Rapid Fire
Municipal Bonds
- 24 Mar 2025
- 2 min read
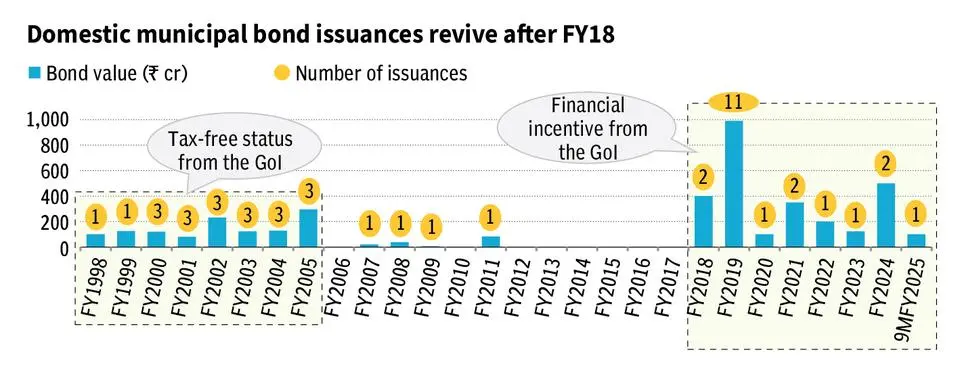
Municipal bonds, an important source of funding for urban infrastructure, have not gained much popularity in India.
- Bonds are debt instruments where investors lend money to issuers in exchange for periodic interest and principal repayment at maturity.
- It includes Treasury, Municipal, Corporate, Floating Rate, Zero-Coupon, Convertible, Inflation-Protected Bonds etc.
Municipal Bonds: Debt instruments issued by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) to fund infrastructure and development projects.
- Advantages: Reduce reliance on government funds, enhance financial autonomy, attract private investment, and enable long-term urban financing.
- Challenges: Low issuance due to heavy dependence on state grants (38% of revenue in FY 24). Only a few cities like Pune, Ahmedabad, Surat, Hyderabad, and Lucknow have issued bonds.
- Spending Pattern (FY18-FY25): Most funds raised by municipalities through bonds were allocated to urban water supply and sewerage, followed by renewable energy and river development.
- Strengthening ULB finances, simplifying regulations, and introducing credit enhancement measures can boost municipal bond adoption and developing a secondary market and offering tax incentives will attract investors.
| Read More: Urban Local Government in India, Bond Yield |