Science & Technology
Need for Local Data Centres
- 12 Apr 2025
- 10 min read
For Prelims: Digital Data, Data Centre, GDPR, DPDP Act, 2023, E-commerce, Fintech, Cloud Computing, IoT, Generative AI, 5G, Cybersecurity.
For Mains: Need for local data centres, opportunities and challenges in setting up local data centers.
Why in News?
India contributes around 20% of the world’s digital data but holds less than 2% of global data centre capacity in India, highlighting a major infrastructure gap to fully utilise available data.
- Underutilizing available data goes against the idea that "data is the new oil," which highlights its growing importance in today’s economy.
What are Data Centers?
- About: A data center is a physical facility that organizations use to house their critical applications and data.
- Its key components include routers, switches, firewalls, storage systems, servers, and application-delivery controllers.
- Types:
- Enterprise (On-Premises): Owned & managed by a single company for full control (e.g., banks, healthcare for compliance).
- Public Cloud (Hyperscale): Run by cloud service providers (CSPs) (e.g., Azure, IBM Cloud) for shared, scalable resources.
- Colocation Facilities: Companies rent space but own their hardware; providers manage power/cooling.
- Edge Data Centers: Smaller, decentralized facilities closer to users to reduce latency (critical for AI, IoT).
- Core Components:
- Network Infrastructure: This connects servers (physical and virtualized), data center services, storage, and external connectivity to end-user locations.
- Storage Infrastructure: Storage systems are used to hold data that acts as fuels of the data center.
- Computing Resources: It provides the processing, memory, local storage, and network connectivity that drive applications.
- Key Benefits:
Why is Data Called the New Oil?
- Fuel for Modern Economy: Like oil in the 20th century, data now powers modern business, with firms like Google, Amazon, and Foursquare built on user data.
- Businesses turn data into value by predicting trends, improving operations, and personalizing services like refining oil into high-value products.
- Data as Strategic Resource: Nations now treat data as a geopolitical resource, regulating its flow (e.g., GDPR, India’s DPDP Act, 2023).
- Foundation of Digital Economy: Powers e-commerce, fintech, cloud computing, and IoT (smart devices, connected cars).
Why Are Local Data Centres Crucial for India?
- India's Digital Footprint: India tops global digital data generation, with the highest number of users on Facebook (450 million), WhatsApp (540M), YouTube (490M), and Instagram (360M) requiring facilities to their data locally.
- Economic Growth: India could attract USD 400 billion in investments by expanding data centres to match its data growth target of 40 GW by 2030.
- It can boost e-commerce, fintech, AI, and cloud computing, key sectors for achieving India’s USD 5 trillion economy goal.
- Job Creation: Data centers can create 1–2 million direct jobs and 3 times more indirect jobs in construction, logistics, and tech services.
- Data Sovereignty: Local data centres ensure sensitive data (financial, health, citizen records) stays within India, complying with the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- Prevents external control over critical data flows, enhancing national security.
- AI & Digital Leadership: Generative AI could add USD 2.6–4.4 trillion/year globally.
- Companies like AWS, Google, and Microsoft are growing their data centers in India positioning the country as a future AI hub.
- Competitive Advantage: While nations like China (rare earth minerals), Australia (iron ore), and Chile (copper) leverage their natural strengths, India generates 20% of global data yet holds less than 2% of the world’s data centre capacity.
- Local data centers can provide global data processing and cloud services, similar to India’s IT services success.
- Infrastructure Boost: India’s data center growth will create demand for 800 million sq ft of construction, boosting real estate, renewable energy, and telecom infrastructure.
What is the Current Status of Data Centres in India?Click Here to Read: Current Status of Data Centres in India What are the Key Reasons for Growth of Data Centres in India?Click Here to Read: Reasons for Growth of Data Centres in India |
What are Key Concerns Related to Local Data Centers in India?
- High Capital Investment: Building 40 GW of data center capacity by 2030 needs USD 400 billion, but long payback periods of 10–15 years may deter private investment.
- Trade & Economic Risks:
- Reciprocal Trade Barriers: If India forces foreign firms to store data locally, other countries may impose similar restrictions on Indian IT firms (e.g., TCS, Infosys).
- Higher Costs for Consumers: Compliance costs may lead to increased prices for cloud services, streaming, and digital products.
- Reduced Competition: Smaller tech firms may exit India due to compliance burdens, leaving only giants (Google, AWS) with resources to adapt.
- WTO & Legal Disputes: Could be seen as a protectionist policy, inviting trade complaints.
- Operational Challenges:
- Unreliable Power Supply: Frequent power outages require expensive backup systems (diesel generators, batteries).
- Cooling Requirements: India’s hot climate increases energy needs for cooling, raising costs.
- Limited Undersea Cables: Most international data flows via foreign-owned cables (e.g., controlled by US/China), creating dependency.
- Sustainability Concerns:
- Energy-Intensive: Data centres used 1.5% of global electricity in 2024 and may reach 3% by 2030. India’s coal-dependent grid raises carbon footprint concerns.
- Water Usage for Cooling: It conflicts with agricultural and drinking water needs in drought-prone regions.
- Cyber Risks: Large data centers become high-value targets for cyberattacks or physical sabotage.
How India Can Promote Data Center Growth?
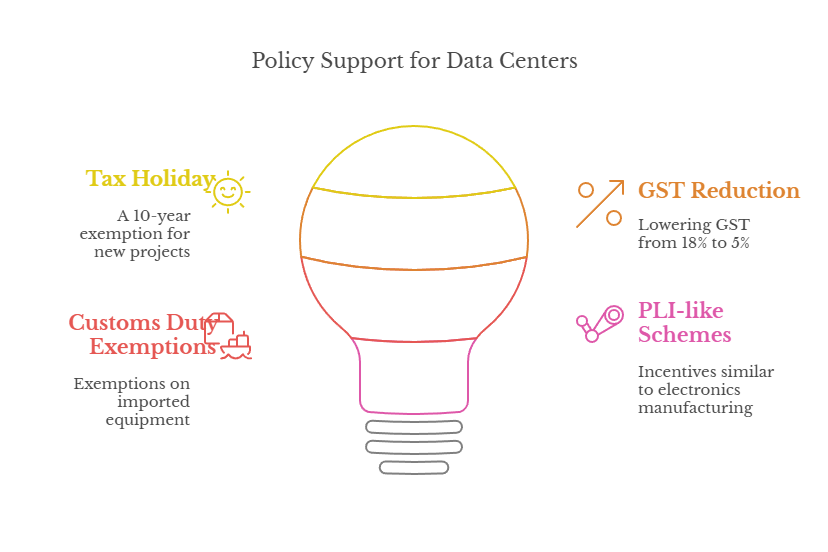
- Policy Support: Support measures for data centers could include:
- Flexibility in Data Localization: Encourage, not mandate, localization via incentives (e.g., tax breaks for firms storing data in India).
- Infrastructure Development: Provide subsidized electricity tariffs (like China’s ultra-low rates) and allow direct power procurement from DISCOMs or renewable sources such as solar and wind.
- Mandate green data centers with incentives for liquid cooling & energy-efficient designs.
- Connectivity & Fiber Networks: Expand undersea cable stations, build a National Fiber Corridor, and develop 5G-ready infrastructure for edge data centers.
- Land & Real Estate: Set up dedicated data center zones in cooler cities (Shimla, Dehradun, Chandigarh) to reduce cooling costs and use PPP models for land allocation near industrial hubs.
- Skill Development & R&D: Promote skill development and innovation through a National Data Center Academy for training in AI, cloud, and cybersecurity, along with R&D grants for indigenous server and cooling technologies.
Conclusion
Despite contributing 20% of global digital data, India lacks adequate data center capacity, limiting its digital potential. Bridging this gap is essential for economic growth, job creation, data sovereignty, and global AI leadership. Strategic investments, policy support, and sustainable infrastructure are critical for realizing India’s digital aspirations.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss how data centre development in India can contribute to achieving the USD 5 trillion economy target. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)