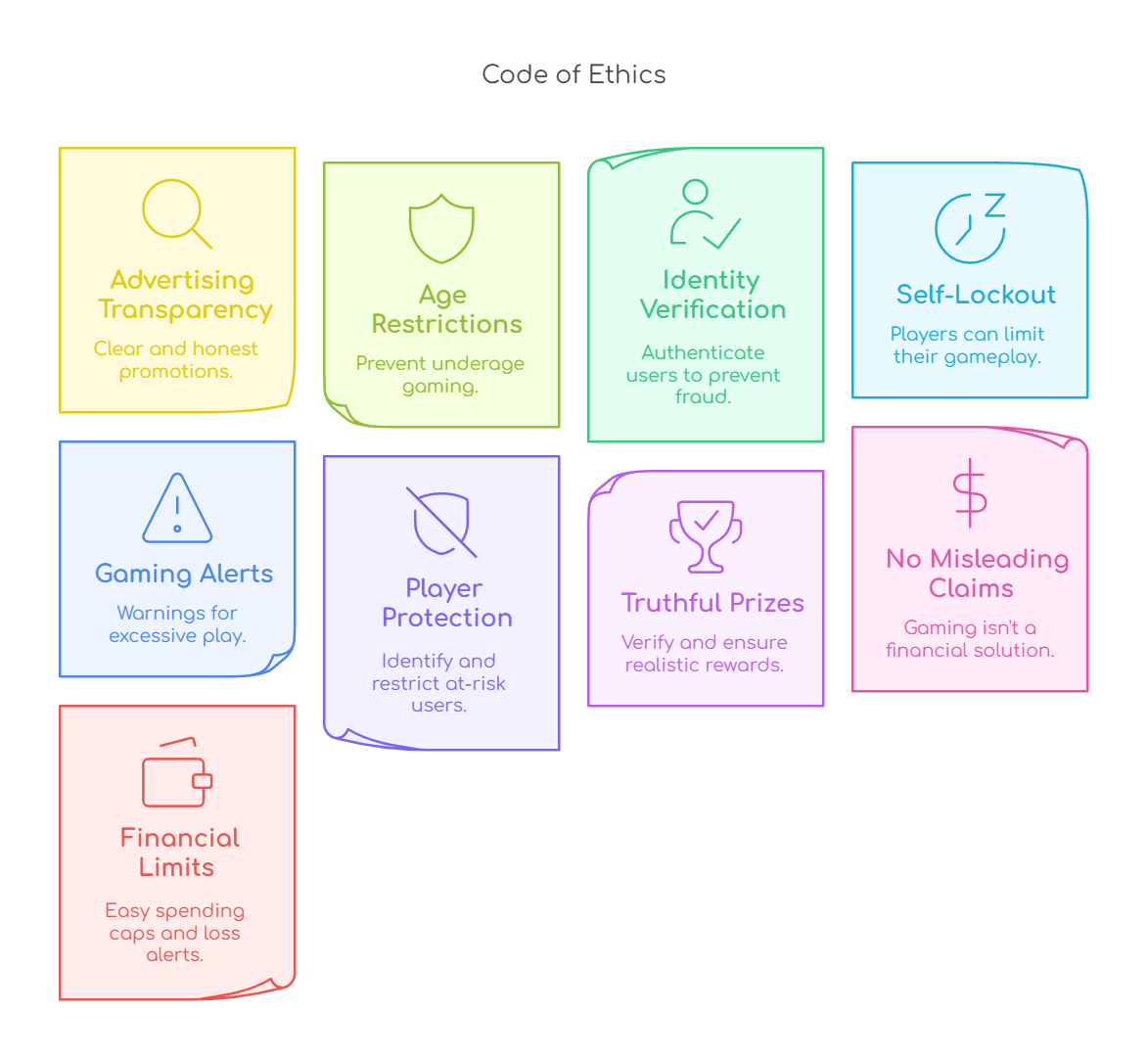
- Additionally, India’s real money gaming (RMG) industry has collectively signed a code of ethics to establish ethical and transparent business practices.
What is the RMG Industry?
- About: It includes platforms such as Dream11 and PokerBaazi, where users stake real money with the potential to win or lose funds and has generated USD 3.8 billion in revenue in FY 2023-24.
- Need of Code of Ethics:
- Legal Pressures: States like Tamil Nadu have attempted to impose strict regulations, including Aadhaar verification and gameplay blackouts (midnight to 5 AM).
- Lack of Central Regulation: The Union government’s proposed rules for the RMG industry are yet to be enforced, creating pressure on firms to self-regulate.
- Industry Image: Self-regulation helps RMG companies demonstrate responsibility and legitimacy.
- Competition from Offshore Platforms: International gambling websites, which bypass GST and ID verification requirements, are growing rapidly, making ethical commitments crucial for domestic platforms to distinguish themselves.
What is Online Gaming?
- About: Online gaming refers to playing video games over the internet, allowing players to connect through computers, gaming consoles, or smartphones.
- It facilitates real-time interaction and competition between players, regardless of their location.
- Classification:
- Skill-Based Games: They prioritize skill over chance and are legal in India. E.g., Game 24X7, Dream11, and Mobile Premier League (MPL).
- Games of Chance: Their outcome depends mainly on luck rather than skill and are Illegal in India. E.g., Roulette, which attracts players primarily for monetary rewards.
- Market Size: In 2023, India became the world's largest gaming market with 568 million gamers and 9.5 billion app downloads.
- The market, valued at USD 2.2 billion in 2023, is projected to reach USD 8.6 billion by 2028.
- Key Drivers of Growth:
- Young Demographic: Nearly half of India's population is under 25 years old, creating a massive gaming audience.
- Smartphone Penetration: The number of smartphone users is expected to grow from 468 million in 2017 to 1.2 billion by 2025.
- Internet Accessibility: India has the 2nd-largest internet user base after China, with users projected to reach 900 million by 2025.
- Localized Content: Games are being adapted to Indian preferences, including regional language options (Gujarati, Bangla, Marathi, Telugu, etc.) and festival-themed events.
- Booming IT Sector: India had 275 online game development companies in 2019, up from just 25 in 2010, contributing to global game development.
- Digital Payments Adoption: Users of digital payment systems increased from 10 crores in 2019 to 46.52 crores in 2025, facilitating online transactions.
- Side Effects:
- Addiction: WHO has officially voted to include ‘gaming disorder’ as a behavioural addiction under the International Classification of Diseases.
- Emotional Symptoms: Restlessness, irritability, social isolation.
- Physical Symptoms: Fatigue and migraine, Carpal tunnel syndrome (pain in finger and hands).
| Click Here to Read: What are the Challenges to the Gaming Sector? |
Distinguishing Between Games of Skill and Games of Chance
|
Aspect |
Games of Skill |
Games of Chance |
|
Definition |
Games where the outcome is primarily determined by the player’s knowledge, strategy, and skill. |
Games where the outcome is primarily based on random factors and luck. |
|
Key Determining Factor |
Player skill, decision-making, and practice. |
Randomness, probability, and luck. |
|
Control Over Outcome |
High – Players' actions directly influence results. |
Low – Players have little to no control over results. |
|
Examples |
Chess, Poker (skill-based), Esports (Dota 2, Counter-Strike), Fantasy Sports, Sports Betting (knowledge-based). |
Slot Machines, Roulette, Lottery, Scratch Cards, Most Casino Games. |
|
Legal Status |
Often exempt from gambling laws or lightly regulated. |
Strictly regulated due to the potential for exploitation and addiction. |
How is Online Gaming Regulated in India?
- Legal Provisions:
- State legislatures have exclusive power to make laws on gaming, betting, and gambling under Entry 34 of the State List in India's Constitution.
- Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Amendment Rules, 2023: It has defined online game, online gaming intermediary, self-regulatory body, online RMG and permissible games.
- Prize Competitions Act, 1955 regulates prize-based competitions.
- Public Gambling Act, 1867 (PGA) exempts skill-based games from penalties.
- FDI Restrictions: India's FDI policy prohibits foreign investment and technology collaboration in lotteries, gambling, and betting, including licensing and brand agreements.
- Under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA), remittances for lottery winnings, income from racing, riding, or hobbies are prohibited.
- Judicial Stand: In the Dr. KR Lakshmanan Case, 1996, the Supreme Court ruled horse race betting as a game of skill, making it exempt from most gaming prohibitions.
- In the Geeta Rani Case, 2019, the Supreme Court is yet to decide whether sports betting qualifies as a game of skill.
- Taxation: The Central Goods and Services Tax (Amendment) Act, 2023 introduced a 28% tax on the full face value of entry amounts in online gaming.
- Under the Income Tax Act, 1961, winnings above Rs 10,000 from lotteries, card games, or any game (including skill-based games) are taxed at 30% (excluding surcharge and cess).
What is the Need for Relaxation of Rules in the Online Gaming Sector?
- Economic Growth and Employment: The online gaming industry is a sunrise sector, with a projected market size of USD 8.6 billion by 2028.
- Deregulation can foster further investment and expansion, leading to the creation of 2-3 lakh additional jobs.
- Enhancing Competitive Advantage: India's vast market potential can be unlocked with regulations that help startups compete globally instead of facing tax and legal hurdles.
- Ensuring Regulatory Clarity: In the Online Gaming Cos vs GST Case, 2025, the Supreme Court’s stay on the Rs 1.12 lakh crore retrospective GST demand highlights the need for clear and stable policies.
- Unclear tax structures create an unpredictable business environment, discouraging investment and growth.
- Preventing Capital Flight: The 28% GST places online gaming in the same category as gambling and liquor, driving businesses to offshore platforms.
- This results in tax revenue loss and higher risks from unregulated online betting.
- Encouraging Innovation: Startups in the sector are forced to divert resources to legal battles instead of innovation and expansion.
- A stable regulatory framework can attract investment, drive technological progress, and establish India as a key player in online gaming.
Way Forward
- Rationalizing Taxation: The government should consider tiered taxation based on game classification (skill-based vs. chance-based) to ensure fairness and reconsider retrospective GST demands for investment stability.
- Categorisation of Gaming Platforms: Categorizing gaming platforms by user base can enhance responsible gaming through targeted regulations. E.g.,
- Children & Teens (Under 18): Parental controls, time limits.
- Young Adults (18-25): Awareness campaigns, spending limits.
- Adults (25+): Betting caps, mental health support.
- Uniform Regulatory Framework: A co-regulatory model involving industry and government can ensure compliance and promote responsible gaming.
- Inculcating inputs from the RMG Code of Ethics in a national gaming policy will further strengthen regulation.
- Responsible Gaming: Awareness campaigns about gaming addiction risks and helpline support should be mandated for platforms. E.g., Tamil Nadu Online Gaming Authority ensures responsible online gaming and prevents addiction, particularly among youth.
- Stricter enforcement of data protection laws should ensure that user data is not exploited.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the key drivers of growth in India’s online gaming industry and the challenges posed by excessive regulation. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect
- Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Discuss how emerging technologies and globalisation contribute to money laundering. Elaborate measures to tackle the problem of money laundering both at national and international levels. (2021)