Microfinance Institutions | 26 Oct 2024
For Prelims: Microfinance Institutions (MFIs), Financial Inclusion, SHGs, Co-operative Societies Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), Companies Act, 2013, NBFC-MFIs, Reserve Bank of India(RBI)
For Mains: Significance of microfinance institutions in financial inclusion, poverty alleviation, and sustainable economic development in India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Financial Services Secretary, while highlighting the crucial role of microfinance institutions (MFIs) in fostering financial inclusion, emphasised that they must avoid reckless lending despite their role in promoting financial inclusion.
Note:
- Many MFIs are under scrutiny for excessive interest rates (averaging around 24% per annum) and high processing fees, with findings of non-compliance in assessing borrowers' income and repayment capacities. A report by Sa-Dhan indicates minor interest rate reductions won’t significantly impact repayment amounts for low-income households.
What are Microfinance Institutions?
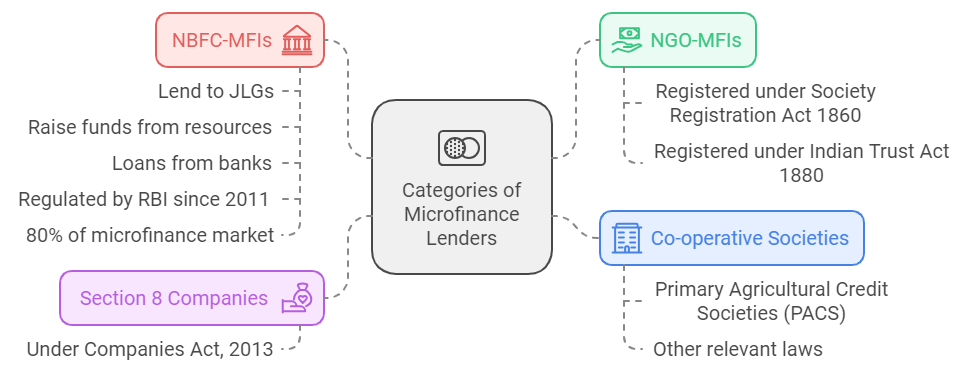
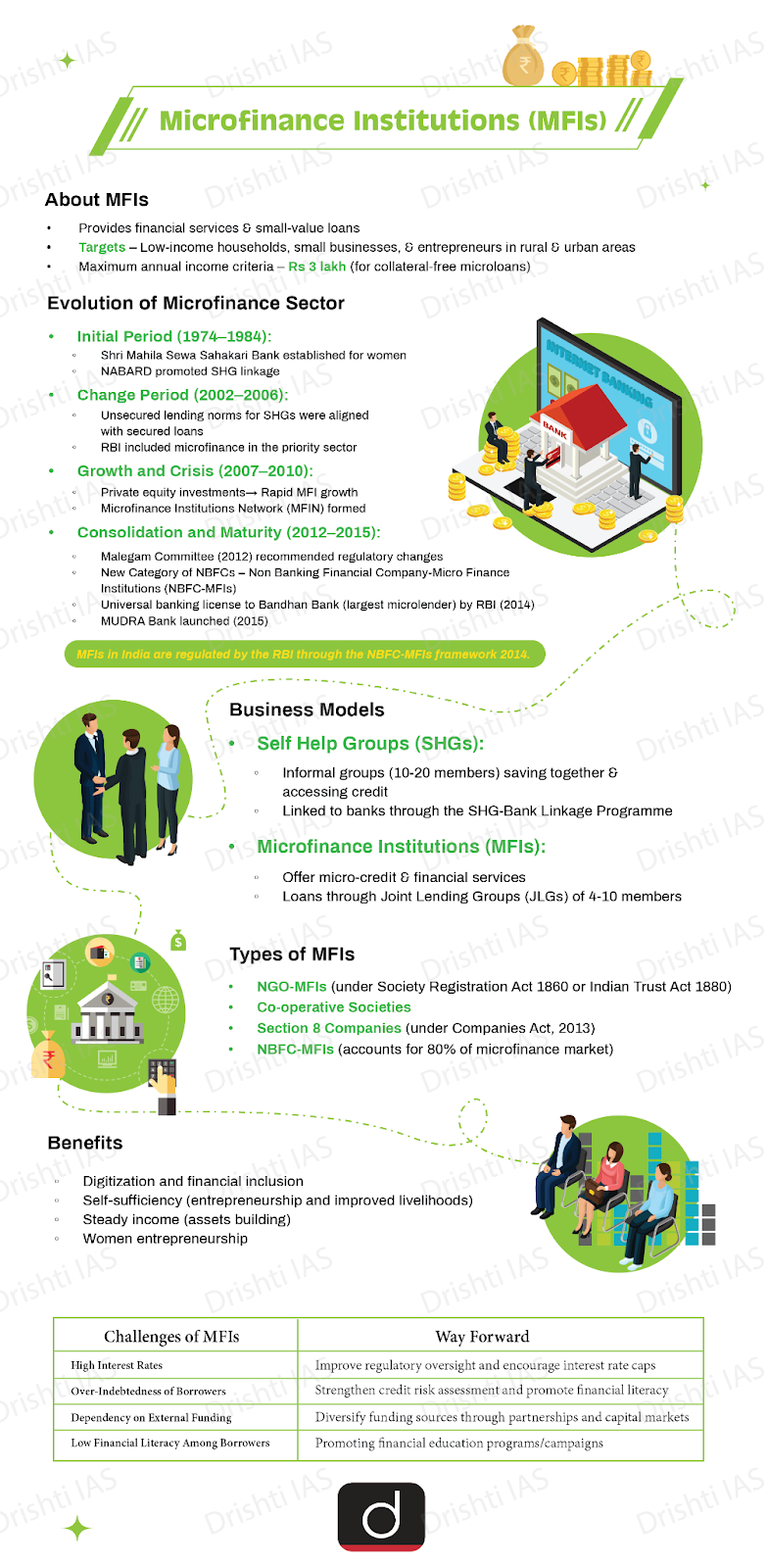
- About: MFIs are financial companies that provide small loans and other financial services to people who don't have access to banking facilities.
- The goal of microfinance is to help low-income and unemployed people become self-sufficient.
- It serves as a powerful tool for financial inclusion, helping marginalised and low-income groups, especially women, to achieve social equity and empowerment.
- Regulatory Framework:
- The RBI regulates MFIs under the NBFC-MFI framework (2014), which covers client protection, borrower safeguards, privacy, and credit pricing.
- Status of MFIs:
- In India, the microfinance sector has grown significantly, with 168 Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) operating across 29 States, 4 Union Territories, and 563 districts.
- These institutions serve over 3 crore clients.
- Business Models Under Microfinance:
- Self-Help Groups (SHGs): SHGs are informal groups of 10-20 members specially women who save collectively to access bank loans through the SHG-Bank Linkage Programme.
- MFIs: MFIs provide microcredit and other financial services like savings, insurance, and remittances.
- Loans are typically offered through Joint Lending Groups (JLGs), informal groups of 4-10 individuals involved in similar activities who jointly repay the loans.
- Categories of Microfinance Lenders:
What are Challenges for Microfinance Institutions (MFIs)?
- Regulatory Action: The RBI has banned certain Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) from issuing loans due to exorbitant interest rates, affecting their operations and growth potential.
- The RBI has directed MFIs to reevaluate lending practices and emphasize affordability in credit offerings.
- Low Financial Literacy: Many borrowers lack the necessary financial literacy to understand loan terms, increasing the risk of defaults and perpetuating poverty cycles.
- Over-Indebtedness of Borrowers: Borrowers often take loans from multiple MFIs, leading to unsustainable debt.
- The RBI noted over 12% of microfinance clients had four or more active loans as of March 2024, reaching 18% in some states, risking defaults and damaging MFIs' reputations.
- Dependency on External Funding: MFIs frequently rely on external funding from banks and investors, creating vulnerabilities during economic downturns.
RBI Guideline Related to Microfinance Lending (2022)
- Microfinance loans are collateral-free for households with incomes up to Rs 3 lakh.
- Entities must have policies for flexible repayment and household income assessment.
- The cap on lenders per borrower is removed; repayments cannot exceed 50% of monthly income.
- 75% of NBFC-MFI loans must qualify as microfinance (down from 85%).
- Entities must report income discrepancies and household income.
- No pre-payment penalties on microfinance loans; late fees apply only to overdue amounts.
What are the Government Schemes Related to Microfinance?
Way Forward
- MFIs must prioritise responsible lending practices to avoid excessive interest rates and assess borrowers' repayment capacities, reducing the risks of over-indebtedness.
- Enhancing financial literacy among borrowers is crucial to empower them to make informed decisions, thereby lowering default risks.
- Implementing Malegam Committee(2010) Recommendations such as capping interest rates, creating a category for NBFC-MFIs, tracking multiple loans to prevent over-indebtedness, and enhancing transparency.
- Establishing a grievance redressal mechanism, and formulating a code of conduct for ethical lending.
- Strict adherence to regulatory frameworks set by the RBI will enhance trust and improve the sector's reputation.
- Additionally, diversifying funding sources can reduce dependency on external capital, while robust support systems—including advisory services—can assist borrowers in managing their loans effectively.
|
Drishti Mains Question What are the challenges faced by microfinance institutions in India, and how can these be addressed? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Microfinance is the provision of financial services to people of low-income groups. This includes both the consumers and the self-employed. The service/ services rendered under microfinance is/are (2011)
- Credit facilities
- Savings facilities
- Insurance facilities
- Fund Transfer facilities
Select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. Can the vicious cycle of gender inequality, poverty and malnutrition be broken through microfinancing of women SHGs? Explain with examples. (2021)