Indian Economy
India’s Automobile Sector
- 27 Mar 2025
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Make in India, Foreign Direct Investment, China Plus One, PM e-Bus Sewa, FAME-II
For Mains: Development of the Automobile Sector in India, Challenges and Opportunities in EV Adoption in India
Why in News?
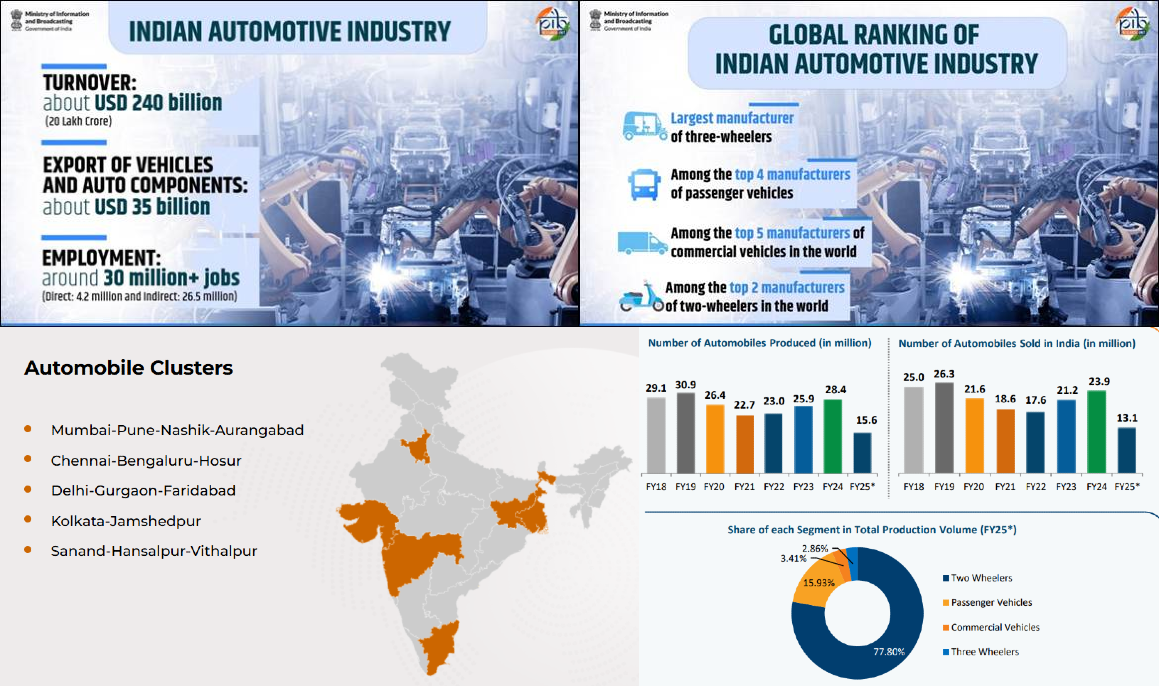
India’s automobile sector under ‘Make in India’ initiative has witnessed record growth in 2023-24, with total vehicle production reaching 28 million units the sector is transforming into a global manufacturing hub, especially for Electric Vehicles (EVs).
What is the Growth Trajectory of India’s Automobile Sector?
- Early Liberalization (Post-1991): The automobile industry was de-licensed in 1991, and subsequent opening up for 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) via the automatic route.
- This opened doors for global manufacturers like Suzuki, Hyundai, and Honda to set up production units in India.
- Production Surge: Vehicle production increased from 2 million units (1991-92) to 28 million (2023-24).
- Contribution to Economy: India's automotive industry has a USD 240 billion turnover, the sector contributes approximately 6% to India’s GDP and supports about 30 million jobs (4.2 million direct and 26.5 million indirect).
- Auto Component Industry: India's auto components industry contributes 2.3% to GDP and directly employs 1.5 million people.
- In FY24, the industry's turnover reached Rs. 6.14 lakh crore (USD 74.1 billion), with 54% of supplies catering to domestic original equipment manufacturers and 18% to exports.
- Growing at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 8.63% (FY16-FY24), exports stood at USD 21.2 billion in FY24 and are projected to reach USD 30 billion by 2026.
- Electric Vehicle Push: EV registrations crossed 4.4 million by August 2024. The EV market penetration stood at 6.6%.
- Trade:
- Export Expansion: Exports touched 4.5 million units in FY24. India's auto component exports are highest to Europe, North America and Asia.
- Imports: The auto component industry exported USD 21.2 billion and imported USD 20.9 billion worth of components during 2023-24, resulting in a trade surplus of USD 300 million.
- FDI and Investments: India attracted USD 36 billion in FDI (2020-2024), and by FY28, the Indian auto industry plans a USD 7 billion investment to localize electric motors and automatic transmissions, reducing imports and leveraging the "China Plus One" strategy.
What are the Key Auto Sector Initiatives Under Make in India?
- Schemes:
- FAME-II (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid & Electric Vehicles) supports EV adoption with 16.15 lakh EVs incentivized and 10,985 charging stations sanctioned.
- PLI-Auto (Production Linked Incentive for Auto & Components) promotes Advanced Automotive Technology (AAT), including EVs & hydrogen fuel-cell components.
- PLI-ACC (Advanced Chemistry Cell Battery Manufacturing) aims for a 50 Gigawatt hours (GWh) battery manufacturing ecosystem (40 GWh allocated to four firms)
- PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement (2024-2026) supports EVs, e-trucks, e-buses, and charging infrastructure.
- The PM e-Bus Sewa Scheme (FY 2024-29) targets deployment of over 38,000 e-buses.
- Policy Measures: Ministry of Finance reduced GST on EVs from 12% to 5%, and Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs amended Model Building Bye Laws, 2016 to mandate EV charging stations in private and commercial buildings.
What are the Challenges to India’s Automobile Sector?
- Import Dependency: India relies on imports for key EV components like lithium-ion cells and semiconductors, making costs and supply vulnerable to global disruptions, limiting full self-reliance.
- Limited EV Penetration: India’s EV penetration remains low compared to 12% globally and 30% in China. Additionally, battery and vehicle costs remain high despite GST reduction.
- Limited charging infrastructure, especially in tier-2/3 cities and rural areas, along with range anxiety, hinders widespread adoption despite projections of 20% penetration by FY30.
- Skilled Workforce Shortage: Despite a large job market, the industry lacks skilled workers in automation, fuel cells, and hydrogen tech, crucial for sustainable mobility.
- Stricter Emission Norms: The upcoming Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (CAFE III & IV) standards (2027-2032) will enforce stricter carbon emission limits, pushing automakers to adopt costly technology upgrades.
- This will likely increase internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle prices as manufacturers invest in cleaner technologies.
- Shared Mobility & Public Transport: Ride-sharing apps and improved public transport options reduce car ownership demand, affecting vehicle sales.
How Can India Accelerate Its Automotive Growth and Sustainability?
- Localization of Auto Components: Accelerate domestic production of rare earths and lithium by exploring reserves like those in Jammu & Kashmir through the Ministry of Mines' National Critical Mineral Mission.
- Scale up Infrastructure: As recommended by NITI Aayog Integrate EV charging infra with city planning, especially in smart cities and urban transport nodes.
- Create Green Mobility Credit Guarantee Funds to support MSMEs and startups in the EV supply chain.
- Foster Circular Economy: Implement the Battery Swapping Framework, as recommended by NITI Aayog.
- Adopt Green Logistics Policies promoting EV fleets in last-mile delivery, building on Logistics Efficiency Enhancement Program (LEEP).
- Policy Harmonization: Streamline EV policies across States and UTs to align with National Electric Mobility Mission Plan targets (achieve 6-7 million sales of hybrid and EVs year on year from 2020 onwards).
- Digitize regulatory approvals using the National Single Window System (NSWS) for ease of doing business.
- Transition from ICVs to EVs: Support CAFE III & IV with financial and technological assistance, especially for MSMEs.
- Address job displacement in the ICV ecosystem through targeted re-skilling under the Skill India Mission and National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme.
- Align the Vehicle Scrappage Policy with the EV transition by incentivizing the retirement of older ICVs and providing linked rebates for EV purchase.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Analyze the role of the ‘Make in India’ initiative in transforming India into a global automobile manufacturing hub. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. What is/are the recent policy initiative(s)of Government of India to promote the growth of the manufacturing sector? (2012)
- Setting up of National Investment and Manufacturing Zones
- Providing the benefit of ‘single window clearance’
- Establishing the Technology Acquisition and Development Fund
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. “Success of ‘Make in India’ program depends on the success of ‘Skill India’ programme and radical labour reforms.” Discuss with logical arguments. (2019)
Q. How is efficient and affordable urban mass transport key to the rapid economic development in India? (2019)