Mental Health at Workplace and Economic Productivity | 06 Feb 2025
For Prelims: Economic Survey 2025, World Health Organization (WHO), Annual Survey of Industries (ASI)
For Mains: Impact of informal Work on Mental Health, Impacts of Poor Mental Health, Steps Taken by the Government, steps that can be taken to Improve Mental Health
Why in News?
The Economic Survey 2025 highlighted the significant impact of workplace culture, working hours, and lifestyle on mental health and worker productivity.
- It stressed the urgent need for improved workplace conditions and healthier lifestyles to boost employee well-being, which in turn, can enhance economic growth.
What are the Key Factors Affecting Mental Health?
- Workplace Culture: A positive workplace culture boosts mental well-being. The survey finds that employees with good relationships with managers and colleagues report 33% higher mental well-being scores.
- A sense of purpose at work further enhances well-being.
- Workload Management: Excessive workloads negatively impact mental health. Employees with manageable workloads report 27% greater mental well-being than those overwhelmed by work.
- Long working hours (55-60 per week) increase stress and anxiety.
- Impact of Remote Work: While remote work offers flexibility, fully remote employees report 17% lower mental well-being scores than those in-office or in hybrid models.
- Social interaction at work is crucial for mental health.
- Lifestyle Choices and Mental Well-being:
- Dietary Choices: Individuals who avoid ultra-processed and packaged foods report better mental well-being.
- Physical Activity: Lack of exercise is linked to higher stress levels and lower productivity.
- Social Media Usage: Excessive social media consumption is correlated with declining mental health.
- Family Ties: Strong family relationships contribute significantly to better mental well-being.
Increase in Self-Employed Workers as per Economic Survey 2024-25
- Rise in Self-Employment: The proportion of self-employed workers increased from 52.2% (2017-18) to 58.4% (2023-24).
- Sectoral Trends: Agriculture remains dominant in employment, rising from 44.1% to 46.1% during the same period.
- Decline in Regular Jobs: The share of salaried employment fell from 22.8% in 2017-18 to 21.7% in 2023-24.
- Casual employment also declined from 24.9% to 19.8%, indicating a shift toward structured self-employment.
- Unemployment Reduction: The unemployment rate (15+ age group) declined from 6% (2017-18) to 3.2% (2023-24).
- Formal Sector Growth: Net additions to EPFO subscriptions more than doubled, rising from 61 lakh (2018-19) to 1.31 crore (2023-24), with 61% of new payroll additions from youth (<29 years).
What are the Key Implications of Poor Mental Health on the Economy?
- Lost Productivity: Mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety contribute to reduced work efficiency, absenteeism, and presenteeism (working while unwell).
- As per WHO, globally, depression and anxiety lead to a loss of 12 billion work days annually, amounting to an economic cost of nearly USD 1 trillion.
- In India, this translates to a loss of approximately Rs 7,000 per affected worker per day.
- As per WHO, globally, depression and anxiety lead to a loss of 12 billion work days annually, amounting to an economic cost of nearly USD 1 trillion.
- Absenteeism and Turnover: Mental health conditions can result in higher rates of sick days, early departures, and increased job turnover, further disrupting workflow and incurring costs associated with recruitment and training replacements.
- Economic Survey 2024-25 noted that individuals with poor mental well-being lose about 15 working days per month, compared to 2-3 days for healthier individuals.
- Increased Healthcare Expenditure: Poor mental health leads to higher healthcare costs due to frequent medical visits, hospitalizations, and long-term treatment, increasing the burden on public health infrastructure, diverting resources from other critical areas.
- Decline in Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Poor mental health hampers creativity, risk-taking, and decision-making, slowing technological and business advancements, especially in high-performance sectors facing stress and burnout.
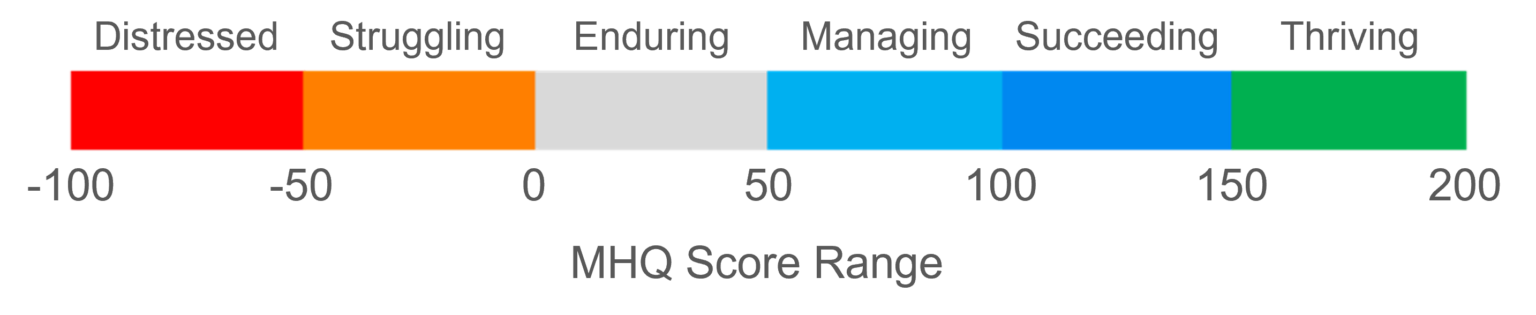
Mental Health Quotient (MHQ)
- MHQ is a standardized measure assessing mental well-being and cognitive functioning.
- The evaluation is based on self-reported responses to a standardized questionnaire, assessing mental well-being across key domains like emotional resilience, cognitive function, social well-being, and risk factors.
- The MHQ score ranges from -100 to +200, assessing overall mental well-being. Higher scores indicate better mental health
What are Suggestions Provided by Economic Survey 2024-25?
- Workplace Reforms: Foster a supportive work culture by improving interpersonal relationships, reducing workplace stress, and promoting a sense of purpose.
- Implement work-hour regulations to prevent burnout and enhance productivity.
- Flexible Work Models: Encourage hybrid work policies to balance flexibility and social interaction, mitigating the negative effects of full remote work.
- Health and Lifestyle Interventions: Employers and the government should promote healthy eating, physical activity, and digital detox to improve mental well-being.
- Awareness and Mental Health Programs: Implement large-scale mental health awareness initiatives, counseling services, and employee assistance programs to support workplace well-being.
- Policy and Legislative Measures: Strengthen occupational health policies by integrating mental health considerations into labor laws, ensuring workplaces adopt mental health-friendly practices.
Conclusion
The Economic Survey 2024-25 highlights mental well-being as a national priority. A healthy workforce is key to productivity, resilience, and economic growth. Prioritizing workplace mental health through supportive policies will strengthen India’s path to becoming a global economic powerhouse.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. In order to enhance the prospects of social development, sound and adequate health care policies are needed particularly in the fields of geriatric and maternal health care. Discuss.(2020)
Q. Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieve ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. (2018)