India’s Engagement at ASEAN Meet | 03 Aug 2024
Why in News?
Recently, India's External Affairs Minister's (EAM) visit to Vientiane, Laos, for the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) meetings has garnered significant attention. This visit has provided a platform for high-level dialogues with several global leaders, aiming to strengthen bilateral relations.
What are the Key Highlights of the ASEAN Meet?
- ASEAN in India’s Foreign Policy: EAM emphasised ASEAN as the cornerstone of India's Act East Policy and Indo-Pacific vision.
- 2024 marks 10 years since India’s Act East Policy was announced at the 9th East Asia Summit in 2014.
- The policy aims to enhance commerce, connectivity, and capacity building. strategic, and cultural relations with the Asia-Pacific region.
- India views the ASEAN partnership as crucial for its political, economic, and security cooperation.
- Highlighted India's vision for the Indo-Pacific in promoting a free, open, inclusive, and peaceful region based on a rules-based international order.
- Focus Areas: Discussions involved expanding people-to-people linkages and bilateral cooperation.
- The visit aims to solidify partnerships and advance mutual interests in the region.
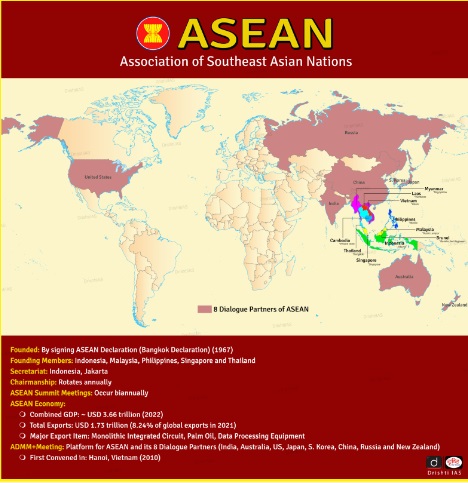
What is the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) ?
- About: The ASEAN is a regional intergovernmental organization founded on 8th August 1967, in Bangkok, Thailand.
- Creation was formalised through the ASEAN Declaration
- Initially signed by Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand.
- ASEAN was expanded to include Brunei Darussalam (1984), Vietnam (1995), Laos PDR and Myanmar (1997), and Cambodia (1999).
- The region has one of the largest economies in the world; believed to have the 4th-largest economy in the world by 2050.
- The bloc’s biggest success in recent years has been promoting economic integration among members. It also helped negotiate the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership, the world’s largest free trade agreement.
- ASEAN Charter (2008): Provided ASEAN with a legal status and institutional framework. It codified norms, rules, and values, enhancing accountability and compliance.
- ASEAN Summit: The highest policy-making body, comprising the Heads of State or Government of ASEAN member states, meets twice annually.
- The first summit was held in Bali, Indonesia, in 1976.
- India-ASEAN Relations:
- India began formal engagement with ASEAN in 1992 as a "Sectoral Dialogue Partner" and subsequently as a "Dialogue Partner" in 1995.
- Partnership elevated to a Strategic Partnership in 2012 and a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership in 2022.
- India began formal engagement with ASEAN in 1992 as a "Sectoral Dialogue Partner" and subsequently as a "Dialogue Partner" in 1995.
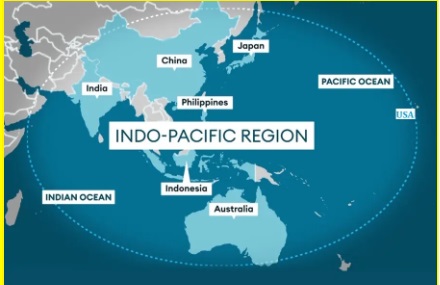
Indo-Pacific Region
- The Indo-Pacific region is a vast geographic area encompassing the Indian and western/central Pacific Oceans, home to diverse cultures and ecosystems.
- It has geopolitical importance, with major powers like China, India, Japan, and the US, and accounts for more than half the world’s population, and it accounts for 60% of global GDP as well as 2/3rd of global economic growth.
- However, it faces security challenges like territorial disputes, piracy, terrorism, and nuclear proliferation, as well as environmental concerns.
- China's rapid growth has contributed to the region's increasing global significance.
- Indian vision for Indo-Pacific: India advocates a "free, open and inclusive Indo-Pacific" and calls for peaceful resolution of disputes while respecting sovereignty and territorial integrity of all nations.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q2. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Q1. India is a member of which among the following? (2015)
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
- Association of South-East Asian Nations
- East Asia Summit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) India is a member of none of them
Ans: (b)
Q. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)