Social Issues
Global Hunger Index 2024
- 22 Oct 2024
- 9 min read
For Prelims: Global Hunger Index, Child Stunting, Undernourishment, National Food Security Act, Poshan Abhiyan (National Nutrition Mission), PM Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKAY), National Mission for Natural Farming
For Mains: Issues Related to Poverty & Hunger in India, Role of reliable data in formulating effective public health strategies, Food security, Government initiatives, and the socio-economic factors contributing to hunger.
Why in News?
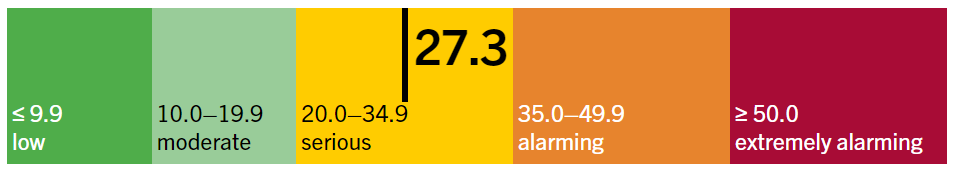
Recently, India ranks 105th out of 127 countries in the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2024 with a score of 27.3, highlighting a "serious" hunger crisis driven by ongoing challenges of food insecurity and malnutrition.
What is GHI?
- The Global Hunger Index (GHI) is a peer-reviewed report, published on an annual basis by Concern Worldwide and Welthungerhilfe.
- The GHI is a tool designed to comprehensively measure and track hunger at global, regional, and national levels, reflecting multiple dimensions of hunger over time.
- The GHI score is calculated on a 100-point scale reflecting the severity of hunger - 0 is the best score (implies no hunger) and 100 is the worst.
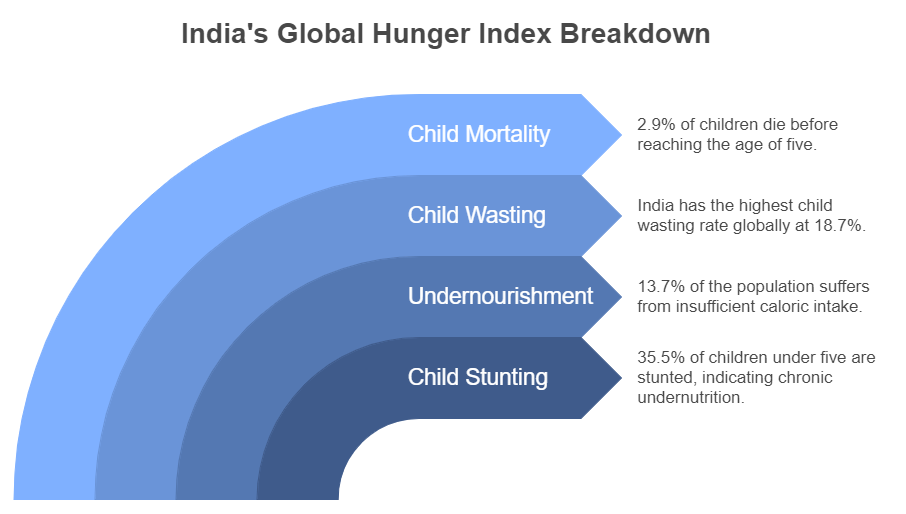
- Four Component Indicators:
- Undernourishment: The share of the population whose caloric intake is insufficient; It refers to Insufficient calorie intake to sustain a healthy life, as defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- Child Stunting: The share of children under the age of five who have low height for their age, reflecting chronic undernutrition;
- Child Wasting: The share of children under the age of five who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition; and
- Child Mortality: The share of children who die before their fifth birthday, reflecting in part the fatal mix of inadequate nutrition and unhealthy environments.
Note:
- Concern Worldwide is an international humanitarian organization focused on addressing poverty and alleviating suffering in the world’s poorest countries.
- Welthungerhilfe, founded in 1962 as the German branch of the "Freedom from Hunger Campaign," is a private aid organization based in Germany.
What are the Key Findings of the Report?
- India-Specific Findings: GHI Score (2024) - 27.3 (‘serious’) slightly improved from GHI Score (2023) - 28.7 (‘serious’).
- Undernourished children - 13.7%
- Stunted children - 35.5%
- Wasted children - 18.7% (highest globally)
- Child mortality rate - 2.9%
- Global Trends in GHI 2024:
- The 2024 GHI score for the world is 18.3, a slight improvement from 18.8 in 2016, and is considered "moderate."
- South Asian neighbours like Bangladesh, Nepal, and Sri Lanka perform better, ranking in the "moderate" category.
- Recognizing India's Efforts: The report acknowledges India's significant efforts to improve the food and nutrition landscape through various initiatives such as Poshan Abhiyan (National Nutrition Mission), PM Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKAY), National Mission for Natural Farming.
- Insufficient GDP Growth: The report highlights that Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth does not guarantee reduced hunger or improved nutrition, urging the need for policies focused on pro-poor development and addressing social and economic inequalities.
What is India's Response to GHI 2024?
- Faulty Methodology: The Ministry of Women and Child Development criticized the absence of data from their Poshan Tracker, which reportedly indicates a much lower child wasting rate of 7.2%.
- Focus on Child Health: The government noted that three out of the four GHI indicators pertain to children's health and may not provide a complete representation of the entire population.
- Small Sample Size: The government expressed doubts about the accuracy of the "Proportion of Undernourished Population" indicator, as it is based on a small sample size opinion poll.
What are the Indian Government Initiatives to Address Hunger?
What are the Challenges Related to Hunger in India?
- Inefficient Public Distribution System (PDS): Despite improvements, India's PDS still faces challenges in reaching all intended beneficiaries.
- The National Food Security Act covers 67% of the population, but more than 90 million eligible people have been excluded from legal entitlements under the Targeted Public Distribution System (TDPS).
- Income Inequality and Poverty: While India has made strides in poverty reduction (24.82 crore Indians escape Multidimensional Poverty in the last 9 years), significant income disparities persist, affecting food access.
- Nutritional Challenges and Dietary Diversity: Food security in India often focuses on calorie sufficiency rather than nutritional adequacy.
- Urbanization and Changing Food Systems: Rapid urbanization in India is transforming food systems and consumption patterns.
- A 2022 study by the Tata-Cornell Institute found that 51% of urban slum households in Delhi experienced food insecurity.
- Gender-Based Nutritional Gap: Gender-based disparities worsen hunger and malnutrition in India. Women and girls often face unequal access to food within households, receiving smaller portions or lower-quality meals.
- This inequity, combined with the demands of maternal and child care, increases their vulnerability to chronic undernutrition.
Way Forward
- PDS Enhancement: Revamp the Public Distribution System (PDS) to enhance transparency, reliability, and affordability of nutritious food, benefiting the economically disadvantaged.
- Social Audit and Awareness: Implement social audits of the mid-day meal scheme in all districts with local authority involvement, enhance program monitoring through IT, and establish community-driven nutrition education programs in local languages, focusing on balanced diets for women and children.
- Complementing With SDGs: The Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), particularly SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) and SDG 2 (Zero Hunger), focuses on sustainable consumption pattern.
- Investment in Agriculture: A holistic food systems approach promoting diversified and nutritious food production, including nutri-cereals like millets.
- Addressing food wastage is critical. One key approach is improving warehousing and cold storage infrastructure to reduce post-harvest losses.
- Health Investments: Focus on maternal and child health through better water, sanitation, and hygiene practices.
- Interlinking Factors: In policy-making, it is crucial to recognize the interconnection between gender, climate change, and nutrition, as these factors significantly impact public health, social equity, and sustainable development.
|
Drishti Mains Question Critically analyze India's 2024 Global Hunger Index ranking and its implications for food security and nutrition. Evaluate the effectiveness of government initiatives like the National Food Security Act and suggest strategies for improvement. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is/are the indicator/indicators used by IFPRI to compute the Global Hunger Index Report? (2016)
- Undernourishment
- Child stunting
- Child mortality
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 onlY
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q: Food Security Bill is expected to eliminate hunger and malnutrition in India. Critically discuss various apprehensions in its effective implementation along with the concerns it has generated in WTO. (2013)