Important Facts For Prelims
5 New Classical Languages and Change in Criteria
- 05 Oct 2024
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet has approved the recognition of five more languages as "classical," expanding the nation's list of culturally significant tongues.
- Other than 6 languages, Marathi, Pali, Prakrit, Assamese, and Bengali have been included in the prestigious category.
What is a Classical Language?
- About:
- In 2004, the Indian government began designating languages as "Classical Languages" to acknowledge and preserve their ancient legacy.
- The 11 classical languages of India serve as custodians of the nation's rich cultural heritage, representing key historical and cultural milestones for their communities.
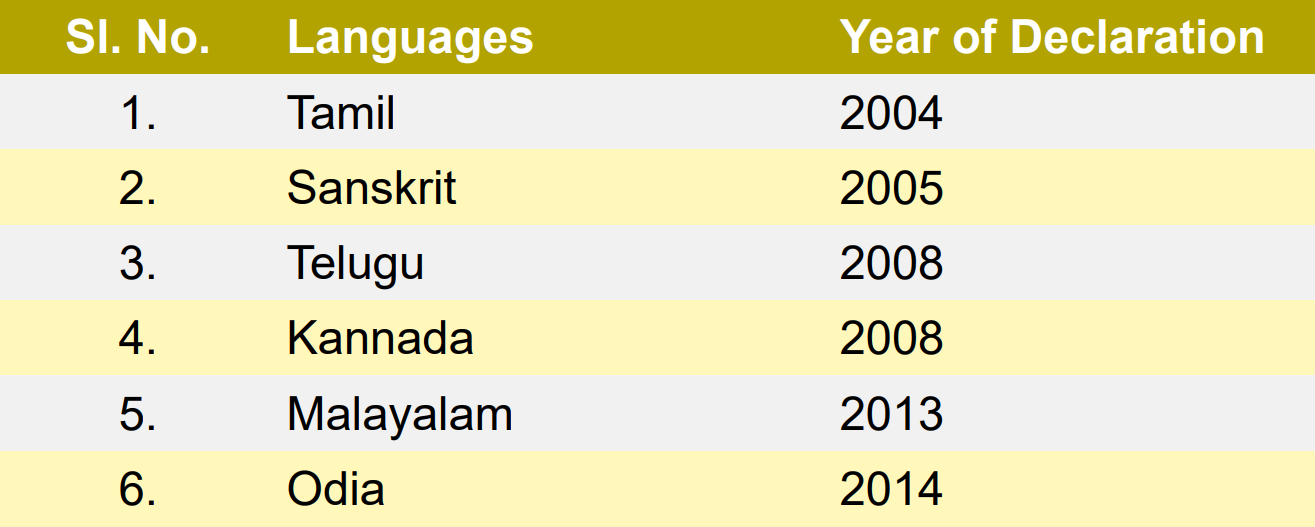
- Indian classical languages (Shastriya Bhasha) are languages with a rich historical legacy, profound literary traditions, and distinctive cultural heritage.
- Significance:
- These languages have played a key role in the intellectual and cultural evolution of the region.
- Their texts provide valuable insights into diverse fields such as literature, philosophy, and religion.
- Criteria: It was revised in 2005 and 2024 on the recommendations of Linguistic Experts Committees (LEC) under Sahitya Akademi.
-
Revised criteria in 2005 are as follows:
- High Antiquity: Early texts and recorded history spanning 1,500–2,000 years.
- Ancient Literature: Possession of a body of ancient literature/texts considered valuable heritage by generations.
- Knowledge Texts: Presence of an original literary tradition not borrowed from another speech community.
- Distinct Evolution: The classical language and literature are distinct from modern, there can also be a discontinuity between the classical language and its later forms or its offshoots.
- In 2024, criteria for declaring a language as classical were revised.
- Under which “Knowledge Texts: Presence of an original literary tradition not borrowed from another speech community” was replaced by “Knowledge texts, especially prose texts in addition to poetry, epigraphical and inscriptional evidence”.
-
- Benefits:
- Languages designated as 'classical' receive various government benefits aimed at promoting their study and preservation.
- Two international awards are given annually to scholars who have made notable contributions to the research, teaching, or promotion of classical Indian languages.
- These are the Presidential Award of Certificate of Honour and the Maharshi Badrayan Samman Award.
- The University Grants Commission (UGC) supports the creation of Professional Chairs in central universities and research institutions to focus on classical Indian languages.
- To safeguard and promote these linguistic treasures, government established the Center of Excellence for Studies in Classical Languages at the Central Institute of Indian Languages (CIIL) in Mysore.
What are the Other Provisions to Promote Language?
- Eighth Schedule: To promote the progressive use, enrichment and promotion of the language. Consists of 22 languages:
- Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, Bodo, Santhali, Maithili and Dogri.
- Article 344(1) provides for the constitution of a Commission by the President on the expiration of five years from the commencement of the Constitution for the progressive use of Hindi .
- Article 351 provides that it shall be the duty of the Union to promote the spread of the Hindi language
- Other Efforts to Promote Languages:
- Project ASMITA: The project ASMITA aims to produce 22,000 books in Indian languages within five years.
- New Education Policy (NEP): The NEP policy aims to turn Sanskrit universities into multi-disciplinary institutions.
- Central Institute of Indian Languages (CIIL): This institute works to promote four classical languages: Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam, and Odia.
- Central Sanskrit Universities Bill, 2019: It granted Central status to three deemed Sanskrit universities: the Rashtriya Sanskrit Sansthan and Shri Lal Bahadur Shastri Rashtriya Sanskrit Vidyapeeth in Delhi, and the Rashtriya Sanskrit Vidyapeeth in Tirupati.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following languages: (2014)
- Gujarati
- Kannada
- Telugu
Which of the above has/have been declared as ‘Classical Language/Languages’ by the Government?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)




