Indian Economy
Increased Recovery Under IBC
- 03 Jun 2024
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016, Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI), Financially stressed companies, Bankruptcy, National Companies Law Tribunal (NCLT), Debt Recovery Tribunal (DRT), Committee of Creditors (CoC), Insolvency professionals
For Mains: Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016, Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI)
Why in News?
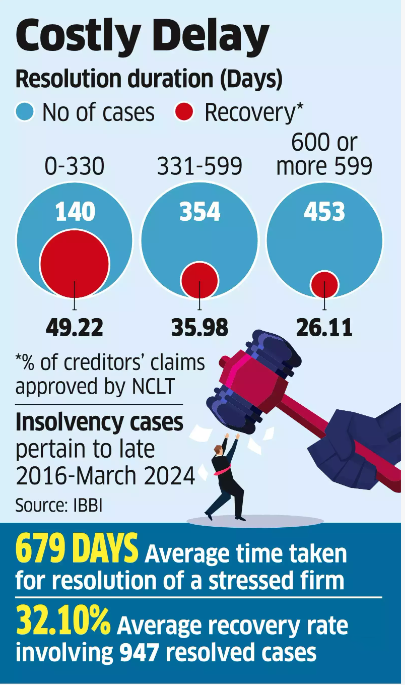
Recent data from the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) shows, creditors in India have retrieved almost half of their claims under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016 when resolutions are concluded within the 330-day deadline, although delays have diminished the proportion of money recovered.
What are the Key Highlights of the Latest Data?
- Recovery Rates and Timeliness:
- Data shows that 947 financially stressed companies' resolutions resulted in creditors receiving ₹3.36 lakh crore, equivalent to 32.1% of their claims since the inception of the IBC (2016).
- Stress resolution under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016 has improved in recent years, but recoveries have not kept pace.
- Recoveries by creditors were at 54% in FY18 and FY19 but dropped to 22% in FY21 due to the pandemic.
- Recoveries inched up to 23% in FY22 and 36% in FY23 before declining again to 27% in FY24.
- The number of resolutions reached a record 269 in the last fiscal year (FY 24), up from 189 in FY23 and 144 in FY22, mainly due to government filling National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) vacancies in the past two years.
- Creditors have experienced stronger cumulative recoveries compared to the fair value of stressed companies upon insolvency admission, at 85%.
- In terms of liquidation value, the recovery rate has reached 161.8% of the assets.
- Experts stress the importance of timely initiation of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) for stress resolution, as delays (averaging 679 days) have lowered recovery rates to 26%, impacting asset value and debt recovery.
What are the Proposed Measures to Strengthen IBC?
- Reduce Delays: Efficiently resolving insolvency cases within the IBC's 330-day deadline is imperative, with the current average duration of 679 days underscoring the need for streamlining processes and reducing litigation.
- Improve Recovery Rates: While the IBC has led to resolutions, the percentage of claims recovered by creditors needs improvement. It dropped from 49% for on-time resolutions to 26% for delayed ones. It can be achieved by:
- Ensure sufficient judges and staff at the NCLT to handle cases efficiently to expedite processing and reduce delays caused by backlogs.
- Review and simplify the IBC procedures to eliminate unnecessary steps and expedite approvals involving standardising processes.
- Sector-Specific Regimes: Consider specialised insolvency regimes for sectors like real estate, which may have unique challenges compared to other industries.
- Cross-Border Insolvency Framework: Establish an effective legal framework based on the UNCITRAL (United Nations Commission on International Trade Law) to handle insolvency cases involving companies with assets in multiple countries.
- Review Timelines: Re-evaluate the timelines mandated by the IBC to ensure they are efficient and minimise unnecessary delays.
- Formal Prepack for All Companies: Allow a formal pre-packaged insolvency process for all companies, not just Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME). This involves agreeing on a resolution plan before initiating formal bankruptcy proceedings.
What are the Key Highlights of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016?
- About:
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016 provides a framework for resolving the bankruptcy and insolvency of companies, individuals, and partnerships in a time-bound manner.
- Insolvency is a state where the liabilities of an individual or an organisation exceed its assets and that entity is unable to raise enough cash to meet its obligations or debts as they become due for payment.
- Bankruptcy is when a person or company is legally declared incapable of paying their due and payable bills.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (Amendment) Act, 2021 modified the 2016 Code to offer a more efficient insolvency resolution framework for MSMEs, ensuring quicker, cost-effective, and value-maximising outcomes for all stakeholders.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), 2016 provides a framework for resolving the bankruptcy and insolvency of companies, individuals, and partnerships in a time-bound manner.
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI):
- IBBI serves as the regulatory authority overseeing insolvency proceedings in India.
- The IBBI's Chairperson and three full-time members are appointed by the government and are experts in the fields of finance, law, and insolvency.
- It also has ex-officio members.
- Adjudication of Proceedings:
- National Companies Law Tribunal (NCLT) adjudicates proceedings for companies.
- Debt Recovery Tribunal (DRT) handles proceedings for individuals.
- They play a pivotal role in approving the initiation of the resolution process, appointing professionals, and endorsing the final decisions of creditors.
- Procedure for Insolvency Resolution under the Code: Initiated by either debtor or creditor upon default, insolvency professionals manage financial information and debtor assets, with a 180-day legal action prohibition during resolution.
- Committee of Creditors (CoC): The CoC, formed by insolvency professionals and comprising financial creditors, determines the fate of outstanding debts through debt revival, repayment schedule changes, or asset liquidation, with a 180-day deadline before the debtor's assets are liquidated.
- Liquidation Process: Proceeds from the sale of the debtor’s assets are distributed first to insolvency resolution costs, second to secured creditors, third to dues for workers and employees, and fourth to unsecured creditors.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the challenges faced in the implementation of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) in India and suggest measures to strengthen its effectiveness. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following statements best describes the term ‘Scheme for Sustainable Structuring of Stressed Assets (S4A)’, recently seen in the news? (2017)
(a) It is a procedure for considering ecological costs of developmental schemes formulated by the Government.
(b) It is a scheme of RBI for reworking the financial structure of big corporate entities facing genuine difficulties.
(c) It is a disinvestment plan of the Government regarding Central Public Sector Undertakings.
(d) It is an important provision in ‘The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code’ recently implemented by the Government.
Ans: (b)





-min.jpg)