Primary Agricultural Credit Societies | 10 Jun 2023
For Prelims: Primary Agricultural Credit Societies, Sahkar Se Samridhi, Cooperatives, Fertilizers, Atmanirbhar Bharat.
For Mains: Primary Agricultural Credit Societies.
Why in News?
In the direction of realizing the Prime Minister’s vision of “Sahkar Se Samridhi”, the Government has taken five new decisions to increase the income of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), as well as increase the employment opportunities in rural areas.
- Government aims to achieve overall prosperity in the country through the mantra of “Sahkar Se Samriddhi”. It was proposed to strengthen Cooperatives by bringing transparency, modernization, and creating competitiveness.
What are the New Five Decisions?
- PACS which are not functioning as fertilizer retailers will be identified and they will be encouraged to function as retailers on the basis of feasibility in a phased manner.
- PACS which are not currently functioning as Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samridhi Kendras (PMKSK) will be brought under the ambit of PMKSK.
- The Prime Minister inaugurated 600 PMKSK in 2022 under the Ministry of Chemicals & Fertilisers.
- PMKSK will cater to a wide variety of needs of the farmers and provide agri-inputs, testing facilities for soil, seeds, and fertilisers.
- PACS will be connected with the marketing of organic Fertilizers, especially Fermented Organic Manure (FoM) / Liquid Fermented Organic Manure (LFOM) / Phosphate Enriched Organic Manure (PROM).
- Under the Market Development Assistance (MDA) scheme of Department of Fertilizers, fertilizer companies will act as an aggregator for small bio-organic producers to market the end product, in this supply and marketing chain of bio-organic fertilizers PACS will also be included as wholesalers/retailers.
- PACS can also be employed as Drone entrepreneurs for spraying fertilizers and pesticides. Drones can also be used for survey of property.
What are Primary Agricultural Credit Societies?
- About:
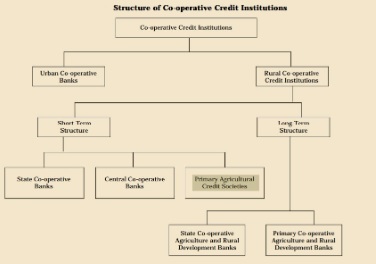
- PACS are village level cooperative credit societies that serve as the last link in a three-tier cooperative credit structure headed by the State Cooperative Banks (SCB) at the state level.
- Credit from the SCBs is transferred to the District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs), which operate at the district level. The DCCBs work with PACS, which deal directly with farmers.
- PACSs provide short-term, and medium-term agricultural loans to the farmers for the various agricultural and farming activities.
- The first PACS was formed in 1904.
- PACS are village level cooperative credit societies that serve as the last link in a three-tier cooperative credit structure headed by the State Cooperative Banks (SCB) at the state level.
- Status:
- A report published by the Reserve Bank of India on December 27, 2022 put the number of PACS at 1.02 lakh. At the end of March 2021, only 47,297 of them were in profit.
- Significance:
- Access to Credit:
- They provide small farmers with access to credit, which they can use to purchase seeds, fertilizers, and other inputs for their farms. This helps them to improve their production and increase their income.
- Financial Inclusion:
- PACS help to increase financial inclusion in rural areas, where access to formal financial services is limited. They provide basic banking services, such as savings and loan accounts, to farmers who may not have access to formal banking services.
- Convenient Services:
- PACS are often located in rural areas, which makes it convenient for farmers to access their services. PACS have the capacity to extend credit with minimal paperwork within a short time.
- Promoting Savings Culture:
- PACS encourage farmers to save money, which can be used to improve their livelihoods and invest in their farms.
- Enhancing Credit Discipline:
- PACS promote credit discipline among farmers by requiring them to repay their loans on time. This helps to reduce the risk of default, which can be a major challenge in the rural financial sector.
- Access to Credit:
What are the Issues with the PACS?
- Inadequate Coverage:
- Though geographically active PACS cover about 90% of 5.8 villages, there are parts of the country, especially in the north-east, where this coverage is very low.
- Further, the rural population covered as members is only 50% of all the rural households.
- Inadequate Resources:
- The resources of the PACS are much too inadequate in relation to the short-and medium-term credit needs of the rural economy.
- The bulk of even these inadequate funds come from higher financing agencies and not through owned funds of societies or deposit mobilization by them.
- Overdues and NPAs:
- Large over-dues have become a big problem for the PACS.
- As per the RBI report in 2022, PACS had reported lending worth Rs 1,43,044 crore and NPAs of Rs 72,550 crore. Maharashtra has 20,897 PACS of which 11,326 are in losses.
- They curb the circulation of loanable funds, reduce the borrowing as well as lending power of societies, and give them the bad image that the societies of defaulting debtors are willful.
- Large over-dues have become a big problem for the PACS.
Way Forward
- PACS are important institutions in India's rural financial sector and can contribute significantly to the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat (self-reliant India) and the Vocal for Local campaign. These century-old institutions can serve as the foundation for a self-reliant village economy.
- To maximize their potential, PACS need to be made more efficient, financially sustainable, and accessible to farmers. This requires improvements in their operations and management.
- Additionally, the regulatory framework governing PACS must be strengthened to ensure effective governance and the ability to meet the needs of farmers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- In terms of short-term credit delivery to the agriculture sector, District Central Cooperative Banks (DCCBs) deliver more credit in comparison to Scheduled Commercial Banks and Regional Rural Banks.
- One of the most important functions of DCCBs is to provide funds to the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q2. With reference to ‘Urban Cooperative Banks’ in India, consider the following statements: (2021)
- They are supervised and regulated by local boards set up by the State Governments.
- They can issue equity shares and preference shares.
- They were brought under the purview of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 through an Amendment in 1966.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q.“In the villages itself no form of credit organization will be suitable except the cooperative society.” – All India Rural Credit Survey. Discuss this statement in the background of agricultural fi nance in India. What constraints and challenges do financial institutions supplying agricultural fi nance face? How can technology be used to better reach and serve rural clients? (2014)