Invasive Species in Gulf of Mannar Islands | 08 Apr 2023
Why in News?
A recent study has revealed that the native vegetation and biodiversity in the Gulf of Mannar are under threat from an alien invasive plant, Prosopis chilensis.
- In addition, the coral reef has been destroyed in several places despite being outlawed for industrial purposes, and human settlements have impacted some islands.
What are Invasive Species?
- About:
- An invasive species is an organism that is not indigenous, or native, to a particular area and causes harm to the native species.
- They are capable of causing extinctions of native plants and animals, reducing biodiversity, competing with native organisms for limited resources, and altering habitats.
- They can be introduced to an area by ship ballast water, accidental release, and most often, by people.
- An invasive species is an organism that is not indigenous, or native, to a particular area and causes harm to the native species.
- About Prosopis Chilensis:
- The Chilean mesquite (Prosopis chilensis (Molina) Stuntz) is a small to medium-sized legume tree and has a shallow and spreading root system.
- It is a common ruderal weed, either growing singly or in groups
- It is found in arid and semi-arid regions with ground water of between 3 and 10 m below the surface.
- It is a drought-resistant plant native to South American countries namely Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, and Peru.
- The Chilean mesquite (Prosopis chilensis (Molina) Stuntz) is a small to medium-sized legume tree and has a shallow and spreading root system.
- International Instruments and Programmes on Invasive Species:
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
- It was one of the key agreements adopted at the 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro.
- The Rio de Janeiro Convention on Biodiversity (1992) had also recognised the biological invasion of alien species of plants as the second-worst threat to the environment after habitat destruction.
- Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species (CMS) or Bonn Convention (1979):
- It is an intergovernmental treaty that aims to conserve terrestrial, marine and avian migratory species throughout their range.
- It also aims to control or to eliminate already present invasive alien species.
- Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES):
- It is an international agreement adopted in 1975 that aims to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival.
- It also considers the problems of invasive species when it is involved in trade and threatens the survival of live animals or plants.
- Ramsar Convention (1971):
- The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of wetlands.
- It also addresses the environmental, economic and social impact of invasive species on wetlands within their jurisdictions and to take account of the methods of control and solutions for combating invasive species.
- Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD):
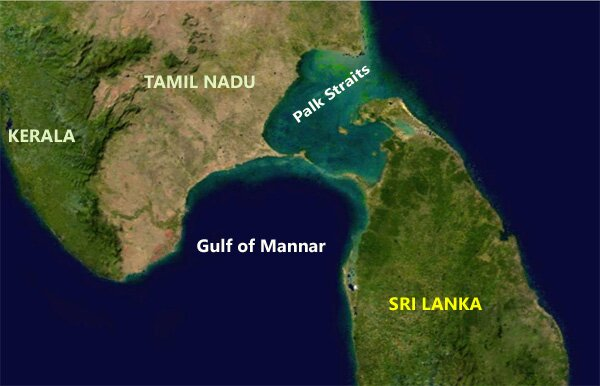
- Gulf of Mannar:
- It is an inlet of the Indian Ocean, between southeastern India and western Sri Lanka.
- It is bounded to the northeast by Rameswaram (island), Adam’s (Rama’s) Bridge (a chain of shoals), and Mannar Island.
- It receives several rivers, including the Tambraparni (India) and the Aruvi (Sri Lanka).
- The gulf is noted for its pearl banks and sacred chank (a gastropod mollusk).
- Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve (GoMBR):
- The GoMBR is home to 21 islands that serve as habitats for coastal birds migrating as far as the Arctic Circle.
- It is India’s first marine biosphere reserve.
- Most of the islands have sand dunes along their coastlines with salt-dominant plant species.
- “Corals, seagrass, and mangroves are among the three unique ecosystems present on the islands
- The GoMBR is home to 21 islands that serve as habitats for coastal birds migrating as far as the Arctic Circle.