International Marine Protected Areas Congress | 09 Feb 2023
Prelims: Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity, CCAMLR, Marine Protected Areas in India.
Mains: Marine Protected Areas.
Why in News?
Recently, the 5th International Marine Protected Areas Congress (IMPAC5) was held in Canada in order to discuss the solutions to address the Funding Gap of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs).
- This meeting is crucial since nations agreed to protect 30% of Earh’s lands and oceans by 2030 at the 15th Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity held in 2022.
Note: Canada is bordered by three oceans - the Pacific, Arctic and Atlantic - and has the longest coastline in the world.
What are the Highlights of the Meet?
- Sustainable and Resilient MPA networks:
- As many as 70% of MPAs are underfunded. A well-managed and sufficiently funded MPA can restore good health to vulnerable ecosystems.
- Achieving sustainable and resilient MPA networks depends on an overall commitment to protection, leadership, engagement from stakeholders, institutions, governments and organizations, Indigenous peoples, coastal communities, and individuals in an inclusive and equitable manner to advance ocean protection.
- IMPAC5 aims to provide a forum for sharing knowledge, successes and best practices in an open and respectful environment for the exchanging of ideas among a diversity of views.
- Significance of MPAs:
- MPAs can generate sustainable revenues for their own management.
- Revenue can be generated from statutory and non-statutory MPA fees for tourism programmes, blue carbon credits generated from mangrove conservation and avoided deforestation as well as seaweed farming and sustainable coastal fisheries.
What are Marine Protected Areas?
- About:
- MPAs are designated areas of the ocean that are set aside for the protection and conservation of marine ecosystems and their biodiversity.
- Within the region, certain activities are limited, or entirely prohibited, to meet specific conservation, habitat protection, ecosystem monitoring or fisheries management objectives.
- MPAs do not necessarily exclude fishing, research or other human activities; in fact, many MPAs are multi-purpose areas.
- Need for Establishing MPAs:
- Biodiversity Conservation:
- MPAs help to conserve the diversity of marine species and their habitats, preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems and the services they provide, such as food and oxygen production.
- Sustainable Fisheries:
- MPAs can help to regulate fishing activities and prevent overfishing, ensuring that fish populations are able to recover and remain healthy, which in turn supports sustainable fishing practices.
- Climate Change Mitigation:
- MPAs can serve as carbon sinks, helping to absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and mitigate the impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems.
- Research and Education:
- MPAs can provide valuable opportunities for scientific research and educational activities, helping to increase our understanding of the marine environment and promote ocean literacy.
- Economic Benefits:
- MPAs can contribute to local economies by attracting tourists, providing opportunities for sustainable tourism and recreation, and supporting local fishing communities.
- Biodiversity Conservation:
- Treaties, Conventions and Agreements:
- Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans of the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area:
- It specifically aims to establish a network of 'specially protected areas to conserve cetaceans. It prohibits the deliberate killing of cetaceans in national waters.
- Bern Convention:
- Formulated under the aegis of the European Community Council in 1979, it has been in force since 1982 and covers European states.
- CITES:
- Formulated under UNEP in 1973, Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) has been in force since 1975 and has worldwide application. CITES regulates international trade of species listed on three appendices.
- EU Habitats Directive:
- Formulated by the European Community Council in 1992, the EU Habitats Directive applies to all EU states, including the Azores and Madeira (part of Portugal) and the Canary Islands.
- CCAMLR:
- Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) is a multilateral response to concerns that unregulated increases in krill catches in the Southern Ocean could be detrimental for Antarctic marine ecosystems particularly for seabirds, seals, whales and fish that depend on krill for food.
- Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans of the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area:
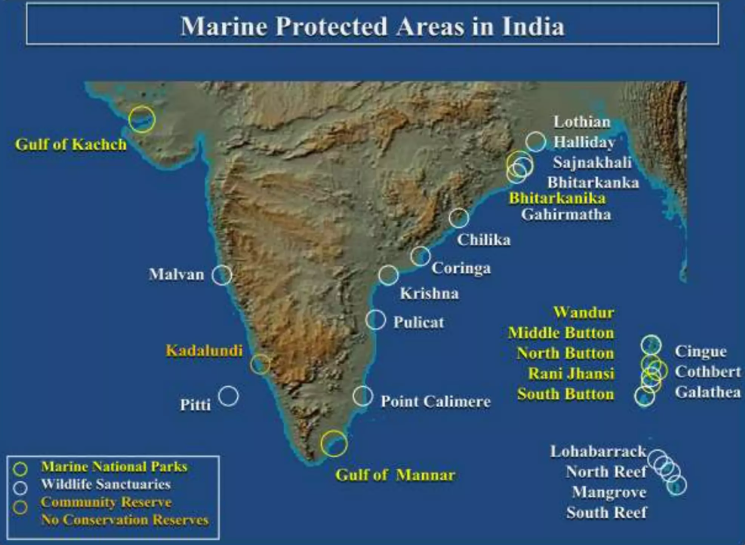
What are the Marine Protected Areas in India?
- In India, there are 33 national parks and wildlife sanctuaries designated under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972 that make up the country's MPAs.
- Marine National Park and Marine Sanctuary in the Gulf of Kutch form one unit and Bhitarkanika National Park and Bhitarkanika Sanctuary are an integral part of one MPA. Thus, there a total of 31 MPAs in India.
- MPAs cover less than 4.01% of the total area of all Protected Areas of India.
What is IMPAC?
- IMPAC congresses are a collaborative effort between the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and the chosen host country.
- The congress brings together scientists, policy makers, practitioners, and stakeholders from around the world to discuss the latest scientific knowledge, best practices and challenges in the management of MPAs.
- The goal of IMPAC is to advance the conservation and sustainable use of the world's marine biodiversity and to support the implementation of the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity's goals for marine conservation and management.