Lightning | 26 Apr 2025
Why in News?
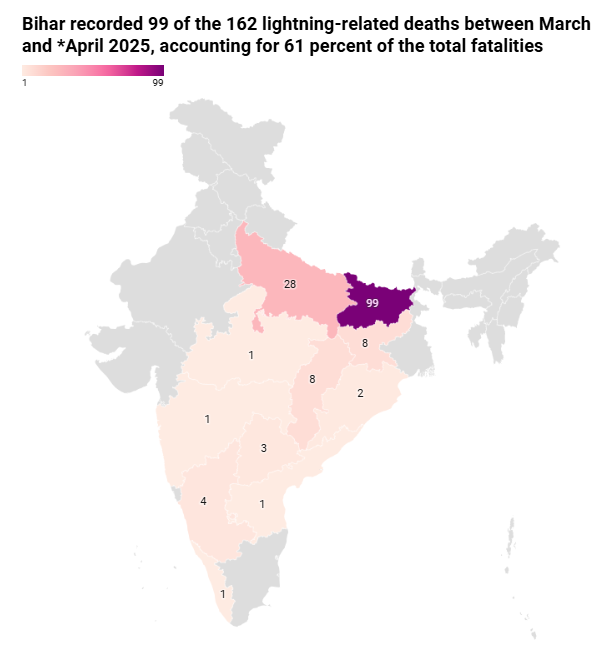
India witnessed a 184% surge in lightning deaths during March-April 2025 across 12 states compared to the same period in 2024, making it the deadliest lightning spell since 2022, according to the Centre for Science and Environment.
What is Lightning?
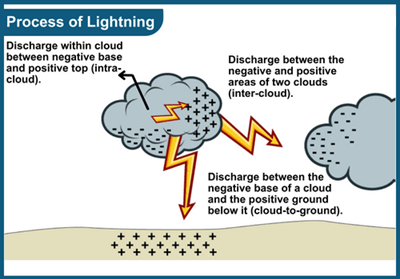
- About: Lightning is a giant spark of electricity that occurs in the atmosphere. It is a rapid discharge of electrical energy that can occur within a cloud (intra-cloud), between different clouds (cloud-to-cloud), or between a cloud and the ground (cloud-to-ground).
- Formation: In the early stages of a thunderstorm, positive and negative charges build up in different parts of the cloud, with air acting as an insulator between them.
- When the electrical potential becomes strong enough, the air’s insulating capacity breaks down, resulting in a sudden flow of electricity leading to lightning.
- Thunder: It is caused when lightning passes through the air, rapidly heating it to temperatures as high as 50,000 degrees Fahrenheit (which is five times hotter than the surface of the sun), causing it to expand and create a shockwave. This shockwave results in the sound of thunder.
- Lightning Rod: Also known as a lightning conductor, a lightning rod is a metal rod installed on a structure to divert lightning strikes safely into the ground, preventing damage and harm.
- Deaths Due Lightning: National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB)’s Crimes in India Report, 2022 reveals that lightning caused a significant portion of deaths attributed to natural disasters, accounting for 35.8%, surpassing deaths from torrential rains and landslides.
- According to the Annual Lightning Report 2023-24 by the Climate Resilient Observing Systems Promotion Council (CROPC), Madhya Pradesh and Bihar ranked top nationally in lightning-related deaths between 2014 and 2024.
What are the Causes for Rise in Lightning?
- Unstable Weather Conditions: Lightning outbreaks are linked to unstable weather conditions caused by humid easterly winds moving from the Bay of Bengal towards the Himalayan foothills.
- These winds meet western disturbances and the jet stream, intensifying convective activity, which creates ideal conditions for thunderstorms and lightning.
- Pollution and Aerosols: Air pollution, including aerosols and particulate matter, can impact cloud formation and electrical activity in storms.
- Anthropogenic emissions may increase the frequency and intensity of thunderstorms, potentially leading to more lightning strikes.
- Urbanization: It creates the "urban heat island effect," where cities are warmer than surrounding areas due to increased human activity, energy consumption, and impervious surfaces.
- This localized heat can lead to more thunderstorms and, consequently, more lightning strikes.
India’s Key Initiatives Related to Lightning
- Disaster Mitigation Projects: In 2015, a high-level committee, has approved Rs 3,027 crore for disaster mitigation projects, focusing on lightning safety in 50 lightning-prone districts and drought risk mitigation in 49 drought-prone districts, funded by the National Disaster Mitigation Fund (NDMF).
- Lightning Warning System: Indian Meteorological Department has developed a Lightning Warning System since 2018, offering location-specific forecasts for up to 48 hours. The Damini App provides real-time lightning information.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. During a thunderstorm, the thunder in the skies is produced by the (2013)
- meeting of cumulonimbus clouds in the sky
- lightning that separates the nimbus clouds
- violent upward movement of air and water particles
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) None of the above produces the thunder
Ans: (d)
- Thunder is the sound produced by the rapid expansion of air, when it is heated by a lightning bolt.
- The air expands so quickly that it makes a loud sound called thunder.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.