RBI Surplus Transfer to Government | 23 May 2024
Why in News?
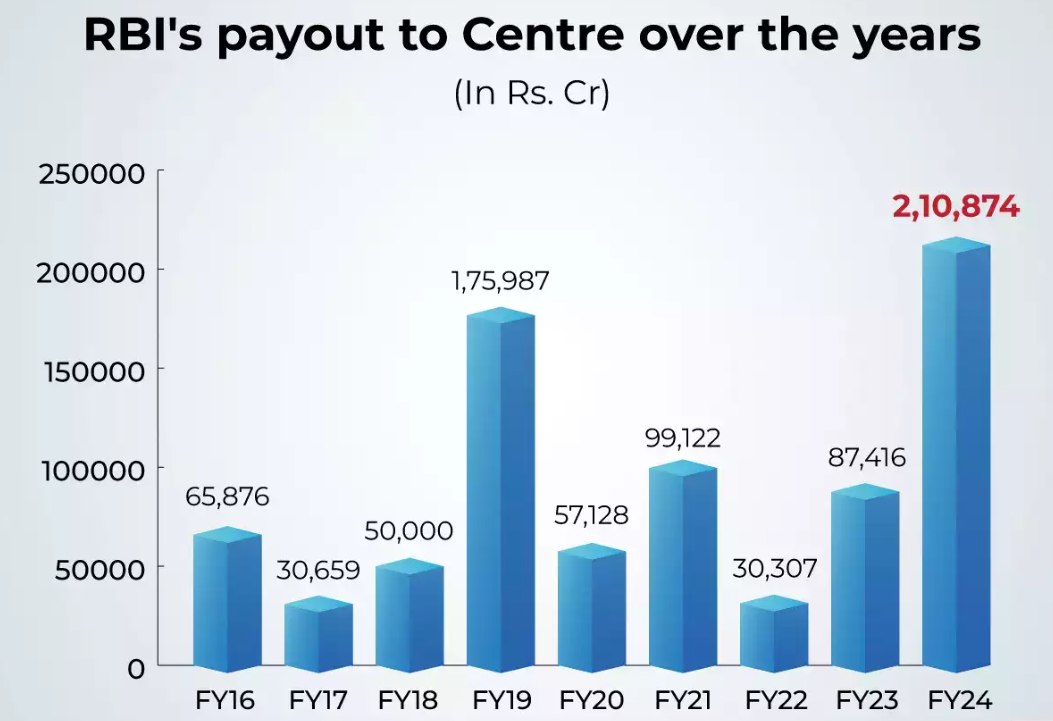
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has approved a significant surplus transfer of Rs 2.11 lakh crore to the Central Government for the accounting year 2023-24.
- This transfer marks a substantial increase from the previous year's dividend, showcasing a notable rise in surplus income.
How does the RBI Determine the Allocation of Dividends?
- The surplus calculation was based on the Economic Capital Framework (ECF) recommended by the Bimal Jalan committee, which advised the RBI to maintain a Contingent Risk Buffer (CRB) between 5.5% and 6.5% of its balance sheet.
- This risk provisioning is made primarily from retained earnings and only then is the surplus income transferred to the government as dividends.
- This range includes provisions for monetary and financial stability risks as well as credit and operational risks.
- RBI transfers its surplus, which is the excess of income over expenditure, to the government as per Section 47 of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- Reasons for the Increase in RBI's Surplus: As of March 2024, the RBI had USD 646 billion in foreign exchange reserves, with USD 409 billion parked in top-rated sovereign securities.
- The RBI’s gross dollar sales were lower in FY24 (USD 153bn) compared to FY23 (USD 213 bn).
- Despite lower dollar sales in FY24 compared to FY23, the RBI's management of foreign currency assets ensured continued high revenue.
- Income from Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF) operations also contributed to the overall surplus.
- The RBI’s gross dollar sales were lower in FY24 (USD 153bn) compared to FY23 (USD 213 bn).
| Reserve Bank of India's Sources of Income | |
| Source of Income |
|
| Expenditure |
|
| Surplus |
|
Bimal Jalan Committee Recommendations
- Formation:
- The RBI in 2018 constituted a six-member committee, chaired by former governor Dr Bimal Jalan, to review the current economic capital framework (ECF), after the Ministry of Finance asked the central bank to follow global practices.
- Recommendations:
- The panel proposed a clear separation of RBI's economic capital into two parts: Realised equity and Revaluation balances.
- Revaluation reserves include unrealised gains/losses in foreign currencies, gold, securities, and a contingency fund.
- Realised equity, or CRB, is funded by retained earnings to cover risks and losses.
- The committee suggested that the RBI should maintain a CRB within the range of 6.5% to 5.5% of the RBI's balance sheet.
- This would provide an adequate buffer against market risks, credit risks, and operational risks.
- The committee recommended that the RBI should transfer its surplus funds to the government only after maintaining the CRB within the suggested range.
- This would ensure that the RBI's financial resilience is not compromised while supporting the government's fiscal needs.
- The panel also suggested that the RBI’s ECF should be reviewed every five years.
- The panel proposed a clear separation of RBI's economic capital into two parts: Realised equity and Revaluation balances.
Note:
- The RBI Board's technical Committee, led by Y H Malegam in 2013, recommended a higher transfer of reserves and surplus to the government, which typically averages around 0.5% of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) with a few exceptions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (2017)
- It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: A
Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do? (2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: B