Prioritizing the Poor, Youth, Women, and Farmers | 03 Jan 2024
For Prelims: Multidimensional Poverty Index, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), Global Gender Gap Index, National Crime Records Bureau, Women’s Reservation Bill, 2023, World Bank, Unemployment
For Mains: Multidimensional Poverty and Unemployment, Empowering Women, Factors Contributing to Agricultural Distress, Related Government Initiatives
Why in News?
The Prime Minister of India has underscored the imperative of prioritizing the well-being of four groups: the poor, youth, women, and farmers.
- This emphasis reflects a commitment to ensuring dignity and respect for the deprived.
What are the Socioeconomic Dynamics of the Highlighted Groups in India?
- Poor:
- Multidimensional Poverty Index:
- India has more than 230 million poor people.
- According to the 2023 Global Multidimensional Poverty Index, published by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative, some 415 million Indians escaped poverty between 2005-06 and 2019-21.
- Approximately 18.7% of the population falls into the category of being 'vulnerable' to multidimensional poverty, as defined by the UNDP.
- This refers to individuals who, while not classified as poor, but have experienced deprivations in 20-33.3% of all weighted indicators.
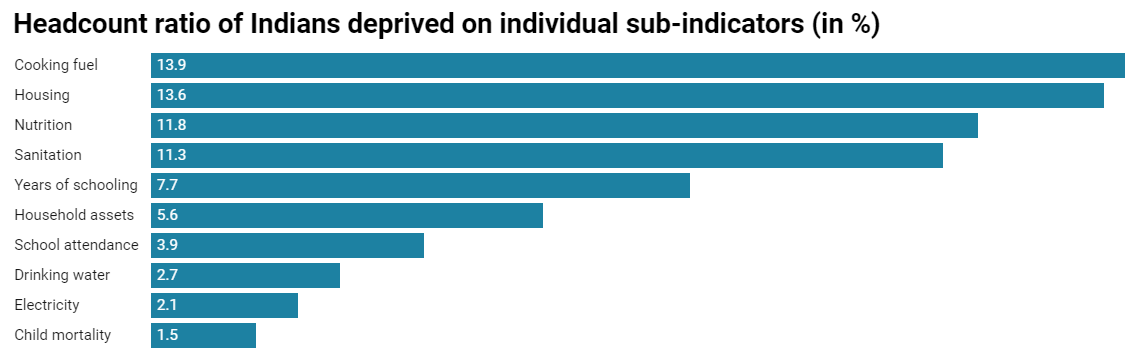
- Cooking fuel, housing, and nutrition are major areas of deprivation. Approximately 13.9%, 13.6%, and 11.8% of the population were classified as deprived in these respective metrics.
- Unemployment:
- India's unemployment rate rose to the highest level in over two years in October 2023, with rural areas experiencing an increase in joblessness.
- The National Sample Survey Office's Periodic Labour Force Survey for 2022-23 revealed a decrease in unemployment from 5.3% to 2.4% in rural areas and from 7.7% to 5.4% in urban areas compared to 2017-18.
- The proportion of self-employed individuals in the total employed population increased from 52% in 2018-19 to 57% in 2022-23.
- Self-employment covers various activities such as running a tea stall, farming, assisting in household enterprises, practising medicine, and undertaking unpaid work within one's economic activities.
- A high level of self-employment levels indicates a lack of alternatives, with individuals often adhering to these less rewarding jobs.
- Typically, countries with lower per capita income tend to have higher proportions of self-employed populations.
- Multidimensional Poverty Index:
- Women:
- India ranked 127 out of 146 countries in the Global Gender Gap Report 2023 released by the World Economic Forum showing an improvement of 1.4% points and eight positions from 135 in 2022.
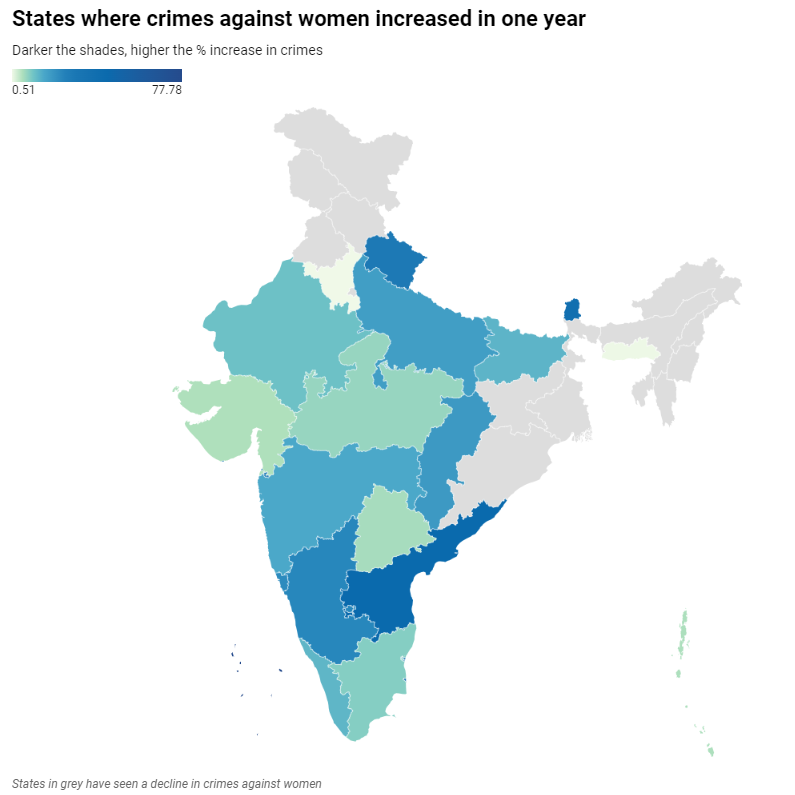
- According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) reports Crimes against women rose by 4% in 2022 compared to 2021, with over 4.45 lakh crimes registered.
- Majority of crimes were related to cruelty by husbands or relatives, kidnapping, assault, and rape.
- 12 states and Union territories recorded crime rates higher than the national average.
- The Women’s Reservation Act, 2023 also known as the Nari Shakti Vandan Adhiniyam,was passed to reserve one-third of seats in legislative assemblies and Lok Sabha for women.
- Farmers:
- Farmers lost standing crops to excess and untimely rain, leading to a significant blow to their incomes.
- Southwest monsoon was below normal and erratic, impacting Kharif crop yields in many parts of the country.
- States like Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Jharkhand are facing drought and drought-like conditions.
- Recurring losses due to the pink bollworm pest on the BT cotton crop in north India added to farmers' distress.
- NCRB data revealed an increase in deaths by suicide among those involved in farming.
- At least one farmer died by suicide every hour in India, with 11,290 suicide cases reported in 2022.
- Deaths by the suicide of agricultural labourers were higher than farmers/cultivators, with 53% of the suicide cases being agricultural labourers.
- The dependence of an average agricultural household for income has been increasing on wages from farming rather than crop production.
- Farmers lost standing crops to excess and untimely rain, leading to a significant blow to their incomes.
- Youth:
- According to the World Bank the youth unemployment rate in India was at 23.2%, higher than its neighbours Pakistan (11.3%), Bangladesh (12.9%), and Bhutan (14.4%), in 2022.
- The unemployment rate in China stood at 13.2%, South Korea 6.9% and Singapore 6.1%.
- Although the youth unemployment rate in India dropped from 23.9% in 2021, it is still marginally higher than the 22.9% recorded in the Pre-Covid year of 2019.
- The youth unemployment rate refers to those in the workforce who are aged 15 to 24 years and without a job, but actively seeking one.
- The State of Working India 2023 study found that unemployment among graduates under the age of 25 was at 42.3% in 2021-2022, while the overall joblessness rate was 8.7%.
- According to the World Bank the youth unemployment rate in India was at 23.2%, higher than its neighbours Pakistan (11.3%), Bangladesh (12.9%), and Bhutan (14.4%), in 2022.
What are the Related Initiatives Aimed at Addressing these Specific Groups?
- Poor:
- Women:
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Scheme
- Ujjawala Yojna
- Pradhan Mantri Mahila Shakti Kendra Scheme
- One Stop Centre
- The Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act, 2013
- The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO), 2012
- NARI SHAKTI PURASKAR
- Mahila police Volunteers
- Mahila Shakti Kendras (MSK)
- Farmers:
- Youth:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. The Multi-dimensional Poverty Index developed by Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative with UNDP support covers which of the following? (2012)
- Deprivation of education, health, assets and services at household level
- Purchasing power parity at national level
- Extent of budget deficit and GDP growth rate at national level
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Q2. Disguised unemployment generally means (2013)
(a) large number of people remain unemployed
(b) alternative employment is not available
(c) marginal productivity of labour is zero
(d) productivity of workers is low
Ans: (c)
Q3. Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for which of the following purposes? (2020)
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets
- Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini trucks
- Consumption requirements of farm households
- Post-harvest expenses
- Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q4. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- The nation-wide ‘Soil Health Card Scheme’ aims at expanding the cultivable area under irrigation.
- Enabling the banks to assess the quantum of loans to be granted to farmers on the basis of soil quality.
- Checking the overuse of fertilizers in farmlands.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q1. Most of the unemployment in India is structural in nature. Examine the methodology adopted to compute unemployment in the country and suggest improvements. (2023)
Q2. Despite Consistent experience of high growth, India still goes with the lowest indicators of human development. Examine the issues that make balanced and inclusive development elusive. (2016)
Q3.We are witnessing increasing instances of sexual violence against women in the country. Despite existing legal provisions against it, the number of such incidences is on the rise. Suggest some innovative measures to tackle this menace. (2014)