India Stands with the Philippines in the South China Sea | 03 Apr 2024
For Prelims: Philippines, South China Sea, Taiwan, Luzon Strait, Malacca Strait, Nine-dash line, Senkaku Islands, Aegean Sea, Exclusive Economic Zones, Act East Policy, ASEAN, BrahMos supersonic cruise missile.
For Mains: Dispute in the South China Sea Region, Areas of Cooperation Between India and Philippines.
Why in News?
India's Ministry of External Affairs recently expressed firm support for the Philippines in defending its national sovereignty amidst tensions with China over the South China Sea.
- The diplomatic relations between the Philippines and India are approaching their 75th year in 2024. This milestone marks a transformative partnership between the two nations.
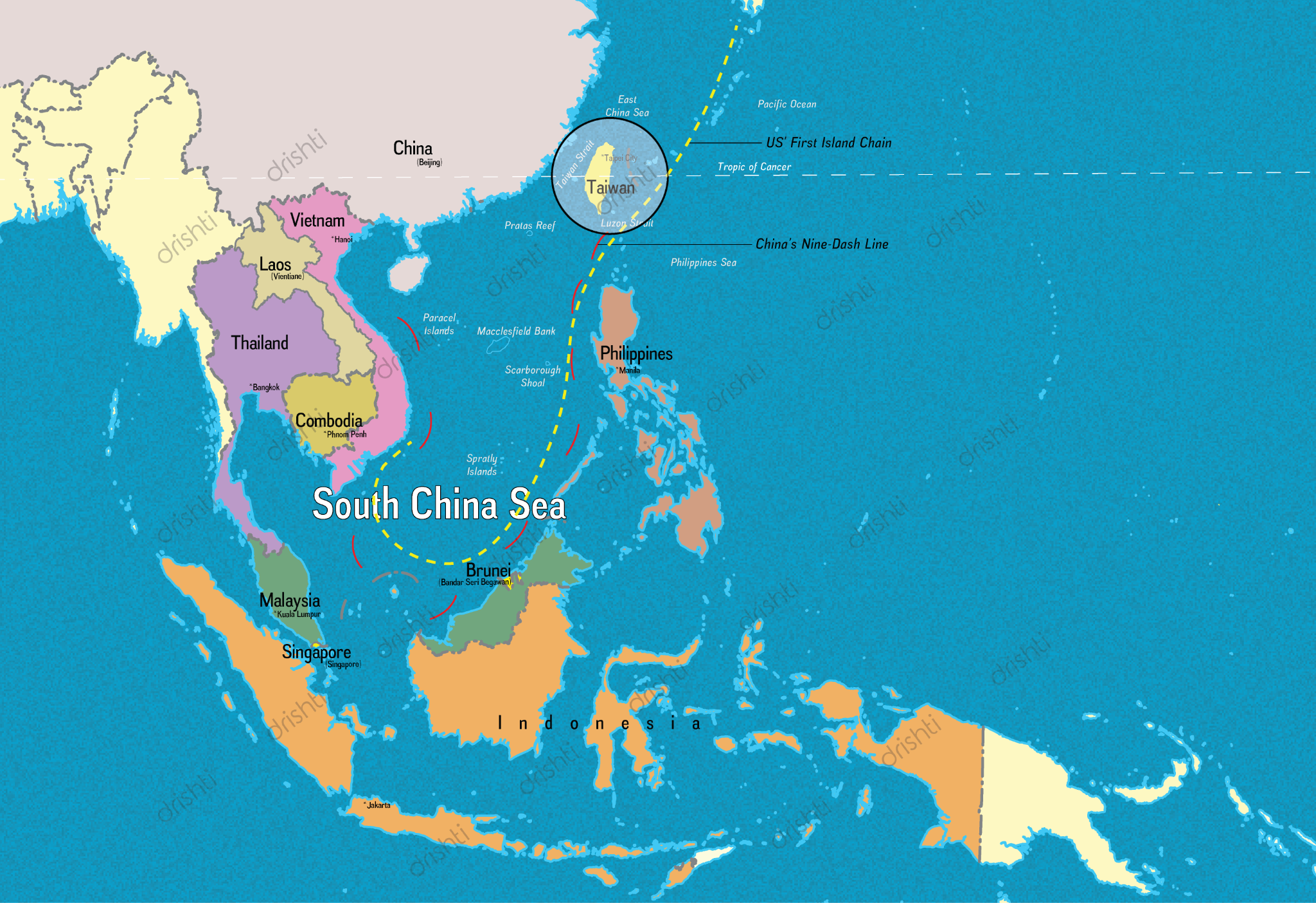
What is the Dispute in the South China Sea Region?
- Significance of South China Sea:
- Strategic Location: The South China Sea is strategically located, bordered by China and Taiwan to the north, the Indo-Chinese peninsula (including Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, and Singapore) to the west, Indonesia and Brunei to the south, and the Philippines to the east (referred to as the West Philippine Sea).
- the Luzon Strait with the Philippine It is connected by the Taiwan Strait with the East China Sea and by Sea (both marginal seas of the Pacific Ocean)
- Trade Importance: One-third of all global shipping passes through the South China Sea. Over 64% of China's maritime trade passes through the South China Sea.
- Over 55% of India's trade passes through the South China Sea and Malacca Strait.
- Fishing Ground: The South China Sea is also a rich fishing ground, providing a vital source of livelihood and food security for millions of people in the region.
- It supports a diverse marine ecosystem and sustains fisheries, contributing significantly to regional economies and food supplies.
- Dispute:
- The core of the South China Sea dispute involves competing claims over land features like islands and reefs and their surrounding waters.
- The involved parties in these disputes include China, Brunei, Taiwan, the Philippines, Vietnam, and Malaysia.
- China's "nine-dash line" claim encompasses up to 90% of the sea, leading to tensions as it has expanded islands and built military installations to reinforce control, especially in the Paracel and Spratly Islands.
- Key areas include the Spratly Islands, Paracel Islands, Pratas, Natuna Islands, and Scarborough Shoal.
- The core of the South China Sea dispute involves competing claims over land features like islands and reefs and their surrounding waters.
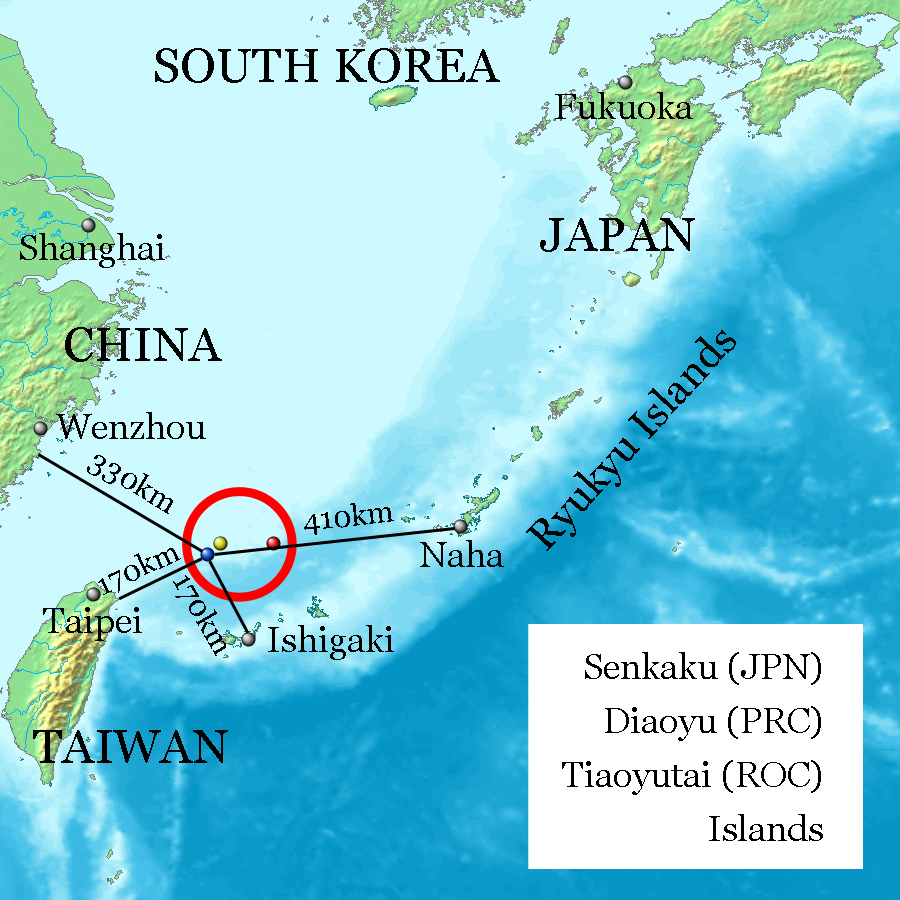
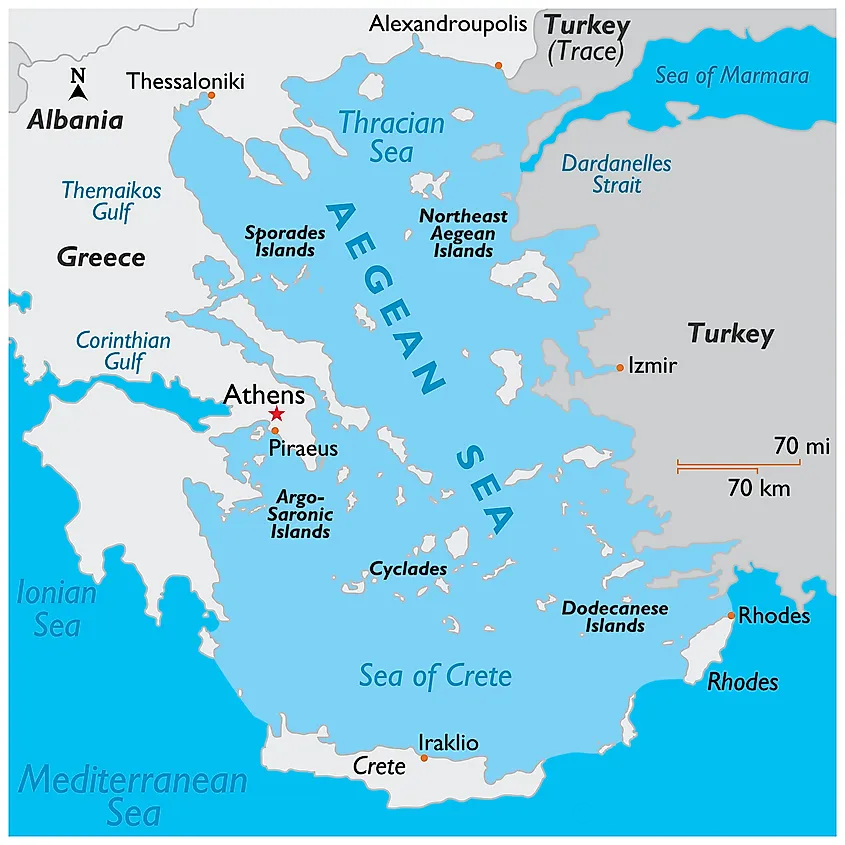
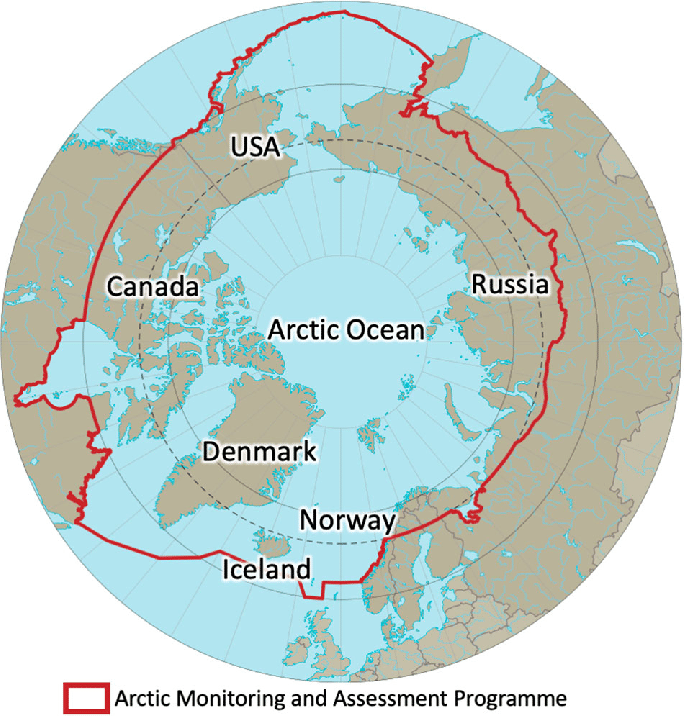
What are Other Major Water Bodies Facing Territorial Disputes?
What is Salami Slicing Technique in Maritime Disputes?
- About: It involves countries incrementally asserting control over maritime areas through small, gradual actions over time.
- It avoids direct confrontation, exploits legal ambiguities, and aims to assert influence and create irreversible situations in disputed waters.
- Example: China has been accused of employing the salami slicing technique in the South China Sea through actions like building artificial islands, conducting resource exploration, and imposing fishing bans to assert control and limit access for other countries.
- For instance, recently Chinese coast guard ships blocked Philippine vessels at Second Thomas Shoal, resulting in escalated tensions in the region.
What are the Areas of Cooperation Between India and the Philippines?
- About: India and the Philippines formally established diplomatic relations on 26th November 1949.
- With the Act East Policy initiated in 2014, the relationship with the Philippines has diversified further into political security; trade, industry, and people-to-people realms.
- Bilateral Trade: As per the official trade figures of the Department of Commerce, Government of India, bilateral trade between India and the Philippines crossed the USD 3 billion mark for the first time in 2022-23.
- India exports engineering goods, automobile parts, petroleum products, pharmaceuticals, bovine meat, oilseeds, tobacco, and groundnuts to the Philippines.
- Imports from the Philippines to India include electrical machinery, semiconductors, ores, copper, plastics, pearls, waste from the food industry, and animal fodder.
- Health and Medicine: The Philippines was the first ASEAN member to grant Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for Bharat Biotech's Covaxin.
- Currently, the Philippines accounts for about 20% of India's pharmaceutical exports to ASEAN, with India being its largest supplier.
- Science and Technology: A Bilateral Programme of Cooperation (POC) in Science and Technology was signed in October 2019, covering areas like agricultural biotechnology, material science, and ocean science.
- India signed a deal with the Philippines in January 2022 to supply a shore-based anti-ship variant of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile.
- This underscores the global demand for India's advanced defence capabilities.
- India signed a deal with the Philippines in January 2022 to supply a shore-based anti-ship variant of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Assess the potential economic and security implications of unresolved maritime disputes on regional stability and global order in context of recent disputes in the South China Sea. Q. Evaluate the evolving relationship between India and the Philippines, considering geopolitical and geoeconomic dimensions. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2018)
Regions sometimes Country mentioned in news
- Catalonia — Spain
- Crimea — Hungary
- Mindanao — Philippines
- Oromia — Nigeria
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2 and 4 only
Ans: c
Q. Southeast Asia has captivated the attention of global community over space and time as a geostrategically significant region. Which among the following is the most convincing explanation for this global perspective? (2011)
(a) It was the hot theatre during the Second World War
(b) Its location between the Asian powers of China and India
(c) It was the arena of superpower confrontation during the Cold War period
(d) Its location between the Pacific and Indian oceans and its preeminent maritime character
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: c
Q. Consider the following countries: (2009)
- Brunei Darussalam
- East Timor
- Laos
Which of the above is/are member/members of ASEAN?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: C
Mains:
Q. Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. (2016)