Indian Economy
RBI Guidelines for Asset Reconstruction Companies
- 27 Apr 2024
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Asset Reconstruction Companies, SIDBI, NABARD, Non-Performing Assets (NPAs), SARFAESI Act(2002)
For Mains: Significance of Asset Reconstruction Companies, Banking Sector and Non-Performing Assets.
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has issued a direction outlining updated guidelines for Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs), effective from 24th April 2024.
What are the RBI Guidelines for Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs)?
- Increased Minimum Capital Requirement:
- ARCs are now required to have a minimum capital of Rs 300 crore, a significant increase from the previous requirement of Rs 100 crore.
- Existing ARCs are granted a transition period to achieve the new minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF) threshold of Rs 300 crore by 31st March 2026.
- ARCs must ensure a minimum capital of Rs 200 crore by 31st March 2024, as part of the transition towards the higher capital requirement.
- In case of non-compliance at any of the above stages, the non-complying ARC shall be subject to supervisory action, including a prohibition on undertaking incremental business till it reaches the required minimum NOF applicable at that time.
- Eligibility as Resolution Applicants:
- ARCs with a minimum NOF of Rs 1000 crore are permitted to act as resolution applicants in the asset resolution process under Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (IBC).
- Investment Opportunities:
- ARCs are allowed to deploy funds in government securities and deposits with scheduled commercial banks, Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI), National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) or such other entities as may be specified by the central bank from time to time.
- Additionally, ARCs can invest in short-term instruments like money market mutual funds, certificates of deposit, and corporate bonds/commercial papers with a short-term rating equivalent to AA- or above by an eligible credit rating agency.
- However, there is a cap of 10% of the NOF on the maximum investment in such short-term instruments.
What are Asset Reconstruction Companies?
- About:
- ARCs are financial institutions that buy Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) or bad assets from banks and financial institutions.
- This allows the banks and institutions to clean up their balance sheets.
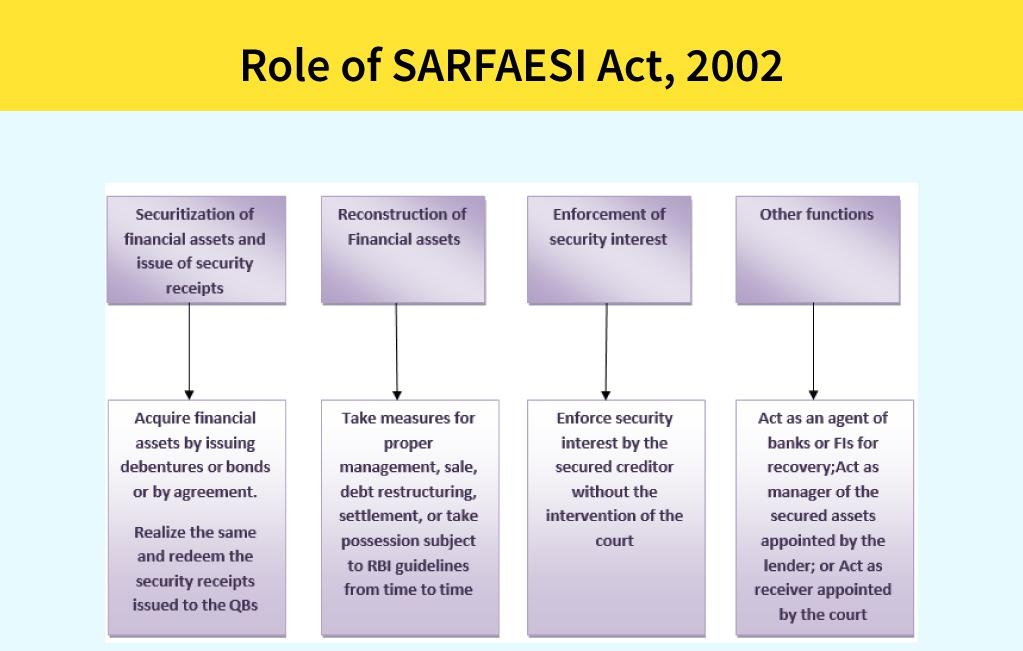
- It is incorporated under the Companies Act, 2013 and registered with the Reserve Bank of India under the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- ARCs are financial institutions that buy Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) or bad assets from banks and financial institutions.
- Examples:
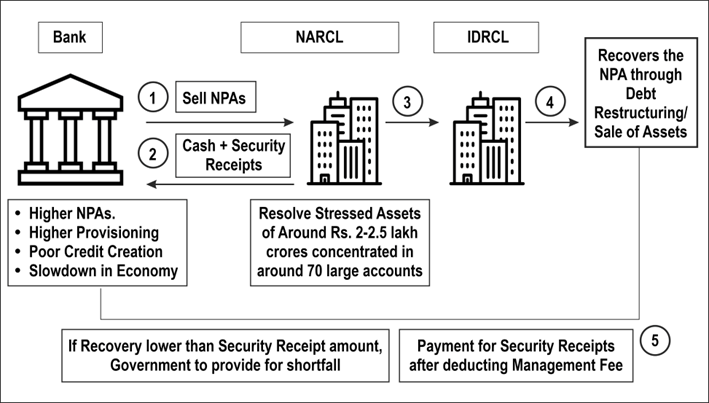
- National Asset Reconstruction Company Limited (NARCL) has been established by banks to aggregate and consolidate stressed assets for subsequent resolution. It is majority-owned by Public Sector Banks (PSBs) with a 51% stake.
- India Debt Resolution Company Ltd. (IDRCL) is another entity that will then attempt to sell the stressed assets in the market.
- PSBs and Public Financial Institutes (FIs) will hold a maximum of 49% stake in IDRCL. The remaining 51% stake will be with private-sector lenders.
- Function:
- Empowered by the SARFAESI Act, 2002. ARCs specialize in the recovery and turnaround of distressed assets.
- They purchase bad debt from lenders either in cash or through a combination of cash and security receipts.
- Empowered by the SARFAESI Act, 2002. ARCs specialize in the recovery and turnaround of distressed assets.
- Business Model:
- Acquisition of Stressed Loans: Lenders sell stressed loans to ARCs at a discount, freeing up their resources to focus on fresh loans.
- Security Receipts: ARCs issue security receipts to lenders, redeemable upon recovery of the specific loan.
- They also charge a management fee of 1.5% to 2% of the asset value annually and earn from recoveries, sharing upside with the selling financial institutions.
- Challenges:
- ARCs often deal with aged NPAs, which present challenges in terms of valuation and recovery due to prolonged delinquency.
- Aggregating debt from multiple lenders to the same borrower can be complex, requiring coordination and agreement among various stakeholders.
- ARCs face difficulties in raising funds on their balance sheets, limiting their capacity to acquire distressed assets or provide necessary support to borrowers for revival.
- Determining the fair value of distressed assets for acquisition and recovery purposes can be challenging, particularly when dealing with illiquid or complex assets.
- Recent Changes in ARC Regulations by RBI:
- Strengthening Corporate Governance: RBI mandated that the chair of the board and at least half the directors in a board meeting must be independent directors to enhance corporate governance at ARCs.
- Increased Transparency: ARCs are required to disclose their track record on returns generated for security receipt investors and engage with rating agencies for schemes floated in the last eight years to improve transparency.
- Investment Requirements: ARCs must invest in security receipts (SRs) at a minimum of either 15% of the transferors' investment in such receipts or 2.5% of the total receipts issued, whichever is higher, as against the previous requirement of 15% of total security receipts in all cases.
- SRs are instruments issued by ARCs to Qualified Buyers (QB) in exchange for their purchase of distressed assets from banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs).
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Evaluate the challenges faced by Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) in the Indian financial landscape and suggest measures to address them effectively |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the governance of public sector banking in India, consider the following statements:(2018)
- Capital infusion into public sector banks by the Government of India has steadily increased in the last decade.
- To put the public sector banks in order, the merger of associate banks with the parent State Bank of India has been affected.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The government has done capital infusion in state owned banks to support credit expansion and to help them tide over losses resulting from the provisions that are to be made for non-performing assets (NPAs). But the capital infusion trend in state-owned banks
- has not been specific in a direction, like increasing or decreasing trend. While it has increased in some years, it has also decreased in a few years. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Union Government in February 2017 had approved the merger of five associate banks along with the Bharatiya Mahila Bank with SBI. The purposes of the merger were rationalisation of public bank resources, reduction of costs, better profitability, and lower cost of funds leading to a better rate of interest to the public at large and improve productivity and customer service of the public sector banks. Parliament passed the State Banks (Repeal and Amendment) Bill, 2017 to merge six subsidiary banks with State Bank of India to affect rationalisation of public bank.
- Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Q2. With reference to the Non-banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) in India, consider the following statements: (2010)
- They cannot engage in the acquisition of securities issued by the government.
- They cannot accept demand deposits like Savings Account.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)