Primary Agricultural Credit Societies | 08 Dec 2023
For Prelims: Primary Agricultural Credit Societies, Model Bye laws, Ministry of Cooperation, Fair Price Shops (FPS), Atmanirbhar Bharat.
For Mains: Primary Agricultural Credit Societies, Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Cooperation has introduced Model Bye laws aimed at revitalizing Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS).
- The Model Byelaws refer to a set of guidelines or regulations formulated by the Ministry of Cooperation to govern the functioning and operations of PACS at the grassroots level.
What is the Purpose of these Bye-Laws?
- These Byelaws are designed to outline the structure, activities, and functioning of PACS, aiming to enhance their economic viability and expand their role in rural areas.
- The Model Byelaws will enable PACS to diversify their business activities by undertaking more than 25 business activities, including dairy, fishery, floriculture, setting up godowns, procurement of foodgrains, fertilizers, seeds, short-term & long-term credit, custom hiring centers, Fair Price Shops (FPS), community irrigation, Business Correspondent activities, etc.
- Provisions have been made to make the membership of PACS more inclusive and broad-based, giving adequate representation to women and Scheduled Castes/Schedules Tribes.
What are Primary Agricultural Credit Societies?
- About:
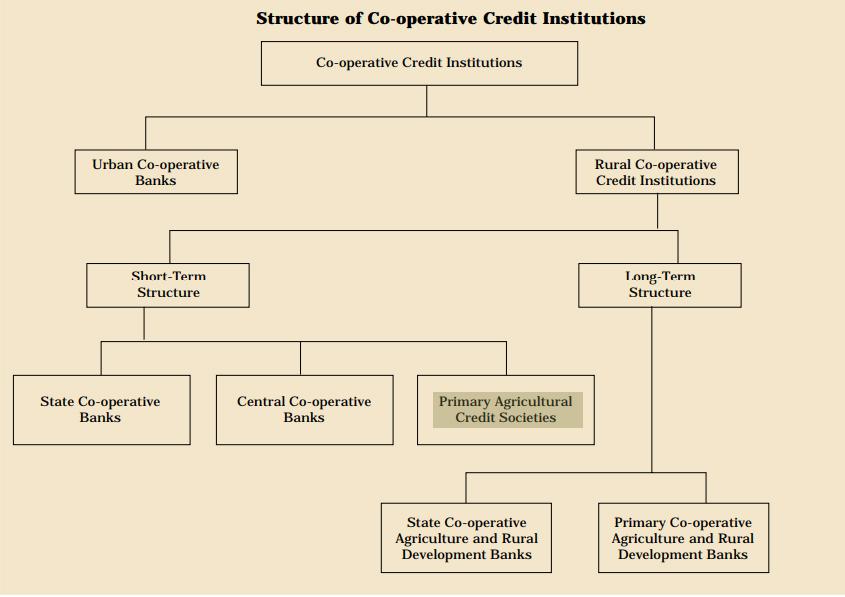
- PACS are village level cooperative credit societies that serve as the last link in a three-tier cooperative credit structure headed by the State Cooperative Banks (SCB) at the state level.
- Credit from the SCBs is transferred to the District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs), which operate at the district level. The DCCBs work with PACS, which deal directly with farmers.
- PACSs provide short-term, and medium-term agricultural loans to the farmers for the various agricultural and farming activities.
- The first PACS was formed in 1904.
- PACS are village level cooperative credit societies that serve as the last link in a three-tier cooperative credit structure headed by the State Cooperative Banks (SCB) at the state level.
- Status:
- According to a December 2022 report by the Reserve Bank of India, there were 1.02 lakh PACS in the country. However, only 47,297 of them made a profit by the end of March 2021.
- Significance of PACS:
- PACS provide small farmers with access to credit, which they can use to purchase seeds, fertilizers, and other inputs for their farms. This helps them to improve their production and increase their income.
- PACS are often located in rural areas, which makes it convenient for farmers to access their services.
- PACS have the capacity to extend credit with minimal paperwork within a short time.
What are the Issues with the PACS?
- Inadequate Coverage:
- Though geographically active PACS cover about 90% of 5.8 Lakh villages, there are parts of the country, especially in the north-east, where this coverage is very low.
- Further, the rural population covered as members is only 50% of all the rural households.
- Inadequate Resources:
- The resources of the PACS are much too inadequate in relation to the short-and medium-term credit needs of the rural economy.
- The bulk of even these inadequate funds come from higher financing agencies and not through owned funds of societies or deposit mobilization by them.
- Overdues and NPAs:
- Large over-dues have become a big problem for the PACS.
- As per the RBI report, PACS had reported lending worth Rs 1,43,044 crore and NPAs of Rs 72,550 crore. Maharashtra has 20,897 PACS of which 11,326 are in losses
- They curb the circulation of loanable funds, reduce the borrowing as well as lending power of societies, and give them the bad image that the societies of defaulting debtors are willful.
- Large over-dues have become a big problem for the PACS.
Way Forward
- These more than a century-old institutions deserve another policy push and can occupy a prominent space in the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat as well as Vocal for Local of the Government of India, as they have the potential to be the building blocks of an Atmanirbhar village economy.
- PACS have played a crucial role in the rural financial sector and have the potential to play an even greater role in the future. To achieve this, PACS must be made more efficient, financially sustainable, and accessible to farmers.
- At the same time, the regulatory framework must be strengthened to ensure that PACS are effectively governed and able to serve the needs of farmers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- In terms of short-term credit delivery to the agriculture sector, District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) deliver more credit in comparison to Scheduled Commercial Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
- One of the most important functions of DCCBs is to provide funds to the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q2. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
- Co-operative banks are financial entities which belong to its members, who are at the same time the owners and the customers of their bank. They are established by State laws.
- Co-operative banks in India are registered under the Cooperative Societies Act. They are also regulated by the RBI and governed by Banking Regulations Act, 1949 and Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies) Act,1955.
- Cooperative banks lend as well as accept deposits. They are established with the aim of funding agriculture and allied activities and financing village and cottage industries.
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) is the apex body of cooperative banks in India.
- Urban Co-operative Banks (UCB) are regulated and supervised by State Registrars of Co-operative Societies (RCS) in case of single-state co-operative banks and Central Registrar of Co-operative Societies (CRCS) in case of multi-state co-operative banks and by the RBI. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The banking related functions such as issue of license to start new banks/branches, matters relating to interest rates, loan policies, investments and prudential exposure norms are regulated and supervised by the Reserve Bank under the provisions of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 after an amendment in 1966. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- The Reserve Bank of India came out with draft guidelines allowing primary UCBs to augment capital through issuance of equity shares, preference shares and debt instruments.
- The UCBs could raise share capital by issue of equity to persons within their area of operation enrolled as members and also through additional equity shares to the existing members. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q.“In the villages itself no form of credit organization will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All India Rural Credit Survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agricultural fi nance in India. What constraints and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural fi nance face? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients? (2014)