International Relations
India-Bhutan Ties and Subnational Diplomacy
- 01 Feb 2025
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Five Year Plan, Gelephu Mindfulness City Project, Punatshangchhu-II hydro Project, Town Twinning, Farakka Water-Sharing Treaty 1996, Union List, GDP, Manas National Park, Royal Manas National Park.
For Mains: India-Bhutan ties, Potential of subnational diplomacy in advancing India’s national interests.
Why in News?
Following the King of Bhutan visit to India, both countries committed to strengthening India and Bhutan ties in which Subnational diplomacy by states like Assam can further strengthen economic and cultural relations.
What were the Key Outcomes of the Visit?
- Strengthened Cooperation: Bhutan expressed gratitude for India’s continued support for its 13th Five Year Plan (2024-29) and for India's contributions to Bhutan’s Economic Stimulus Programme.
- Economic Development: India has assured continued support for the Mindfulness City project, a sustainable economic hub.
- Hydropower Cooperation: Significant progress has been made in the 1020 MW Punatshangchhu-II hydro project and both countries agreed to expedite the completion of the Punatsangchhu-I project.
- Cross-Border Connectivity: The Integrated Check Post (ICP) at Darranga, Assam, was inaugurated to boost tourism and economic activities in Bhutan's eastern region and Assam's border areas.
What is Subnational Diplomacy?
- About: Subnational diplomacy (paradiplomacy) refers to subnational entities (like states or regions) engaging in international relations to promote their mutual interests.
- Globalization has fueled subnational diplomacy, with regional governments seeking to advance their goals in an interconnected world.
- Institutional Mechanisms in India:
- States Division: The 'States Division' under the MEA facilitates better Centre-state interaction, helping states develop foreign linkages in trade, tourism, investment, and more.
- Consular Offices and Federal Foreign Affairs Offices: Foster diplomacy with sub-national units.
- City Diplomacy: City Diplomacy, or town twinning, focuses on cultural and economic exchanges. E.g., Kobe-Ahmedabad Sister Cities.
- Global City Diplomacy Examples: Sao Paulo city in Brazil has its own policy for conducting international relations with support from Brazil’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
- Barcelona (Spain), Quebec (Canada), California (USA), London (UK), Vancouver (Canada) also conduct foreign relations.
- Subnational Diplomacy in India: Indian states enjoy some liberty in foreign policy implementation in areas like trade, commerce, and cultural exchange.
- In 2015, Andhra Pradesh's CM led a delegation to China before the Prime Minister's (PM) visit, and West Bengal's CM joined India’s PM in Bangladesh.
- Gujarat's "Vibrant Gujarat Global Investors Summit" promotes investment in Gujarat.
- Other states like Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, and Bihar attract FDI boosting trade opportunities
- In 1992, Maharashtra partnered with MNCs (Enron and General Electric) to finance the Dabhol Power Project.
- The 1996 Farakka water-sharing issue was resolved after West Bengal CM's visit to Bangladesh, resulting in the Farakka Water-Sharing Treaty 1996.
- Benefits:
- State-Level Influence: Indian states shape foreign policy by aligning federal and state policies in sectors like land, labor, and health.
- It can prevent issues like Kachchatheevu Island where the union's decision negatively affected the local population.
- Complementary Strengths: Indian states and their counterparts collaborate in sectors like IT and automotive, adopting tailor made approaches based on the mutual requirements.
- Global Challenges: State cooperation in climate change and pandemic recovery can offer effective solutions at local levels for the global world.
- Long-Term Alliances: Subnational diplomacy fosters grassroots partnerships, encourages P2P and B2B relations, ensuring lasting relations.
- State-Level Influence: Indian states shape foreign policy by aligning federal and state policies in sectors like land, labor, and health.
- Concerns:
- Constitutional Constraints: Foreign affairs are under the Union List in India's Constitution, limiting states' involvement and raising concerns over central authority encroachment.
- National Security Concerns: Subnational diplomacy could impact national security, particularly in sensitive areas like the Northeast or states bordering Pakistan and China.
- External Influence: Local governments may become targets of disinformation, affecting their ability to manage international relations independently.
- Smaller cities may be vulnerable to manipulation by foreign powers.
- Public Backlash: Independent foreign relations by states can lead to public opposition and diplomatic friction if they conflict with national interests.
How Subnational Diplomacy with Assam can Enhance India-Bhutan Ties?
- Trade and Connectivity: Establishing more ICPs like Darranga and developing railway links like Kokrajhar-Gelephu and Banarhat-Samtse, along with Assam's natural resources (tea, oil, Joha rice, Bhut Jolokia), will boost trade with Bhutan.
- Currently, more than 70% of trade between India and Bhutan passes through the Jaigaon Land Customs Station (LCS) in West Bengal.
- Energy Cooperation: Long-term power purchase agreement (PPA) with Bhutan’s hydroelectric companies can help meet Assam’s energy needs.
- The sale of hydro-power accounts for about 63% of Bhutan’s GDP.
- Maritime Connectivity: Bhutan can reduce transport costs to Bangladesh by using Dhubri River port and utilising Assam’s Asom Mala initiative (road infrastructure development program).
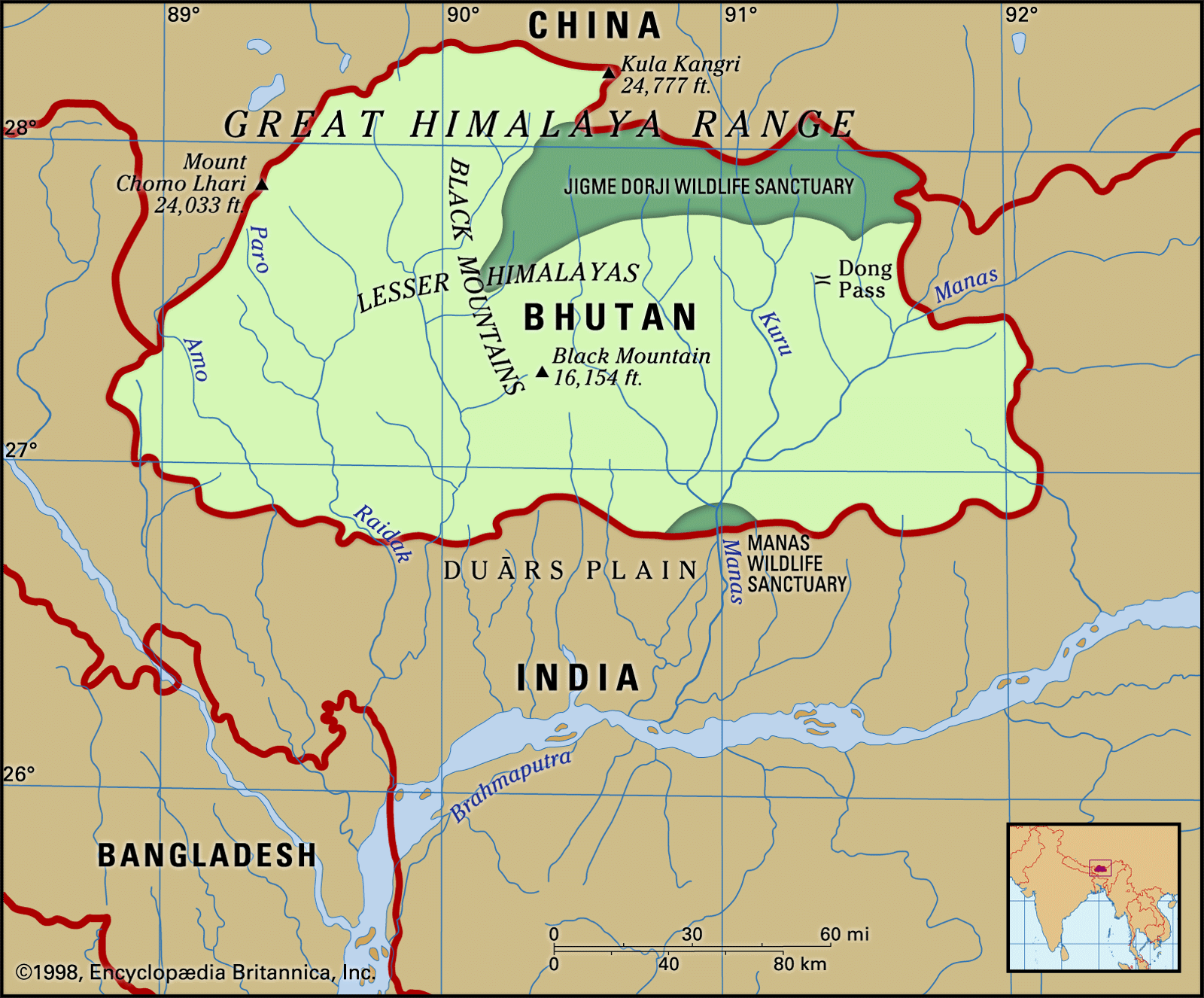
- Ecological Collaboration: Collaboration on Manas National Park (Assam) and Royal Manas National Park (Bhutan) will strengthen conservation and eco-tourism, attracting more tourists.
- Cultural Diplomacy: Assam’s cultural links with Bhutan can foster greater solidarity through cultural exchanges.
Conclusion
Subnational diplomacy, particularly through Assam, plays a vital role in strengthening India-Bhutan ties by enhancing trade, energy cooperation, and cultural exchanges. It offers innovative solutions to global challenges, while also fostering grassroots partnerships for long-term bilateral collaboration.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the potential benefits and concerns of subnational diplomacy in India’s foreign policy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q.Terrorist activities and mutual distrust have clouded India-Pakistan relations. To what extent the use of soft power like sports and cultural exchange could help generate goodwill between the two countries. Discuss with suitable examples. (2015)