International Abhidhamma Divas | 21 Oct 2024
Why in News?
Recently, India’s Prime Minister addressed a ceremony in celebration of International Abhidhamma Divas (IAD) and recognition of Pali as a classical language.
- It was organised by the International Buddhist Confederation (IBC) and the Ministry of Culture.
What are Key Facts About International Abhidhamma Divas?
- About IAD: Abhidhamma Divas commemorates the descent of Lord Buddha from the celestial realm of the thirty-three divine beings (Tāvatiṃsa-devaloka) to Sankassiya (Sankisa Basantapur, Farrukhabad) in Uttar Pradesh.
- The importance of this location is highlighted by the presence of the Asokan Elephant Pillar.
- Story behind Abhidhamma: According to the Pali texts, Buddha preached the Abhidhamma first to the Gods of the Tavatimsa heaven, who were headed by his mother.
- After having returned to the earth again, he conveyed the message to his disciple Sariputta.
- Mark of Event: Abhidhamma Divas coincides with the end of the rainy retreat (Vassa) and the Pavāraņā festival.
- Rainy retreat (Vassa) is an annual three-month monastic retreat practised especially in the Theravada Buddhist tradition during the monsoon season.
- The Pavāraṇā festival marks the conclusion of Vassa, where monks come together to confess any faults or mistakes made during the retreat and invite their fellow monks to point out any shortcomings they may have noticed.
- Pavāraṇā festival is celebrated on full moon day of the 11th lunar month which usually in October.
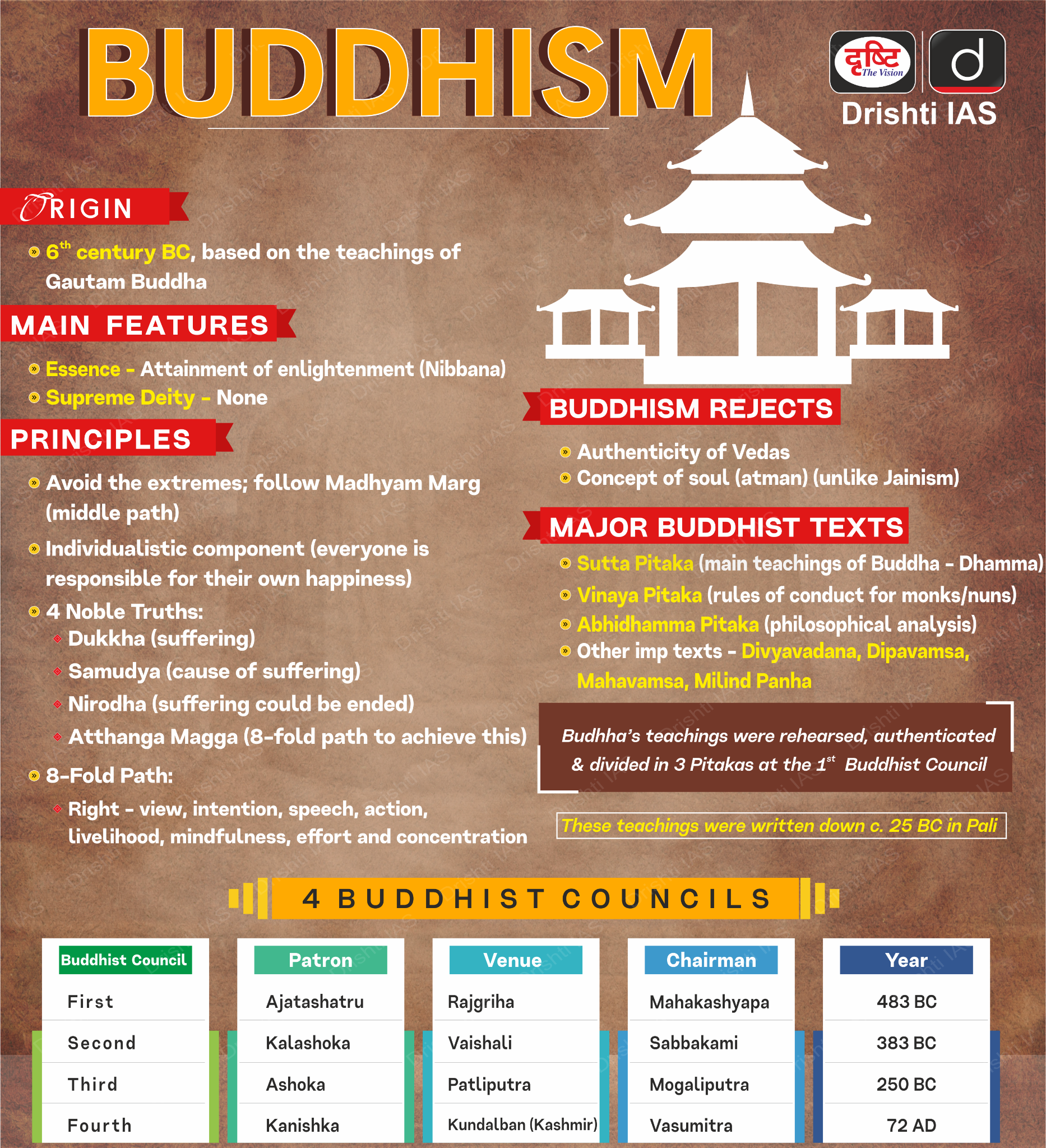
What is Abhidhamma Pitaka?
- The Abhidhamma Pitaka is the last of three Pitakas that constitute to Pali Canon, one of the most popular scriptures of Theravada Buddhism.
- Abhidhamma Pitaka is a detailed scholastic analysis and summary of the Buddha's teachings in the Suttas. It deals with the philosophy, doctrine, psychology, metaphysics, ethics, and epistemology of Buddhism
- The other remaining Pitakas of Tipitaka are Vinaya Pitaka and Sutta Pitaka.
- Vinaya Pitaka is the monastic rules of conduct for monks and nuns of the Sangha.
- Sutta Pitaka contains suttas (teachings/discourses) delivered by the Buddha and his close disciples.
- The Abhidharma Pitaka consists of seven different books.
- Dhammasangani (Enumeration of Phenomena)
- Vibhanga (Book of Treaties)
- Dhatukatha (Discussion with Reference to the Elements)
- Puggalapanatti (Description of Personality)
- Kathavatthu (Points of Controversy)
- Yamaka (Book of Pairs)
- Patthana (Book of Relations)
What are Key Facts About Pali Language?
- Origin of Pali: Pali belongs to the Indo-European language family.
- Initially, Pali was thought to be identical with Magadhi, the language of Magadha (modern-day Bihar).
- Recent studies show Pali has a stronger resemblance to the Prakrits of Western India.
- Classical Language: The Union Cabinet has approved the recognition of Pali alongwith Prakrit, Marathi, Assamese, and Bengali as classical languages.
- Connection with Ashoka: Emperor Ashoka’s inscriptions were written Pali especially in modern-day Uttar Pradesh.
- Connection with Buddhism: Pali is the language of the three Theravada Buddhist canon i.e., Vinaya Pitaka, Sutta Pitaka and Abhidhamma Pitaka.
- Scripts of Pali: Originally it was written in Brahmi and Kharosthi scripts. As Buddhism spread, Pali was written in local scripts like Sinhalese in Sri Lanka, Burmese in Myanmar, Thai in Thailand and Khmer in Cambodia.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.With reference to the cultural history of India, consider the following pairs: (2020)
- Parivrajaka – Renunciant and Wanderer
- Shramana – Priest with a high status
- Upasaka – Lay follower of Buddhism
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q.With reference to the cultural history of India, which one of the following is the correct description of the term ‘paramitas’? (2020)
(a) The earliest Dharmashastra texts written in aphoristic (sutra) style
(b) Philosophical schools that did not accept the authority of Vedas
(c) Perfections whose attainment led to the Bodhisattva path
(d) Powerful merchant guilds of early medieval South India
Ans: (c)
Q. With reference to the religious history of India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- Sthaviravadins belong to Mahayana Buddhism.
- Lokottaravadin sect was an offshoot of Mahasanghika sect of Buddhism.
- The deification of Buddha by Mahasanghikas fostered the Mahayana Buddhism.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)