India’s Trade with Afghanistan and Nepal | 18 Feb 2025
Why in News?
India recorded an unusual trade deficit with Afghanistan in the year 2023-24.
- In another development, soybean oil imports from Nepal surged 14-fold (April-November 2024), possibly due to rule-of-origin (RoO) violations.
What are Key Highlights of India Trade with Afghanistan and Nepal?
- Afghanistan:
- Bilateral Trade Trends: India's exports to Afghanistan fell from USD 825.78 million in 2020-21 to USD 355.45 million in 2023-24, while imports rose from USD 509.49 million in 2020-21 to a record USD 642.29 million in 2023-24.
- Before this, the last time India saw a trade deficit (USD 0.73 million) with Afghanistan was in 2000-01.
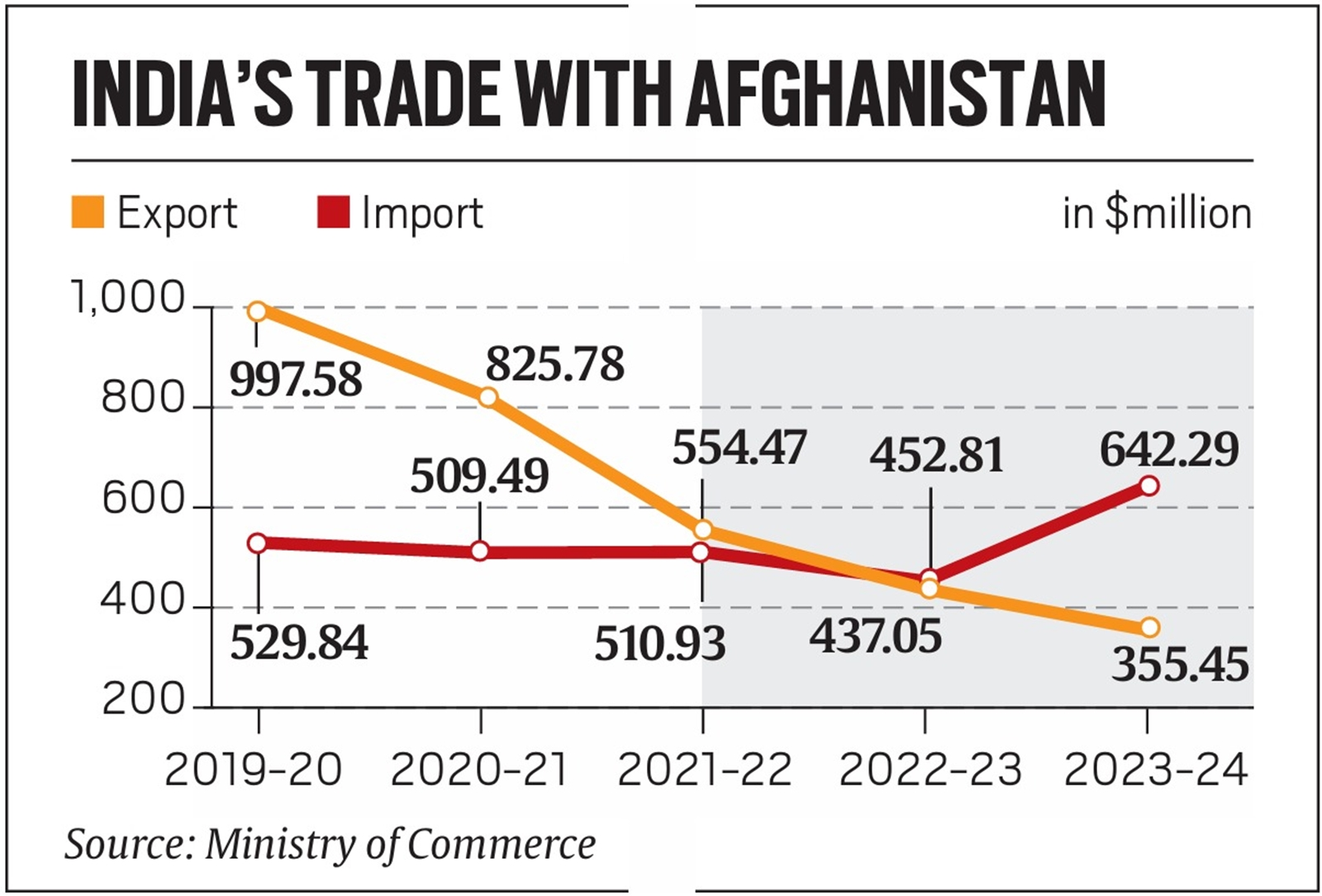
- Before this, the last time India saw a trade deficit (USD 0.73 million) with Afghanistan was in 2000-01.
- Imports: Agricultural products like figs, asafoetida, raisins, apples, garlic, saffron, almonds, onions, pomegranates, and walnuts dominate.
- Exports: Mainly medicines, vaccines, soybean meal, and garments.
- Key Products: In 2023-24, Afghanistan was the primary supplier of asafoetida, raisins, and garlic.
- In 2023-24, Afghanistan became India's 3rd-largest apple supplier, (surpassed Italy and the US) after Iran and Turkey.
- Bilateral Trade Trends: India's exports to Afghanistan fell from USD 825.78 million in 2020-21 to USD 355.45 million in 2023-24, while imports rose from USD 509.49 million in 2020-21 to a record USD 642.29 million in 2023-24.
- Nepal: India’s total soybean oil imports rose by 19% to nearly USD 3 billion (April-November 2024) from USD 2.5 billion in 2023.
- Rule-of-Origin Violation: Nepal imports 98% crude edible oil, refines it, and exports it to India indicating duty structure exploitation.
- Nepal enjoys a 30% tariff advantage over other exporters due to the Nepal-India Treaty of Trade (2009), allowing duty-free exports to India.
- Rule-of-Origin Violation: Nepal imports 98% crude edible oil, refines it, and exports it to India indicating duty structure exploitation.
Note: Rules of Origin (RoO) are the criteria used to determine the country of origin of a product in international trade.
- RoO helps prevent "trade deflection," where goods produced in one country are routed through another country to take advantage of lower tariffs.
- RoO is governed by the World Trade Organization (WTO) through its Agreement on Rules of Origin.
Nepal-India Treaty of Trade 2009
- Duty-Free Access: It provides non-reciprocal duty-free access for all Nepali-manufactured goods except for a negative list (e.g., cigarettes, alcohol, cosmetics).
- Annual Quotas: It had been prescribed only for duty-free exports to India for four sensitive items i.e., vegetable fats, acrylic yarn, copper products, and zinc oxide.
- Trade Mechanism: India-Nepal bilateral trade is conducted in Indian rupees, with the exchange rate fixed at 1.6 Nepali rupee per Indian rupee.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following countries: (2022)
- Azerbaijan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Tajikistan
- Turkmenistan
- Uzbekistan
Which of the above have borders with Afghanistan?
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (c)
