International Relations
India’s Engagement with Taliban
- 10 Jan 2025
- 11 min read
For Prelims: Chabahar Port, Hezbollah, Hamas, Belt and Road initiative, Islamic State Khorasan Province (ISKP), Buddhism, Sufism, SAARC, Moscow Dialogue, Intra-Afghan Peace Talks.
For Mains: India-Afghanistan relations: Significance and Way Forward
Why in News?
India’s Foreign Secretary held talks with Afghanistan’s acting Foreign Minister in Dubai amid global geopolitical instability.
- It is India’s highest-ranking outreach with the Taliban rulers of Afghanistan to secure India’s national and security interests.
What are the Key Outcomes of the Talks?
- Expanding Humanitarian Assistance: India agreed to expand its involvement by taking on development projects alongside ongoing humanitarian aid.
- So far, India has sent 50,000 MT of wheat, 300 tons of medicines, earthquake aid, pesticides, polio and Covid-19 vaccine doses, hygiene kits, winter clothing, and stationery.
- Sports Cooperation: The two sides discussed strengthening sports cooperation, specifically in cricket, which holds significant value for Afghanistan’s youth.
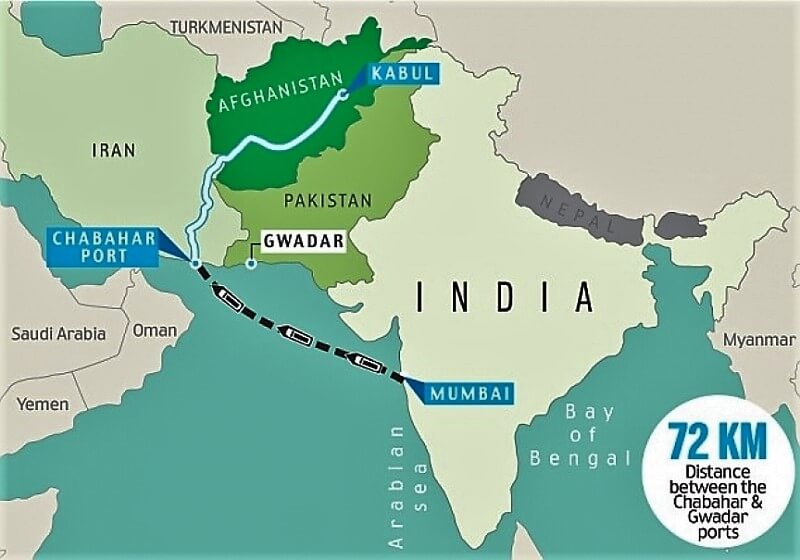
- Chabahar Port: Both parties agreed to promote the use of the Chabahar port as a key gateway to support trade, commercial activities, and the delivery of humanitarian aid to Afghanistan.
- Security Concerns: The Afghan side recognized India’s security concerns and agreed to remain in touch at various levels.
What Factors were Responsible for Recent India-Afghanistan Talks?
- Changing Global Dynamics:
- Change in Taliban-Pakistan Relations: Pakistan, once an ally of the Taliban, has become a source of tension for Taliban.
- It prompted India to engage with the Taliban to prevent losing out on its interests in Afghanistan.
- Iran’s Preoccupation: Iran suffered a blow as Israel dominated Hezbollah and Hamas, and launched missile attacks on Iran. Iran is more focused on deterring Israel than dealing with the Taliban in Afghanistan.
- Hamas and Hezbollah are Iran’s proxies who are fighting against Israel.
- Russia's Strategic Shift: Russia has been caught up with its war in Ukraine, and has been trying to build bridges with the Taliban.
- Russia views Islamic groups from Afghanistan like ISIS as a major security threat and considers the Taliban an ally in fighting terrorism after the Syrian regime fell in December 2024.
- China's Influence: China calls for lifting the freeze on Afghanistan's central bank assets and is involved in urban development projects in Kabul. China eyes Afghanistan's natural resources for its Belt and Road initiative.
- India tries to prevent China's dominance in Afghanistan which can undercut India’s interest.
- Return of Donald Trump: There are concerns that the US might re-engage with the Taliban and India sees this as an opportunity to ensure its interests remain central to any future Afghan developments.
- Change in Taliban-Pakistan Relations: Pakistan, once an ally of the Taliban, has become a source of tension for Taliban.
- Security Concerns: India has urged Taliban to check anti-India elements operating from Afghanistan such as Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM) and Islamic State Khorasan Province (ISKP).
- Development Engagement: Taliban officials had said India’s projects – estimated to be of USD 3 billion in the last 20 years – have been extremely productive and they would like India to stay invested in Afghanistan.
Note: New Delhi does not officially recognise the Taliban regime in Afghanistan but maintained a technical mission in Kabul.
- India's technical mission in Kabul is part of its diplomatic presence in Afghanistan, focusing on developmental and humanitarian efforts rather than full-fledged diplomatic functions.
India-Taliban Relations
- Taliban Rule (1996-2001): India did not establish formal diplomatic ties with the Taliban.
- India supported the Northern Alliance, an opposition group to the Taliban.
- The Taliban assisted India in negotiating with the hijackers of Indian Airlines Flight 814 in 1999, facilitating the safe return of the hostages.
- Pre Afghanistan Takeover (Before 15th August 2021):
- Moscow Dialogue (2017): Moscow Dialogue brought together representatives from Afghanistan, China, India, and other stakeholders to facilitate the reconciliation process in Afghanistan.
- Intra-Afghan Peace Talks (2020): India participated in the intra-Afghan peace talks in Doha, marking a key step in its engagement with the Taliban.
- Post Afghanistan Takeover (After 15th August, 2021):
- First Engagement (August 2021): India’s Ambassador to Qatar met Taliban representatives at their Doha office.
- Continued Engagement (June 2022): Joint Secretary for Pakistan, Afghanistan, and Iran met key Taliban leaders paving the way for sending a technical team at the Indian embassy in Kabul.
- The technical team allows Indian officials to meet with Taliban ministers and representatives in Kabul.
- Afghan Consul General in Mumbai: India allowed the Taliban to appoint a new Consul General in the Afghan Consulate in Mumbai.
What is the Importance of Afghanistan for India?
- Bridge to Central Asia: Central Asia holds significant economic and energy resources, and Afghanistan offers India a route via chabahar port to access these resources while avoiding reliance on Pakistan and China.
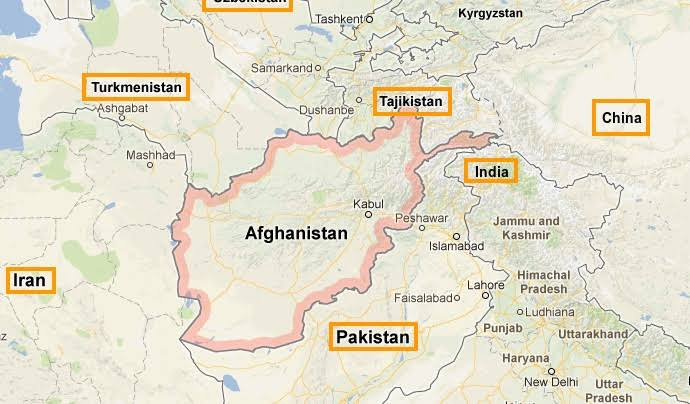
- Afghanistan shares a border with Pakistan, Iran, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and China.
- Countering Pakistan's Influence: By maintaining influence in Afghanistan, India can strengthen its role in the region and enhance its strategic position in South Asia and Central Asia.
- Counter-Terrorism: India's involvement in Afghanistan assert its leadership in the fight against terrorism and extremism in South Asia.
- Mutual Benefits: India has invested over USD 3 billion in various projects in Afghanistan, such as roads, dams, schools, hospitals, parliament building, etc which can facilitate better living for Afghan people and provide mutual benefits to Indians and Afghans.
What are Challenges for India’s Taliban Policy?
- Terrorism: The fall of Afghanistan's democratic government destabilized the country and strengthened extremist networks like the Haqqani Network, al-Qaeda, and Lashkar-e-Taiba, which have targeted India through cross-border terrorism.
- E.g., The presence of terrorist groups may work against India’s interests posing threats to India’s security.
- Pakistan's Strategic Role: Pakistan perceives India’s presence in Afghanistan as a direct threat to its strategic depth policy, which aims to use Afghanistan as a buffer against India.
- Pakistan accuses India of supporting insurgencies in Balochistan and other regions.
- Diplomatic Recognition: India has not officially recognized the Taliban regime due to its refusal to form an inclusive government, respect human rights, and curb terrorism, complicating diplomatic engagement.
- Refugee Crisis: The fall of Kabul caused an influx of Afghan refugees to India, straining resources and raising concerns about security, integration, and potential radical elements among them.
Way Forward
- Focused Financial Investments: India must strategically evaluate and implement smaller, impactful projects focused on friendly projects like education, healthcare, and humanitarian relief to sustain long-term support for Afghanistan’s population.
- Democratic Leadership: India should actively engage with Afghan civil society to promote women and minorities rights.
- Using SAARC for Trade Access: India must leverage the SAARC platform to explore options for overland trade access, thereby benefiting both Afghanistan and India.
- Narrative Building: Efforts must be made to highlight the concerns of the people of Afghanistan and need to resume student education visas.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Evaluate India’s engagement with the Taliban regime in Afghanistan. How does it serve India's national and security interests? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following countries: (2022)
1. Azerbaijan
2. Kyrgyzstan
3. Tajikistan
4. Turkmenistan
5. Uzbekistan
Which of the above have borders with Afghanistan?
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. The proposed withdrawal of the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) from Afghanistan in 2014 is fraught with major security implications for the countries of the region. Examine in light of the fact that India is faced with a plethora of challenges and needs to safeguard its own strategic interests. (2013)