Indian Economy
Microfinance Sector in India
- 20 Feb 2025
- 7 min read
For Prelims: Microfinance Institutions (MFIs), Financial Inclusion, SHGs, Co-operative Societies, Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), Companies Act, 2013, NBFC-MFIs, Reserve Bank of India
For Mains: Significance of microfinance institutions in financial inclusion, poverty alleviation, and sustainable economic development in India.
Why in News?
The microfinance sector in India has played a pivotal role in financial inclusion by providing credit to underserved households. However, rising concerns over credit expansion underscore the need for stronger regulations and responsible lending.
What are Microfinance Institutions (MFI)?
- About:
- MFIs are financial companies that provide small loans and other financial services to people who don't have access to banking facilities.
- Objective:
- It aims to empower low-income and unemployed individuals by fostering self-sufficiency.
- It plays a crucial role in financial inclusion, particularly benefiting marginalized groups, including women, by promoting social equity and economic empowerment.
- Regulatory Framework: The RBI regulates MFIs under the NBFC-MFI framework (2014), which covers client protection, borrower safeguards, privacy, and credit pricing.
- Business Models in Microfinance: Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)
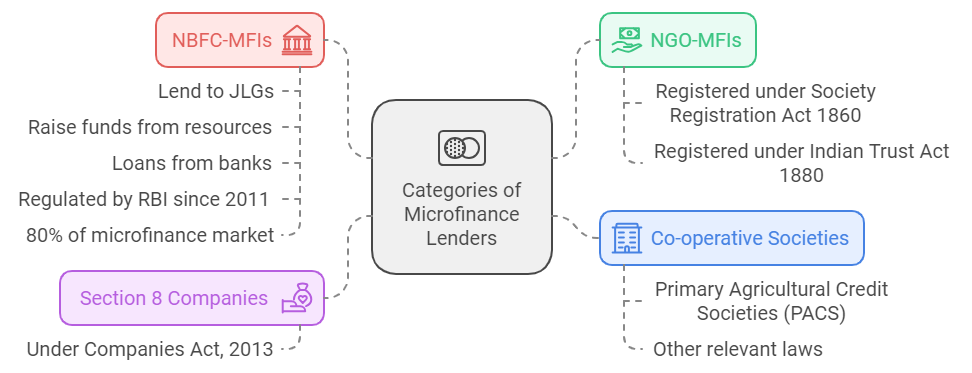
- Categories of Microfinance Lenders:
- MFIs in India:
- As of 31st March 2024, India's microfinance sector comprises 168 MFIs across 29 states, 4 UTs, and 563 districts, serving over 3 crore clients with a loan portfolio of Rs 4.33 lakh crore.
What are the Challenges for Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)?
- Profitability and Economic Sustainability: MFIs rely on subsidies, face high operating costs, and limited capital access. Most MFIs cover costs but only a third are truly profitable after capital expenses.
- To cover costs, they charge high interest rates, which can burden borrowers.
- Regulatory Gaps: The RBI framework mandates household income and liability assessments, but lack of documentary proof and delayed credit bureau data hinder accurate evaluation, especially by unregulated lenders.
- Rising Competition: More regulated and unregulated players in the sector have increased credit supply, sometimes without stringent due diligence.
- Poor Model Selection: MFIs in India mainly use the SHG or JLG lending models whose effectiveness is often questioned and also their selection is often random rather than scientific reasoning.
- The choice of the lending model impacts the repayment burden on weaker sections and affects the long-term sustainability of MFIs.
- Gender Bias: Women face significant barriers in accessing financial services and are 15-20% less likely than men to have a bank account or access formal credit.
- However, studies indicate that women have a 17% higher loan repayment rate compared to men.
RBI Guidelines on Microfinance Lending (2022)
- Microfinance loans are collateral-free for households with annual incomes up to Rs 3 lakh.
- Lenders must ensure flexible repayment policies and assess household income.
- The cap on the number of lenders per borrower is removed, but loan repayments cannot exceed 50% of monthly income.
- The requirement for NBFC-MFIs to maintain 75% of their loan portfolio in microfinance (reduced from 85%).
- Entities must report income discrepancies and household income details.
- No prepayment penalties; late fees apply only to overdue amounts.
What are the Government Schemes Related to Microfinance?
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
- Self-Help Group (SHG) - Bank Linkage Program
- Credit Guarantee Fund for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)
What are the Proposed Reforms for Sustainable Growth of the Microfinance Sector in India?
- Strengthening Credit Assessment: Establish a standardized household income evaluation model and enhance real-time liability tracking by increasing credit bureau data uploads from fortnightly to weekly.
- Enhancing Borrower Identification: Mandate Aadhaar-based KYC for MFIs to prevent credit duplication and ensure accurate liability assessment.
- Expand credit bureau participation to include all institutional lenders (both regulated and unregulated) for greater transparency.
- Adopt Need-based Lending Models: MFIs should choose lending models based on borrower needs rather than relying only on SHG or JLG.
- MFIs should expand beyond credit to include savings, insurance, and micro-investments, ensuring broader financial inclusion and reduced credit dependency.
- Gender-Inclusive Financing: Promote gender-inclusive financial policies by improving women's access to banking and credit.
- Robust Impact Assessment: Conduct comprehensive and unbiased evaluations of microfinance interventions to accurately measure their effectiveness in poverty alleviation and ensure data-driven policy improvements.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the key challenges for microfinance institutions in India, and how can they be mitigated? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Microfinance is the provision of financial services to people of low-income groups. This includes both the consumers and the self-employed. The service/ services rendered under microfinance is/are (2011)
- Credit facilities
- Savings facilities
- Insurance facilities
- Fund Transfer facilities
Select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. Can the vicious cycle of gender inequality, poverty and malnutrition be broken through microfinancing of women SHGs? Explain with examples. (2021)