India's Balance of Payments | 10 Jul 2024
Why in News?
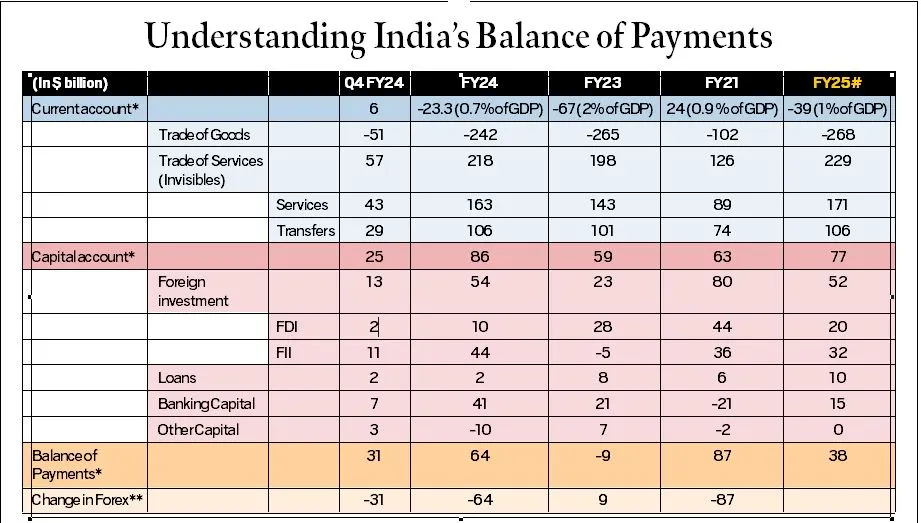
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data revealed that India’s current account registered a surplus in the fourth quarter (Jan-Mar) of the 2023-24 financial year. This was the first surplus in 11 quarters.
- This achievement underscores the significance of India's Balance of Payments (BoP), highlighting its impact on currency exchange rates, sovereign ratings, and overall economic health.
What is Balance of Payments?
- About: The BoP serves as a crucial economic indicator, detailing all financial transactions between India and the rest of the world.
- This comprehensive ledger tracks the inflow and outflow of money where inflows are marked positive and outflows negative, reflecting the country's economic interactions globally.
- It measures the relative demand for the rupee against foreign currencies, crucially influencing exchange rates and economic stability.
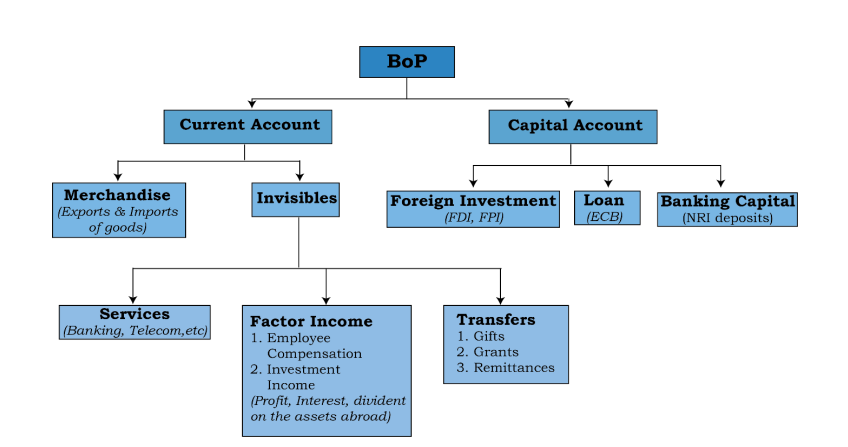
- Constituents of BoP:
- Current Account:
- Trade of Goods: Tracks physical imports and exports, indicating the balance of trade. A deficit suggests higher imports than exports.
- Trade of Services (Invisibles): Includes sectors like IT, tourism, and remittances, contributing positively to India's current account surplus despite trade deficits.
- The net of these two components determines the current account balance. In Q4 of 2023-24, India registered a surplus on the current account, with a surplus in invisible but a deficit in the trade account.
- Capital Account:
- Captures investments such as Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Institutional Investments (FII), essential for economic growth and stability. The capital account flow reflects factors such as commercial borrowings, banking, investments, loans, and capital.
- In Q4 of 2023-24, India showed a net surplus of USD 25 billion on the capital account.
- Captures investments such as Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Institutional Investments (FII), essential for economic growth and stability. The capital account flow reflects factors such as commercial borrowings, banking, investments, loans, and capital.
- Current Account:
- Disequilibrium: A disequilibrium in the balance of payment means its condition of Surplus or deficit.
- A BoP surplus occurs when a country's earnings from exports, services, and investments exceed its expenditures on imports and external obligations.
- Conversely, a deficit indicates higher expenditures than earnings, necessitating external financing or asset sales to cover the shortfall.
- Challenges: BoP calculations include errors and omissions due to complexities in recording international transactions accurately.
- Persistent deficits can strain a nation's economic stability, potentially requiring external borrowing or assistance from international financial institutions like the IMF.
- Contrary to popular perception, deficits aren't inherently negative nor surpluses unequivocally positive. A deficit can signify strategic investments, while a surplus may stem from reduced imports rather than robust economic health.
- Managing BoP:
- Foreign Exchange Reserves: RBI manages BoP fluctuations by adjusting foreign exchange reserves through market interventions and by using tools such as adjusting interest rates, open market operations and influencing borrowing and spending.
- Policy Interventions: Governments implement trade policies and regulatory measures to stabilise BoP dynamics, ensuring sustainable economic growth.
- Deflation is the deliberate reduction of money supply or aggregate demand. It can result in lower domestic prices, which may make exports more competitive, and reduced consumption, including of imports. However, it also poses risks such as economic slowdown or recession and increased unemployment.
- Foreign Investment Promotion: Promoting foreign investment to enhance the capital account by offering tax incentives, improving infrastructure, business environment, and streamlining regulations for foreign businesses.
- This can attract foreign capital and technology, leading to potential improvement in export capacity.
UPSC Civil Services, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following actions which the Government can take: (2011)
- Devaluing the domestic currency.
- Reduction in the export subsidy.
- Adopting suitable policies which attract greater FDI and more funds from FIIs.
Which of the above action/actions can help in reducing the current account deficit?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 3 only
(d) 1 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q2. With reference to Balance of Payments, which of the following constitutes/constitute the Current Account? (2014)
- Balance of trade
- Foreign assets
- Balance of invisibles
- Special Drawing Rights
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 4
Ans: (c)