Agriculture
Declining Cultivation Area of Nutri-Cereals
- 23 Jun 2023
- 14 min read
This editorial is based on Millets need a procurement push which was published in The Hindu Businessline on 19/06/2023. It talks about declining trends in cultivation areas of nutri-cereals.
For Prelim: Minimum support prices (MSP), Millets, Green Revolution, United Nations General Assembly, International Year of Millets, Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Public distribution system
For Mains: Benefits of Increasing Cultivation of Nutri-Cereals, Government Initiatives
Millets, also known as nutri-cereal crops, play a vital role in providing essential micronutrients such as calcium, fiber, protein, iron, and more. Considering the high prevalence of micronutrient deficiencies among India's large population, the ongoing decrease in the cultivation area of these nutri-cereal crops poses a significant threat to nutritional security.
Acknowledging the significance of these crops and aiming to increase their recognition among consumers, the Centre took a proactive step in 2018 by issuing a notification to rename coarse cereals as nutri-cereals.
To incentivize farmers to grow millets, the Centre has regularly announced attractive minimum support prices (MSP) for these crops. However, despite these efforts, the area under cultivation of nutri-cereal crops continues to decline.
Why Cultivation Areas of Nutri-Cereal Continue to Decline?
- Impact of Green Revolution:
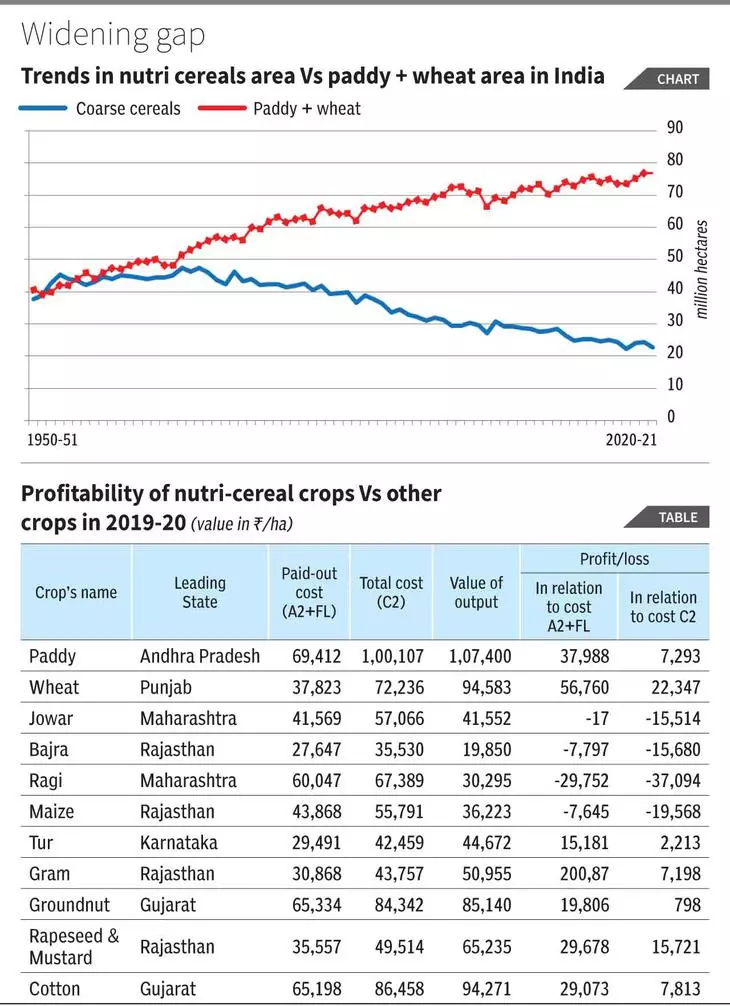
- While enhancing food security, the Green Revolution has also brought some undesirable changes in the cropping pattern. The area under water-intensive crops (paddy, sugarcane, banana, wheat, etc) increased substantially, whereas the area under less-water consuming nutri-cereal crops declined sharply from 44.34 million hectares (mha) in 1965-66 to 22.65 mha in 2021-22, down 49%.
- Low Productivity and Poor infrastructure:
- The low productivity, poor seed availability, inadequate processing and value addition facilities, and weak market linkages for nutri-cereals.
- Nutri cereals have historically been considered as "poor man's food" and faced reduced demand due to preferences for rice and wheat.
- Insufficient market demand and low-price incentives discourage farmers from investing in the cultivation of nutri cereals, resulting in lower productivity.
- Changing Dietary Preferences:
- People's eating habits and preferences shift over time. If there has been a significant change in consumer preferences towards other types of breakfast foods or if there is a growing preference for convenience foods, it could impact the demand for nutri cereals.
- Increased Competition:
- The cereal market is highly competitive, with numerous options available to consumers.
- There may be a proliferation of new breakfast products, including different types of cereals, granolas, breakfast bars, or yogurt-based breakfast options.
- This increased competition could result in a decline in market share for nutri cereals.
- The cereal market is highly competitive, with numerous options available to consumers.
- Lack of Marketing and Innovation:
- Nutri cereals face challenges if there is a lack of effective marketing strategies or innovation in product development.
- Consumers are often attracted to new and exciting products, so if nutri cereals fail to capture their attention through marketing campaigns or fail to introduce new variations or flavors, it may lead to declining sales.
- Perception and Taste Preferences:
- Taste preferences can significantly impact the success of food products. If consumers perceive nutri cereals as bland or unappealing in terms of taste, they opt for other breakfast options that are perceived as more flavorful or enjoyable.
What are the Benefits of Increasing Cultivation of Nutri-Cereals?
- Nutrition:
- Nutri cereals are high in dietary fibre, iron, folate, calcium, zinc, magnesium, phosphorous, copper, vitamins and antioxidants. They can provide nutritional security and act as a shield against nutritional deficiency, especially among children and women.
- Climate Resilience:
- Nutri cereals are drought-tolerant, pest-resistant, and can grow in marginal lands with low inputs. They can adapt to changing climatic conditions and reduce the risk of crop failure.
- Environmental Sustainability:
- Nutri cereals have low water and energy requirements and can improve soil health and biodiversity. They can also reduce greenhouse gas emissions and water pollution compared to rice and wheat.
- Economic Empowerment:
- Nutri cereals can offer income opportunities for small and marginal farmers, especially women and tribal communities, who are the main producers of these crops.
- They can also create value addition and processing potential for rural entrepreneurs.
What are Some Examples?
- Sorghum (Jowar): A gluten-free cereal that is rich in protein, iron, and antioxidants. It can help lower blood sugar and cholesterol levels.
- Pearl millet (Bajra): A drought-tolerant cereal that is high in protein, fiber, and minerals like calcium, magnesium, and zinc. It can help prevent anaemia and improve digestion.
- Finger millet (Ragi): A cereal that has the highest calcium content among all grains. It is also a good source of iron, fiber, and amino acids. It can help strengthen bones and teeth and prevent diabetes.
- Foxtail millet (Kakum): A cereal that is rich in protein, fiber, and antioxidants. It can help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and improve immunity.
- Kodo millet (Kodon): A cereal that has a low glycemic index and is high in fiber and phytochemicals. It can help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent obesity.
- Barnyard millet (Sanwa): A cereal that has the highest fiber content among all millets. It is also high in iron and calcium. It can help prevent constipation and improve blood circulation.
- Little millet (Kutki): A cereal that is high in protein, fiber, and minerals like iron, zinc, and potassium. It can help lower cholesterol levels and prevent cardiovascular diseases.
- Proso millet (Chenna): A cereal that is high in protein, phosphorus, and antioxidants. It can help improve muscle and nerve function, and prevent oxidative stress.
What are the Government Initiatives to Promote Millets Cultivation?
- International Year of Millets:
- Recognizing the significance of millets on a global scale, the United Nations General Assembly, sponsored by India, adopted a resolution designating 2023 as the "International Year of Millets."
- This highlights the importance of millets in addressing nutritional challenges and promoting sustainable agriculture. In India, 2018 was celebrated as the "National Year of Millets" to raise awareness and foster their cultivation and consumption.
- Rebranding:
- In order to promote the consumption of millets, the Indian government has officially designated them as Nutri-Cereals, emphasizing their nutritional value.
- Farmer-friendly schemes:
- Under the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana, the government allocated Rs. 300 crores in 2011-12 to promote millets as Nutri-cereals.
- The objective of this scheme was to demonstrate integrated production and post-harvest technologies, with a visible impact that would stimulate increased millet production nationwide.
- The Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers' Welfare is implementing a Rs 600-crore scheme to increase the cultivation area, production, and yield of nutri-cereals.
- The goal is to match the cultivation of nutri-cereals with the local topography and natural resources. The government is also encouraging farmers to align their cropping patterns with India's diverse 127 agro-climatic zones.
- Under the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana, the government allocated Rs. 300 crores in 2011-12 to promote millets as Nutri-cereals.
- Provision of seed kits and inputs:
- The government is providing farmers with seed kits and necessary inputs to support the cultivation of nutri-cereals.
- Additionally, efforts are being made to build value chains and support the marketability of nutri-cereals through assistance to Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs).
- Increase in Minimum Support Price:
- Recognizing the importance of millets, the government has raised the Minimum Support Price for these crops, providing significant price incentives for farmers. This increase has been a substantial boost to the agricultural sector.
- Inclusion in Public Distribution System:
- To ensure a stable market for millet produce, the government has incorporated millets into the public distribution system. This move enhances accessibility and availability of millets for consumers, further promoting their consumption.
What More Needs to be Done?
- Collaboration with Food Industry:
- Foster partnerships with food manufacturers and retailers to expand the range of nutri cereal products available in the market.
- Encourage the development of new flavors, convenient packaging options, and product innovations that cater to different consumer segments.
- Conducting School and Community Programs:
- Integrate nutri cereals into school feeding programs and community initiatives that promote healthy eating habits.
- This can involve providing nutri cereals in school meals, conducting nutrition workshops, and collaborating with local organizations to raise awareness about their benefits.
- Collaboration with Healthcare Professionals:
- Work closely with healthcare professionals, dietitians, and nutritionists to promote the inclusion of nutri cereals in dietary recommendations and treatment plans for various health conditions.
- This can help build credibility and trust among consumers.
- Work closely with healthcare professionals, dietitians, and nutritionists to promote the inclusion of nutri cereals in dietary recommendations and treatment plans for various health conditions.
- Encouraging Consumer Engagement:
- Encourage consumer participation through contests, challenges, and social media campaigns that promote the consumption of nutri cereals.
- Create platforms for consumers to share their experiences, recipes, and success stories related to incorporating nutri cereals into their diet.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the potential of nutri-cereals to contribute to sustainable agriculture, dietary diversity, and rural livelihoods. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to ‘Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- This initiative aims to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies, and to demonstrate value addition techniques, in anc integrated manner, with cluster approach.
- Poor, small, marginal and tribal farmers have larger stake in this scheme.
- An important objective of the scheme is to encourage farmers of commercial crops to shift to millet cultivation by offering them free kits of critical inputs of nutrients and micro irrigation Equipment.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- ‘Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion’ Scheme aims to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies in an integrated manner with visible impact to catalyse increased production of millets in the country. Besides increasing production of millets, the Scheme, through processing and value addition techniques, is expected to generate consumer demand for millet-based food products. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Technology demonstrations in compact blocks would be organized in selected districts for four categories of millets – sorghum, pearl millet, finger millet and small millets. Poor, small, marginal and tribal farmers have a larger stake in this scheme. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- There is no such provision to encourage farmers of commercial crops to shift to millet cultivation. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Mains:
Question: How has the emphasis on certain crops brought about changes in cropping patterns in recent past? Elaborate the emphasis on millets production and consumption. (2018)