Important Facts For Prelims
Megalithic Site in Kerala
- 20 Sep 2024
- 4 min read
Why in News?
Recently, a rainwater harvesting project in Kerala led to the discovery of a large number of megalithic urn burials.
- These findings were unearthed on Kundlikkad hill (also known as Malampalla or Malappuram hill) in the Nenmara forest division.
- An urn burial is a type of burial where the remains of a deceased person are placed in a pottery vessel, or urn, and buried.
What are the Key Facts about the Discovery of Megalithic Urn Burials?
- Classic Urn Burials: Typically, hilltop burial sites feature cairn heaps with cists, cairn circles, and stone circles burials.
- The presence of these urn burials, which date back over 2,500 years, is rare for a hilltop site.
- Urn Characteristics: The region contained pot sherds from different types of pottery, including black ware, red ware, and black and red ware.
- A notable find includes an urn with fingertip impressions, and smaller pots featured cord-impressed designs, indicating distinct decorative techniques used in pottery.
- Chisel marks were found on rocks across the hill, indicating that circling boulders were crafted using chisels.
- This suggests a more organised approach to burial construction in the area.
- Importance of the Discovery: It offers significant insights into the links between the Mesolithic because of the presence of microliths from the site and Iron Age periods in Kerala.
- Archaeologists say that such combination of mesolithic and iron age remains is unusual.
What is Megalithic Culture?
- About Megalith: Megaliths refer to monuments made from large stones. In most cases, megaliths are burial sites located away from habitation areas.
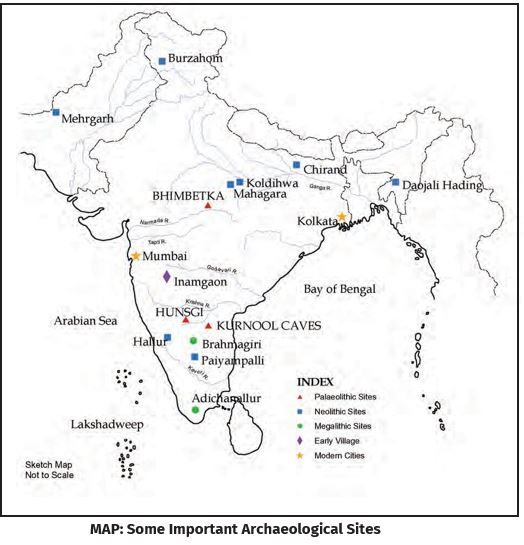
- Chronology of Megaliths: Based on the Brahmagiri excavation, megalithic cultures in South India are dated to between the 3rd century B.C. and 1st century A.D.
- Geographical Distribution of Megaliths in India: The main concentration of megalithic culture is in Deccan, especially south of the Godavari River.
- It has been found across Punjab Plains, Indo-Gangetic basin, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Burzahom in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Important sites include Seraikala (Bihar), Khera (Uttar Pradesh), Deosa (Rajasthan) etc.
- Use of Iron in South India: The Megalithic period in South India was a full-fledged Iron Age culture, where the benefits of iron technology were fully realised.
- Iron objects such as weapons and agricultural implements were found from Junapani in Vidarbha to Adichanallur in Tamil Nadu.
- Subsistence Pattern: They lived on a combination of agriculture, hunting, fishing, and animal husbandry.
- Rock Paintings: Rock paintings found at megalithic sites depict scenes of hunting, cattle raids, and group dancing.
Note:
- Mesolithic period (middle stone) began about 12,000 years ago till about 10,000 years ago. Stone tools found during this period are generally tiny, and are called microliths.
- Microliths were probably stuck on to handles of bone or wood to make tools such as saws and sickles.





-min.jpg)