India's PM Visit to Kuwait | 24 Dec 2024
For Prelims: Gulf nations, International Solar Alliance, United Nations, Gulf Cooperation Council, Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer
For Mains: India’s Foreign Policy and Relations with West Asia, India-Kuwait Bilateral Relations, Energy Diplomacy in India’s Foreign Policy
Why in News?
India and Kuwait have elevated their bilateral relationship to a strategic partnership during Prime Minister Narendra Modi's historic visit to the Gulf nation, marking the second visit by an Indian Prime Minister since Indira Gandhi's visit in 1981.
- This visit signifies a renewed commitment to trade, defence, and broader cooperation between the two nations.
What are the Key Highlights of the PM's Visit to Kuwait?
- Order of Mubarak Al Kabeer: PM Shri Narendra Modi was awarded the ‘Order of Mubarak Al Kabeer,’ the highest honor of Kuwait, in recognition of his contributions to strengthening bilateral ties.
- Strategic Partnership: The two sides elevated their relationship to a ‘Strategic Partnership,’ expanding collaboration across political, trade, defense, energy, and cultural domains.
- Defence Cooperation: Signed an MoU on Defence Cooperation, focusing on joint military exercises, training, coastal defense.
- Cultural and Sports Cooperation: India and Kuwait signed a Cultural Exchange Programme for 2025-2029 and an Executive Programme on Sports Cooperation for 2025-2028.
- Joint Commission on Cooperation (JCC): A JCC was established to monitor bilateral relations, chaired by the Foreign Ministers of both countries.
- New Joint Working Groups (JWGs) were set up in key areas such as education, trade, investments, agriculture, and counter-terrorism.
- Technology and Emerging Sectors: Emphasised collaboration in semiconductors, artificial intelligence, e-Governance, and sharing best practices.
- Energy Cooperation: Both sides agreed to move from a buyer-seller relationship to a comprehensive partnership in the energy sector, with a focus on oil, gas, refining, and renewable energy.
- Multilateral Cooperation: Kuwait’s membership in International Solar Alliance (ISA) was welcomed by India.
- The PM of India congratulated Kuwait on its Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Presidency and emphasized the importance of concluding the India-GCC Free Trade Agreement.
- Both leaders emphasized the need for a reformed United Nations (UN) to tackle global challenges effectively.
Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer
- It is conferred on Heads of State, sovereigns of foreign countries, and members of royal families.
- Instituted in 1974, the award honors Mubarak Al Sabah, also known as Mubarak Al-Kabeer, who ruled Kuwait from 1896 to 1915.
- Mubarak Al Sabah played a pivotal role in shaping Kuwait’s future, securing greater autonomy from the Ottoman Empire.
- Previous recipients of the Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer include notable figures such as Queen Elizabeth II, former US Presidents George HW Bush and Bill Clinton, King Salman of Saudi Arabia, and former French President Nicolas Sarkozy.
How are India-Kuwait Relations?
- Historical Ties: India and Kuwait share a long-standing relationship, dating back to pre-oil times when maritime trade formed the foundation of Kuwait's economy.
- The Indian Rupee was once the legal tender in Kuwait until 1961, emphasizing their strong economic ties.
- Historically, Kuwait traded goods like dates, pearls, and Arabian horses with India. However, after the discovery of oil, Kuwait's economy shifted, with oil now contributing to about 94% of its state income.
- Economic Partnership: Kuwait is one of India’s top trading partners, with bilateral trade valued at USD 10.47 billion in 2023-24.
- Kuwait is India’s 6th largest crude oil supplier, fulfilling 3% of the country’s energy needs.
- Indian exports to Kuwait surpassed USD 2 billion for the first time, reflecting growing trade ties.
- Kuwait Investment Authority’s investments in India exceed USD 10 billion.
- Indian Diaspora in Kuwait: With a population of around 1 million, the Indian community is the largest expatriate group in Kuwait.
- The community plays a vital role in the Kuwaiti economy, particularly in sectors like healthcare, engineering, retail, and business.
What is the Importance of Kuwait in India's Foreign Policy in West Asia?
- Economic Contributions: The remittances from Indian expatriates in Kuwait inject billions of dollars into the Indian economy, which is crucial for economic stability and growth.
- Economic Collaboration: Kuwait’s Vision 2035, aimed at diversifying its economy beyond oil, presents opportunities for India to collaborate in emerging sectors such as renewable energy, infrastructure, and technology.
- This aligns with India’s development goals, particularly the Viksit Bharat 2047.
- Additionally, the energy security from Kuwait is vital for India’s industrial growth and domestic needs.
- Geopolitical Influence: Kuwait's location in the Middle East and its role in the GCC make it a key player in regional politics.
- India's engagement with Kuwait helps it maintain a balanced and influential presence in West Asia
- Labour and Skill Development: Kuwait's demand for a skilled workforce, as part of its Vision 2035, aligns with India’s strengths in skill development, offering a chance for more Indian workers to contribute to Kuwait's growth in various sectors, such as healthcare, technology, and infrastructure.
What is the Gulf Cooperation Council?
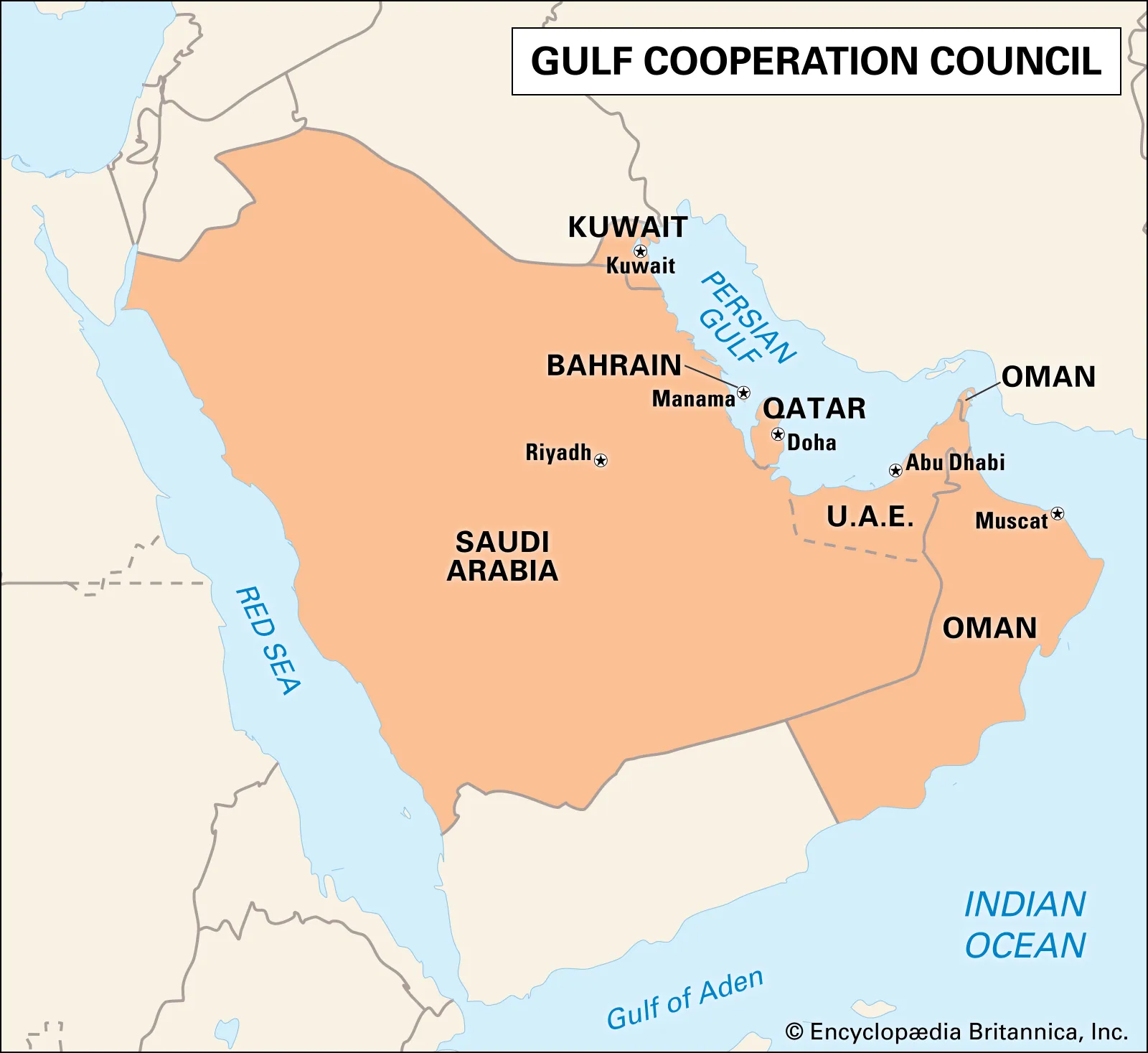
- About: The GCC, established in 1981, is a regional political and economic organization consisting of six Arab states: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and United Arab Emirates.
- The GCC was established in response to regional tensions, notably the Iranian Revolution (1979) and the Iraq-Iran War (1980–1988).
- It aims to promote unity and address shared challenges in the Gulf region.
- The GCC was established in response to regional tensions, notably the Iranian Revolution (1979) and the Iraq-Iran War (1980–1988).
- Organizational Structure: The Supreme Council is the highest decision-making body of the GCC, consisting of heads of state from each member country.
- The presidency of the Supreme Council rotates annually based on the alphabetical order of member countries.
- Headquarters: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
- India’s Relations with GCC: The GCC is a key trading and investment partner for India, with significant investments from the UAE and Saudi Arabia.
- In FY 2023-24, India-GCC bilateral trade stood at USD 161.59 billion. India’s exports were USD 56.3 billion and India’s imports were USD 105.3 billion.
- The GCC remains a key market for India’s exports, including oil, and hosts a large Indian workforce.
- The UAE ranks as India's 3rd largest trading partner and 2nd largest export destination.
- Around 8.9 million Indian expatriates in the GCC contribute significantly to remittances, which, despite a recent decline, remain a major income source for India.
- In FY 2023-24, India-GCC bilateral trade stood at USD 161.59 billion. India’s exports were USD 56.3 billion and India’s imports were USD 105.3 billion.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (2016)
(a) Iran
(c) Oman
(b) Saudi Arabia
(d) Kuwait
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)